please provide correct answers for question 4.32 and 5.27 , 6.25 and 7.23 please prvide answer for all of them as i know i have to post all of them indvidually but i cant afford it i really appreciate it
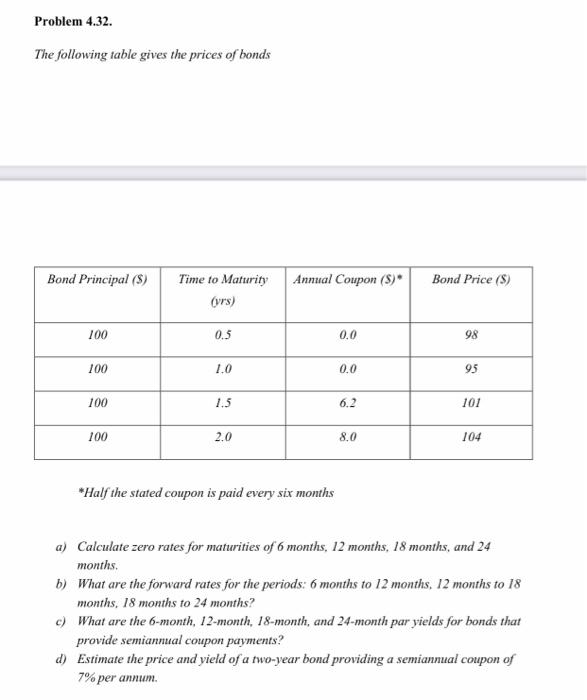
Problem 4.32. The following table gives the prices of bonds Bond Principal (8) Annual Coupon (5) Bond Price (8) Time to Maturity (yrs) 100 0.5 0.0 98 100 1.0 0.0 95 100 1.5 6.2 101 100 2.0 8,0 104 *Half the stated coupon is paid every six months a) Calculate zero rates for maturities of 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months b) What are the forward rates for the periods: 6 months to 12 months, 12 months to 18 months, 18 months to 24 months? c) What are the 6-month, 12-month, 18-month, and 24-month par yields for bonds that provide semiannual coupon payments? d) Estimate the price and yield of a two-year bond providing a semiannual coupon of 7% per annum. Problem 5.27. A stock is expected to pay a dividend of S1 per share in two months and in five months. The stock price is $50, and the risk-free rate of interest is 8% per annum with continuous compounding for all maturities. An investor has just taken a short position in a six-month forward contract on the stock. a) What are the forward price and the initial value of the forward contract? b) Three months later, the price of the stock is $48 and the risk-free rate of interest is still 8% per annum. What are the forward price and the value of the short position in the forward contract? Problem 6.25 It is March 10, 2011. The cheapest-to-deliver bond in a December 2011 Treasury bond futures contract is an 8% coupon bond, and delivery is expected to be made on December 31 31, 2011. Coupon payments on the bond are made on March 1 and September I each year The term structure is flat, and the rate of interest with continuous compounding is 5% per annum. The conversion factor for the bond is 1.2191. The current quoted bond price is $137. Calculate the quoted futures price for the contract. Problem 7.23. Under the terms of an interest rate swap, a financial institution has agreed to pay 10% per annum and receive three-month LIBOR in return on a notional principal of $100 million with payments being exchanged every three months. The swap has a remaining life of 14 months. The average of the bid and offer fixed rates currently being swapped for three-month LIBOR is 12% per annum for all maturities. The three-month LIBOR rate one month ago was 11.8% per annum. All rates are compounded quarterly. What is the value of the swap? Problem 4.32. The following table gives the prices of bonds Bond Principal (8) Annual Coupon (5) Bond Price (8) Time to Maturity (yrs) 100 0.5 0.0 98 100 1.0 0.0 95 100 1.5 6.2 101 100 2.0 8,0 104 *Half the stated coupon is paid every six months a) Calculate zero rates for maturities of 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months b) What are the forward rates for the periods: 6 months to 12 months, 12 months to 18 months, 18 months to 24 months? c) What are the 6-month, 12-month, 18-month, and 24-month par yields for bonds that provide semiannual coupon payments? d) Estimate the price and yield of a two-year bond providing a semiannual coupon of 7% per annum. Problem 5.27. A stock is expected to pay a dividend of S1 per share in two months and in five months. The stock price is $50, and the risk-free rate of interest is 8% per annum with continuous compounding for all maturities. An investor has just taken a short position in a six-month forward contract on the stock. a) What are the forward price and the initial value of the forward contract? b) Three months later, the price of the stock is $48 and the risk-free rate of interest is still 8% per annum. What are the forward price and the value of the short position in the forward contract? Problem 6.25 It is March 10, 2011. The cheapest-to-deliver bond in a December 2011 Treasury bond futures contract is an 8% coupon bond, and delivery is expected to be made on December 31 31, 2011. Coupon payments on the bond are made on March 1 and September I each year The term structure is flat, and the rate of interest with continuous compounding is 5% per annum. The conversion factor for the bond is 1.2191. The current quoted bond price is $137. Calculate the quoted futures price for the contract. Problem 7.23. Under the terms of an interest rate swap, a financial institution has agreed to pay 10% per annum and receive three-month LIBOR in return on a notional principal of $100 million with payments being exchanged every three months. The swap has a remaining life of 14 months. The average of the bid and offer fixed rates currently being swapped for three-month LIBOR is 12% per annum for all maturities. The three-month LIBOR rate one month ago was 11.8% per annum. All rates are compounded quarterly. What is the value of the swap










