Please read the game instructions then fill in the finianical statement and decision sheet for the prediction of the next year. thank you!!
game instructions:
Valor game
General presentation of the case
1 - Introduction
VALOR is a business game (or a management simulation) designed to train students in
accounting concepts and financial reports. Participants have to establish their balance
sheets, income statements, statement of retained earnings and cash flow statements.
2- Your company and the market
On January 1* 2020, the company is a growing small sized company that sells hair
dryers in a market limited to the national market. At the beginning of the game, the
market is evenly divided among companies of comparable size.
The average market of the year 2020 per company is approximately 100,000 units
Presumably the market will develop at a later time by about 10% per year, but it depends
on the decisions taken by companies, in particular prices, advertising budget, etc. Your
market is extremely sensitive to the proposed price.
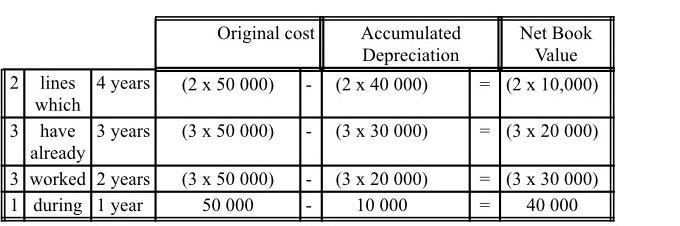
3 - Industrial equipment
On January 1$ 2020, the production capacity of each company is 9 assembly lines. A line
can produce a maximum of 10,000 devices per year.
An investment in a new line represents an investment of $50,000, depreciated on a linear
basis over five years (i.e. $10,000 per year).
Depreciation expense on the assembly lines is considered Manufacturing overhead
Specifically, the equipment on January 1* 2020 consists of (see also the Balance Sheet)
Each company may acquire new lines that can be used as soon as the purchase period.
Once the machine is fully amortized, the machine is being scrapped (i.e., you cannot use
it for your production).
4 - Inventories
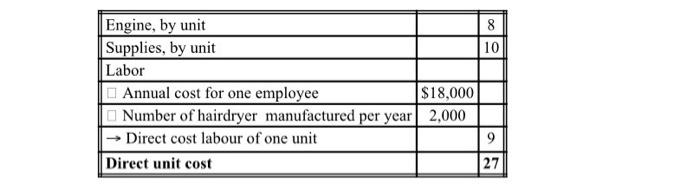
To mount the hairdryer, companies buy their raw materials: engines and other supplies.
The engines cost is $8 per unit in 2020 and the cost of supplies is $10. Therefore, total
cost of raw materials: $18.
On January 1*, the raw materials inventory is 10,000 sets of engines and supplies. The
company also has an inventory of 5,000 finished products (ready for sale) valued at their
direct cost: material + productive labor: $27. See Table below.
5- Staff
On January 1*, 50 people are working in the production. Each worker can mount
normally 2,000 items per year.
You can hire or dismiss people. In case of dismissal, the employee is entitled to
severance payment equal to four-month gross salary (no payroll deductions).
At year 2020, the gross remuneration per employee is $12,000 per year. The employers'
payroll taxes are estimated at 50% of that amount, or a total cost per employee of
$18,000. An increase may be granted to all workers, according to the requests made by the staff representatives. (Beware, a strike is not impossible!)
The administrative staff has an overall gross compensation of $200,000 per year growing
at the same rate as the remuneration of the production staff. You also need to add the
employers' payroll taxes which also represent 50%. This staff cannot be dismissed
6 - Financing
The starting balance sheet (see below) indicates that shareholders have brought $250,000
and that the company has made profits in the past since accumulated retained earnings are
$110,000 and the net income of the year 2019 is $90,000.
A loan of $200,000 was contracted in 2018 at the interest rate of 8%. It has to be repaid
on December 31 2021, interest being payable every year-end.
You can negotiate a new loan with your banker (me) based on your financing needs.
Moreover, you can also request a capital increase that must be reviewed by the
shareholders (me). The decision is made based on your situation.
Temporary financing needs can be covered by an overdraft granted by the Bank, but you
must meet your banker to negotiate the interest rate to be applied to the potential
overdraft.
Balance sheet at 31 December 2019 (in thousands)


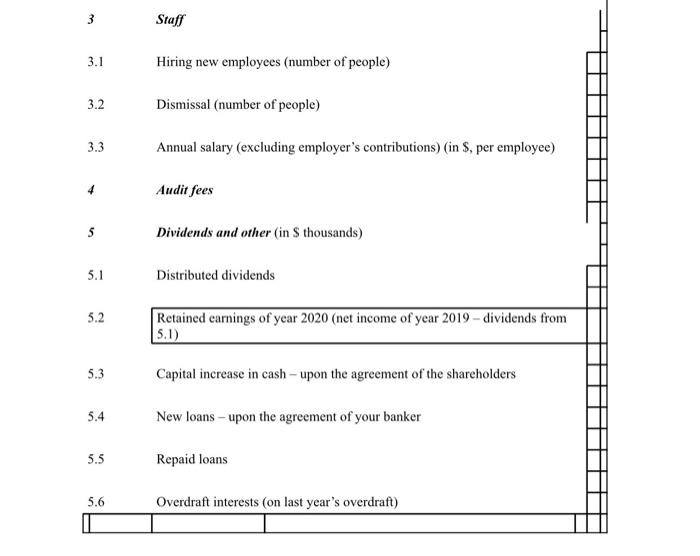
Decision sheet:
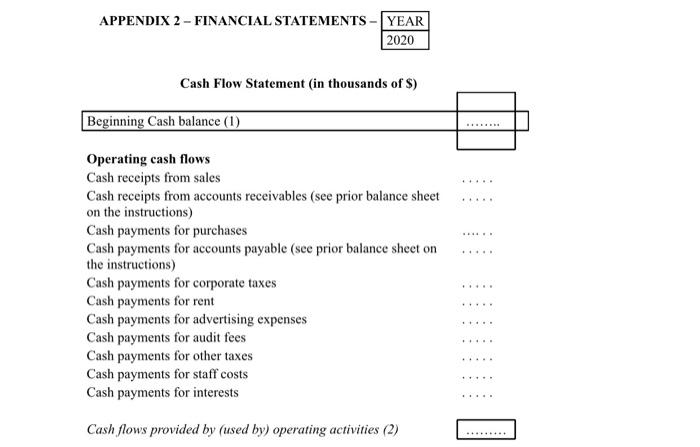
finanical sheet:
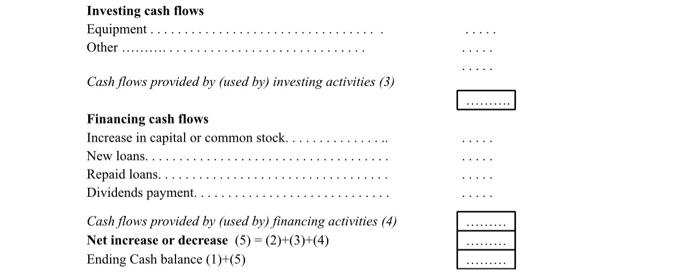

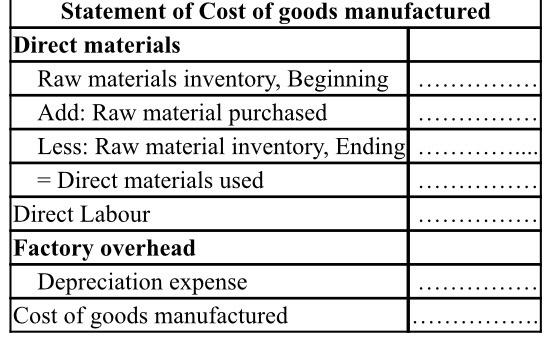
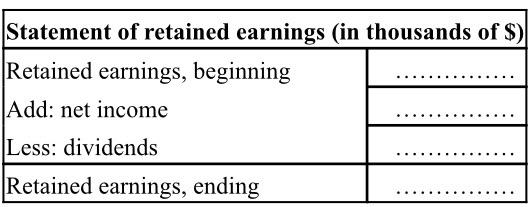
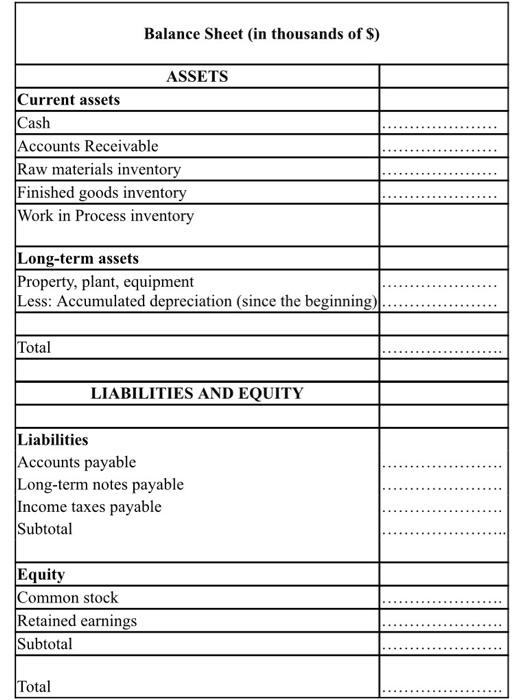
Original cost Accumulated Depreciation (2 x 40 000) Net Book Value (2 x 10,000) (2 x 50 000) 2 lines 4 years which 31 have 3 years already 3 worked 2 years 1 during 1 year (3 x 50 000) (3 x 30 000) (3 x 20 000) (3 x 50 000) 50 000 (3 x 20 000) 10 000 (3 x 30 000) 40 000 = 8 10 Engine, by unit Supplies, by unit Labor Annual cost for one employee $18,000 Number of hairdryer manufactured per year 2,000 - Direct cost labour of one unit Direct unit cost 9 27 Balance sheet at 31 December 2019 (in thousands) 120 ASSETS Current assets Cash Accounts Receivable Raw materials inventory Finished goods inventory Work in Process inventory 3500 1801 135 10 Long-term assets Property, plant, equipment 1450 Less: Accumulated depreciation 240 Total 19451 LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Liabilities Accounts payable Long-term notes payable Income taxes payable Subtotal 2351 200 160 14951 Equity Common stock Retained earnings Subtotal 1250 2001 4501 Total 19451 7 - Other costs For the year 2020: The rental cost of office is $300,000. Other taxes are of $40,000. Other costs depend on your decisions: advertising expenditures. This expenditure represents 2 to 5% of the cost of products (before advertising expenses). 8 - Suppliers and customers All of the above costs (general expenses) and the wages and investments are paid on the reporting period. 90% of purchases of raw materials are paid on the period, the remaining 10% on the next period (ie, accounts payable) The customers pay 85% of deliveries/invoices over the period. The remaining 15% are accounts receivables 9 Tax - dividends In case of a profit (we can be optimistic), your company has to pay corporate income taxes at a rate of 40%. This tax is paid in the following year for the sake of simplification In case of a net loss, tax is 0 The net income can be distributed wholly or partially in the form of dividends to shareholders. The amount of dividends distributed (if it is not zero), is based on the net income of the previous year. 10 - Operating constraints Sales quantities cannot be greater than the quantity available at the beginning of period (beginning inventory), to which we add the production of the yeat. Second part: Work to do 1 - Decisions to be taken by the Management Committee. Submit your decision sheet for 2020. 2 - Simulation for 2020 A- Preparation of predicted reports for 2020 to test your decisions. It is desirable that the documents are balanced, but it is not a requirement. Do not hesitate to email the accountant of the company (me) if you need help. B-Market verdict: each team takes note of the amount of its actual sales in 2020. This amount is based on the decisions of the company and its competitors. C-Establishment of the realized reports. These documents must be balanced this time. Indeed, before being submitted to the annual general meeting, they will be certified by the auditor of the company (me) Third part: list of appendices Appendix 1: Decision sheet Appendix 2: Financial statements (for predicted figures). I suggest you to start completing the financial statements in the following order: 1. Cash flow statement 2. Cost of Goods manufactured report 3. Income statement 4. Statement of Retained Earnings 5. Balance sheet APPENDIX 1: DECISION SHEET YEAR N [ COMPANY NAME 1 Production 1.1 Quantity produced 1.2 Investment (number of assembly lines) 1.3 Purchases of raw materials (quantity) 1.4 Consumption of raw materials (quantity) 2 Sales 2.1 Quantity sold 2.2 Advertising expenditures 2.3 Unit selling price (in $) 3 Staff 3 Staff 3.1 Hiring new employees (number of people) 3.2 Dismissal (number of people) 3.3 Annual salary (excluding employer's contributions) (in $, per employee) 4 Audit fees S Dividends and other in thousands) 5.1 Distributed dividends 5.2 Retained earnings of year 2020 (net income of year 2019 - dividends from 5.1) 5.3 Capital increase in cash - upon the agreement of the shareholders 5.4 New loans - upon the agreement of your banker 5.5 Repaid loans 5.6 Overdraft interests (on last year's overdraft) APPENDIX 2 - FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - YEAR 2020 Cash Flow Statement in thousands of $) Beginning Cash balance (1) ... Operating cash flows Cash receipts from sales Cash receipts from accounts receivables (see prior balance sheet on the instructions) Cash payments for purchases Cash payments for accounts payable (see prior balance sheet on the instructions) Cash payments for corporate taxes Cash payments for rent Cash payments for advertising expenses Cash payments for audit fees Cash payments for other taxes Cash payments for staff costs Cash payments for interests Cash flows provided by (used by) operating activities (2) Investing cash flows Equipment... Other Cash flows provided by (used by) investing activities (3) Financing cash flows Increase in capital or common stock. New loans...... Repaid loans... Dividends payment.. Cash flows provided by (used by) financing activities (4) Net increase or decrease (5) = (2)+(3)+(4) Ending Cash balance (1)+(5) 3 Income Statement in thousands of S) Revenue Sales Cost of Goods Sold Finished Goods inventory, Beginning Cost of Goods manufactured Less: Finished Goods inventory, Ending| Cost of Goods sold Gross Profit = sales - COGS Operating expenses Advertising expense Administrative salaries Severance expense (if layoff) Rent expenses Audit fees Other taxes Total operating expenses Interest expense Income before taxes Income tax expense Net Income Statement of Cost of goods manufactured Direct materials Raw materials inventory, Beginning Add: Raw material purchased Less: Raw material inventory, Ending = Direct materials used Direct Labour Factory overhead Depreciation expense Cost of goods manufactured - Statement of retained earnings (in thousands of $) Retained earnings, beginning Add: net income Less: dividends Retained earnings, ending Balance Sheet (in thousands of $) ASSETS Current assets Cash Accounts Receivable Raw materials inventory Finished goods inventory Work in Process inventory Long-term assets Property, plant, equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation (since the beginning) Total LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Liabilities Accounts payable Long-term notes payable Income taxes payable Subtotal Equity Common stock Retained earnings Subtotal Total Original cost Accumulated Depreciation (2 x 40 000) Net Book Value (2 x 10,000) (2 x 50 000) 2 lines 4 years which 31 have 3 years already 3 worked 2 years 1 during 1 year (3 x 50 000) (3 x 30 000) (3 x 20 000) (3 x 50 000) 50 000 (3 x 20 000) 10 000 (3 x 30 000) 40 000 = 8 10 Engine, by unit Supplies, by unit Labor Annual cost for one employee $18,000 Number of hairdryer manufactured per year 2,000 - Direct cost labour of one unit Direct unit cost 9 27 Balance sheet at 31 December 2019 (in thousands) 120 ASSETS Current assets Cash Accounts Receivable Raw materials inventory Finished goods inventory Work in Process inventory 3500 1801 135 10 Long-term assets Property, plant, equipment 1450 Less: Accumulated depreciation 240 Total 19451 LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Liabilities Accounts payable Long-term notes payable Income taxes payable Subtotal 2351 200 160 14951 Equity Common stock Retained earnings Subtotal 1250 2001 4501 Total 19451 7 - Other costs For the year 2020: The rental cost of office is $300,000. Other taxes are of $40,000. Other costs depend on your decisions: advertising expenditures. This expenditure represents 2 to 5% of the cost of products (before advertising expenses). 8 - Suppliers and customers All of the above costs (general expenses) and the wages and investments are paid on the reporting period. 90% of purchases of raw materials are paid on the period, the remaining 10% on the next period (ie, accounts payable) The customers pay 85% of deliveries/invoices over the period. The remaining 15% are accounts receivables 9 Tax - dividends In case of a profit (we can be optimistic), your company has to pay corporate income taxes at a rate of 40%. This tax is paid in the following year for the sake of simplification In case of a net loss, tax is 0 The net income can be distributed wholly or partially in the form of dividends to shareholders. The amount of dividends distributed (if it is not zero), is based on the net income of the previous year. 10 - Operating constraints Sales quantities cannot be greater than the quantity available at the beginning of period (beginning inventory), to which we add the production of the yeat. Second part: Work to do 1 - Decisions to be taken by the Management Committee. Submit your decision sheet for 2020. 2 - Simulation for 2020 A- Preparation of predicted reports for 2020 to test your decisions. It is desirable that the documents are balanced, but it is not a requirement. Do not hesitate to email the accountant of the company (me) if you need help. B-Market verdict: each team takes note of the amount of its actual sales in 2020. This amount is based on the decisions of the company and its competitors. C-Establishment of the realized reports. These documents must be balanced this time. Indeed, before being submitted to the annual general meeting, they will be certified by the auditor of the company (me) Third part: list of appendices Appendix 1: Decision sheet Appendix 2: Financial statements (for predicted figures). I suggest you to start completing the financial statements in the following order: 1. Cash flow statement 2. Cost of Goods manufactured report 3. Income statement 4. Statement of Retained Earnings 5. Balance sheet APPENDIX 1: DECISION SHEET YEAR N [ COMPANY NAME 1 Production 1.1 Quantity produced 1.2 Investment (number of assembly lines) 1.3 Purchases of raw materials (quantity) 1.4 Consumption of raw materials (quantity) 2 Sales 2.1 Quantity sold 2.2 Advertising expenditures 2.3 Unit selling price (in $) 3 Staff 3 Staff 3.1 Hiring new employees (number of people) 3.2 Dismissal (number of people) 3.3 Annual salary (excluding employer's contributions) (in $, per employee) 4 Audit fees S Dividends and other in thousands) 5.1 Distributed dividends 5.2 Retained earnings of year 2020 (net income of year 2019 - dividends from 5.1) 5.3 Capital increase in cash - upon the agreement of the shareholders 5.4 New loans - upon the agreement of your banker 5.5 Repaid loans 5.6 Overdraft interests (on last year's overdraft) APPENDIX 2 - FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - YEAR 2020 Cash Flow Statement in thousands of $) Beginning Cash balance (1) ... Operating cash flows Cash receipts from sales Cash receipts from accounts receivables (see prior balance sheet on the instructions) Cash payments for purchases Cash payments for accounts payable (see prior balance sheet on the instructions) Cash payments for corporate taxes Cash payments for rent Cash payments for advertising expenses Cash payments for audit fees Cash payments for other taxes Cash payments for staff costs Cash payments for interests Cash flows provided by (used by) operating activities (2) Investing cash flows Equipment... Other Cash flows provided by (used by) investing activities (3) Financing cash flows Increase in capital or common stock. New loans...... Repaid loans... Dividends payment.. Cash flows provided by (used by) financing activities (4) Net increase or decrease (5) = (2)+(3)+(4) Ending Cash balance (1)+(5) 3 Income Statement in thousands of S) Revenue Sales Cost of Goods Sold Finished Goods inventory, Beginning Cost of Goods manufactured Less: Finished Goods inventory, Ending| Cost of Goods sold Gross Profit = sales - COGS Operating expenses Advertising expense Administrative salaries Severance expense (if layoff) Rent expenses Audit fees Other taxes Total operating expenses Interest expense Income before taxes Income tax expense Net Income Statement of Cost of goods manufactured Direct materials Raw materials inventory, Beginning Add: Raw material purchased Less: Raw material inventory, Ending = Direct materials used Direct Labour Factory overhead Depreciation expense Cost of goods manufactured - Statement of retained earnings (in thousands of $) Retained earnings, beginning Add: net income Less: dividends Retained earnings, ending Balance Sheet (in thousands of $) ASSETS Current assets Cash Accounts Receivable Raw materials inventory Finished goods inventory Work in Process inventory Long-term assets Property, plant, equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation (since the beginning) Total LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Liabilities Accounts payable Long-term notes payable Income taxes payable Subtotal Equity Common stock Retained earnings Subtotal Total