please use C++
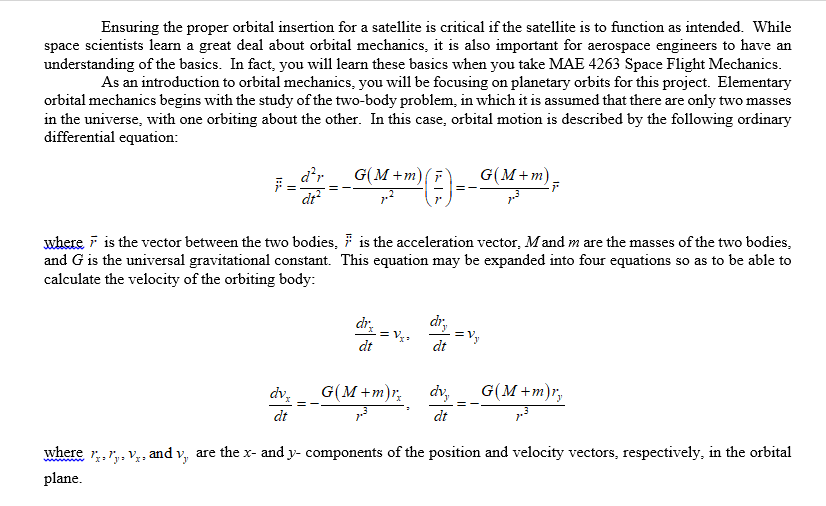



Ensuring the proper orbital insertion for a satellite is critical if the satellite is to function as intended. While space scientists learn a great deal about orbital mechanics, it is also important for aerospace engineers to have arn understanding of the basics. In fact, you will learn these basics when you take MAE 4263 Space Flight Mechanics As an introduction to orbital mechanics, you will be focusing on planetary orbits for this project. Elementary orbital mechanics begins with the study of the two-body problem, in which it is assumed that there are only two masses in the universe, with one orbiting about the other. In this case, orbital motion is described by the following ordinary differential equatiorn where is the vector between the two bodies, i is the acceleration vector, Mand m are the masses of the two bodies and G is the universal gravitational constant. This equation may be expanded into four equations so as to be able to calculate the velocity of the orbiting body: dh dr dt where r..r,, v, and v, are the x- and y- components of the position and velocity vectors, respectively, in the orbital lane Ensuring the proper orbital insertion for a satellite is critical if the satellite is to function as intended. While space scientists learn a great deal about orbital mechanics, it is also important for aerospace engineers to have arn understanding of the basics. In fact, you will learn these basics when you take MAE 4263 Space Flight Mechanics As an introduction to orbital mechanics, you will be focusing on planetary orbits for this project. Elementary orbital mechanics begins with the study of the two-body problem, in which it is assumed that there are only two masses in the universe, with one orbiting about the other. In this case, orbital motion is described by the following ordinary differential equatiorn where is the vector between the two bodies, i is the acceleration vector, Mand m are the masses of the two bodies and G is the universal gravitational constant. This equation may be expanded into four equations so as to be able to calculate the velocity of the orbiting body: dh dr dt where r..r,, v, and v, are the x- and y- components of the position and velocity vectors, respectively, in the orbital lane










