Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please use the information below to calculate the predicted values in tableau please show calculated field used. DECISION TREE 3.25 GPA 650 580 GMAT AMAY
please use the information below to calculate the predicted values in tableau
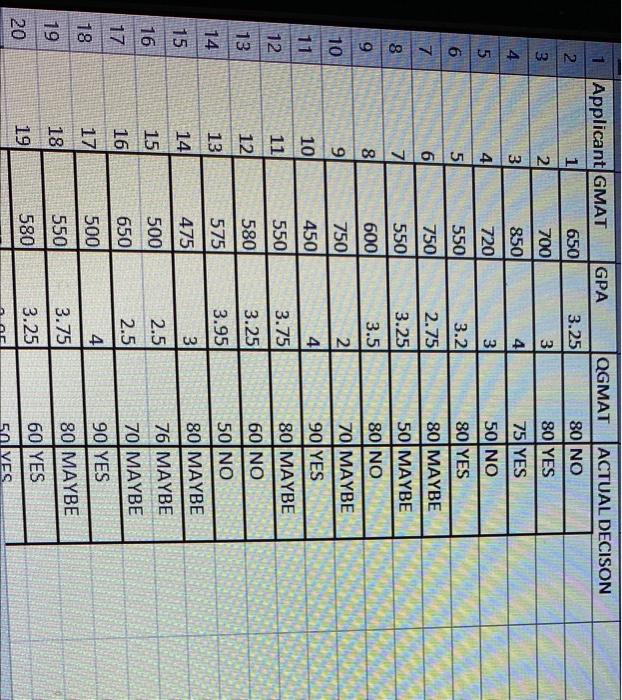
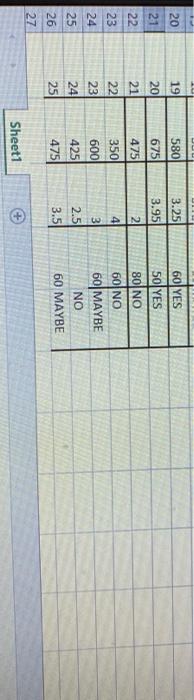
DECISION TREE 3.25 GPA 650 580 GMAT AMAY 80 2.95 YES NO OGMAT GPA YES MAYBE NO MAYBE 2 N 6 1 Applicant GMAT GPA QGMAT ACTUAL DECISON 1 650 3.25 80 NO 3 2 700 3 80 YES 4. 3 850 4 75 YES 5 41 720 3 50 NO 6 5 550 3.2 80 YES 7 6 750 2.75 80 MAYBE 8 7 550 3.25 50 MAYBE 9 8 600 3.5 80 NO 10 9 750 2 70 MAYBE 11 10 450) 4 90 YES 12 11 550 3.75 80 MAYBE 12 13 580 60 NO 3.25 14 13 575 3.95 50 NO 14 3 475 15 80 MAYBE 15 500 2.5 76 MAYBE 16 17 650 2.5 70 MAYBE 171 18 500 4 90YES 18 19 550 3.75 80 MAYBE 20 580 60 YES 19 3.25 50VES 16 BIN 20 19 580 3.25 60 YES 20 675 3.95 50 YES 21 475 80 NO 21 22 23 24 22 3501 41 2 23 6001 31 60 NO 60 MAYBE NO 60 MAYBE 25 24 425 2.51 NOU 25 475 26 27 3.5 Sheet1 1. Given the following validation data on MBA admission APPLICANT_FINAL (applicant. D. GMAT, GPA, QGMAT, Decision) available with exam GMAT is student GMAT score GPA is student GPA QGMAT is quantitative part score of GMAT Decision is actual decision (yes, no or maybe) Jim Smith, MBA director, developed decision tree model (see last page; Appendix A) using training data Task 1. Using data in APPLICANT_FINAL file (assume all of it is validation data), calculate the PREDICTED values in Tableau call it worksheeti. Hint: use if-then-else or if-then-elseif statements for each branch in the decision tree to calculate predicted outcome (yes, no or maybe). DECISION TREE 3.25 GPA 650 580 GMAT AMAY 80 2.95 YES NO OGMAT GPA YES MAYBE NO MAYBE 2 N 6 1 Applicant GMAT GPA QGMAT ACTUAL DECISON 1 650 3.25 80 NO 3 2 700 3 80 YES 4. 3 850 4 75 YES 5 41 720 3 50 NO 6 5 550 3.2 80 YES 7 6 750 2.75 80 MAYBE 8 7 550 3.25 50 MAYBE 9 8 600 3.5 80 NO 10 9 750 2 70 MAYBE 11 10 450) 4 90 YES 12 11 550 3.75 80 MAYBE 12 13 580 60 NO 3.25 14 13 575 3.95 50 NO 14 3 475 15 80 MAYBE 15 500 2.5 76 MAYBE 16 17 650 2.5 70 MAYBE 171 18 500 4 90YES 18 19 550 3.75 80 MAYBE 20 580 60 YES 19 3.25 50VES 16 BIN 20 19 580 3.25 60 YES 20 675 3.95 50 YES 21 475 80 NO 21 22 23 24 22 3501 41 2 23 6001 31 60 NO 60 MAYBE NO 60 MAYBE 25 24 425 2.51 NOU 25 475 26 27 3.5 Sheet1 1. Given the following validation data on MBA admission APPLICANT_FINAL (applicant. D. GMAT, GPA, QGMAT, Decision) available with exam GMAT is student GMAT score GPA is student GPA QGMAT is quantitative part score of GMAT Decision is actual decision (yes, no or maybe) Jim Smith, MBA director, developed decision tree model (see last page; Appendix A) using training data Task 1. Using data in APPLICANT_FINAL file (assume all of it is validation data), calculate the PREDICTED values in Tableau call it worksheeti. Hint: use if-then-else or if-then-elseif statements for each branch in the decision tree to calculate predicted outcome (yes, no or maybe) please show calculated field used. 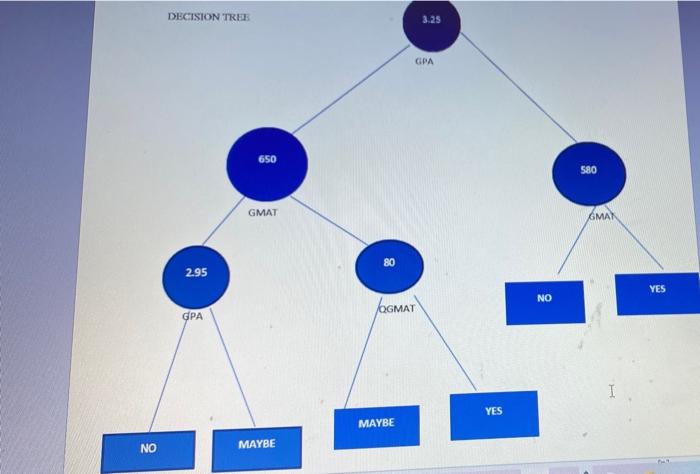





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


