Question
Please USE the template given below: // Declare class Shape with the required attributes // and define the member functions // define getArea() as pure
Please USE the template given below:


// Declare class Shape with the required attributes
// and define the member functions
// define getArea() as pure virtual function
// define read() and print() as virtual function
// Task 3
// Declare class Circle that inherit Shape class
// Define the required attributes and member functions
// Task 4
// Declare class Rectangle that inherit Shape class
// Define the required attributes and member functions
// Task 5
// Complete the following int menu() function that will display this menu
// and get the user choice
//==========[MENU]============
// 1. Add a shape
// 2. Print all shapes
// 3. Calculate total area
// 4. Exit
//
// Enter your choice => 1
int menu()
{
int choice;
// Please complete
return choice;
}
// Given main() program
int main()
{
// to count the number of shapes instance
int shapeCount=0;
// declarations of pointer array named shapes
// that able to store address for various types of shape
Shape *shapes[20];
// get user choice from the menu
int command = menu();
int shapeType;
Shape *newShape;
while (command!=4){
switch (command){
case 1:
cout
cout ";
cin >> shapeType; // user choice from the menu
cout
// Allocating memory based on types of shape
if (shapeType==1)
newShape = new Circle; // allocate memory for Circle
else
newShape=new Rectangle; // allocate memory for Rectangle
// implementing polymorphism
newShape->read(); // polymorphism
shapes[shapeCount]=newShape; // 'using array to store various shape
shapeCount++; // count number of shapes in the array
break;
case 2:
for (int i=0; i
cout
shapes[i]->print(); // 1m
cout
}
break;
case 3:
// Calculating the total area of all shapes in the array
for (int i=0; i
totalArea += shapes[i]->getArea(); // 1m
cout
break;
}
command = menu();
}
return 0;
}
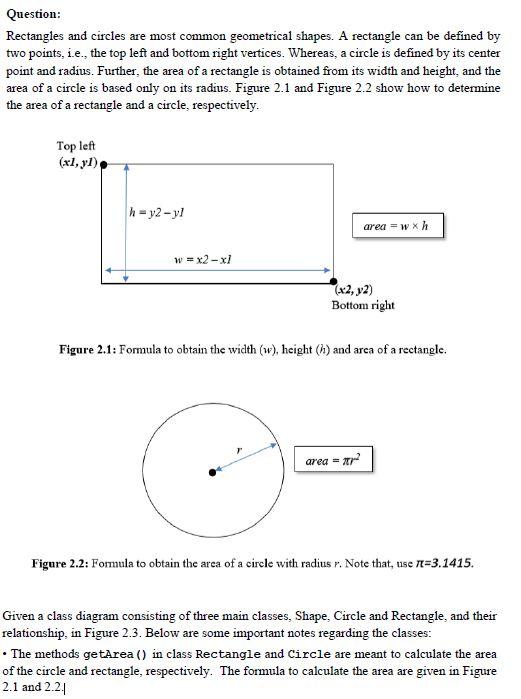
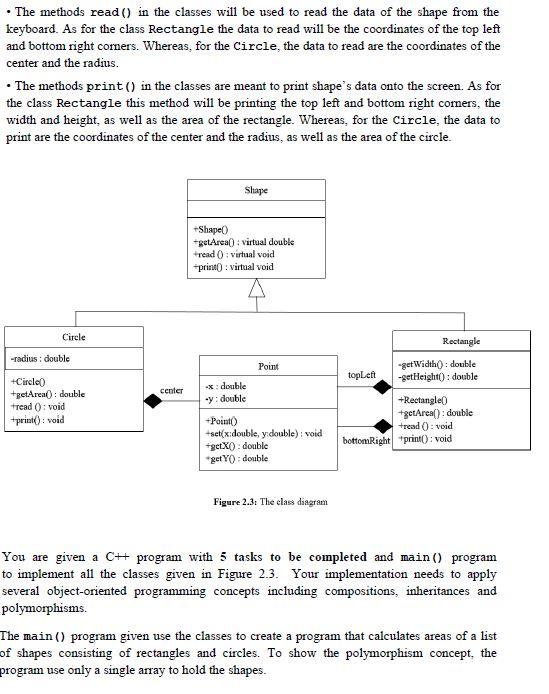
Question: Rectangles and circles are most common geometrical shapes. A rectangle can be defined by two points, i.e., the top left and bottom right vertices. Whereas, a circle is defined by its center point and radius. Further, the area of a rectangle is obtained from its width and height, and the area of a circle is based only on its radius. Figure 2.1 and Figure 2.2 show how to determine the area of a rectangle and a circle, respectively. Top left (x1, y1) h = y2-yl area =w xh w = x2-xl (x2, y2) Bottom right Figure 2.1: Formula to obtain the width (w), height (h) and area of a rectangle. area = ar Figure 2.2: Formula to obtain the area of a circle with radius r. Note that, tise 11=3.1415. Given a class diagram consisting of three main classes. Shape, Circle and Rectangle, and their relationship, in Figure 2.3. Below are some important notes regarding the classes: The methods getArea() in class Rectangle and Circle are meant to calculate the area of the circle and rectangle, respectively. The formula to calculate the area are given in Figure 2.1 and 2.24 The methods read() in the classes will be used to read the data of the shape from the keyboard. As for the class Rectangle the data to read will be the coordinates of the top left and bottom right comers. Whereas, for the Circle, the data to read are the coordinates of the center and the radius. The methods print() in the classes are meant to print shape's data onto the screen. As for the class Rectangle this method will be printing the top left and bottom right comers, the width and height, as well as the area of the rectangle. Whereas, for the Circle, the data to print are the coordinates of the center and the radius, as well as the area of the circle. Shape Shape() #getArea(): virtual double *read(): Virtual void *print) : virtual void Circle Rectangle -radius: double Point top Left -get Width(): double -getHeight(): double center +Circle +getAreal: double tread(): void +print) : void **: double .y: double +Point) #set(xdouble, y double): void + CtX): double "getY(): double +Rectangle +getAreal): double +read(): void bottomRight *print(): void Figure 2.3: The class dangram You are given a C++ program with 5 tasks to be completed and main() program to implement all the classes given in Figure 2.3. Your implementation needs to apply several object-oriented programming concepts including compositions, inheritances and polymorphisms. The main () program given use the classes to create a program that calculates areas of a list of shapes consisting of rectangles and circles. To show the polymorphism concept, the program use only a single array to hold the shapes. Also, the program needs to provide the user a menu-driven interaction with the following options: Menu Options 1. Add a shape 2. Print all shapes 3. Calculate total area Description To insert a new shape (a circle or rectangle) into the array To print the information of all the shapes To calculate and print the total area of all the shapes To end the program 4. Exit Figure 2.4 shows the expected result of your program Note that, all the interactions shown in the figure are continuous in a single run Note also that the bold texts indicate input entered by the user. Interaction 1: The user chooses option to add a circle 1. Add shape 2. Print all shapes 3. Caleulate total area 4. Exit Enter your choice => 1 What type of shape you want to enter? 1. Orele 2. Rectangle Your choice => 1 Enter the center coordinates of the circle (x y)=> 0 O Enter the circle's radius 10 Interaction 2: The user chooses option to add a rectangle. 1. Add a shape 2. Print all shapes 3. Calculate total area 4. Exit Enter your choice > 1 What type of shape you want to enter? 1. Cicole 2. Rectangle Your choice > 2 1 Enter the top left corner coordinates of the rectangle xy => 20 30 Enter the bottom right corner coordinates of the rectangle 1 -> 30 20 Interaction 3: The teer chooser option to add another circle. 1. Add a shape 2. Print all hapes 3. Calculate total area 9. Exit Ence your choice - 1 What type of shape you want to enter? 1. Circle 2. Rectangle Your choice => 1 Enter the center coordinates of the circle (xy-> 50 50 Enter the role radius 50 Interaction 4: The tser chooses option 2 to print the information of all the shapes that hashe has erred THENO 1. Add a shape 2. Deint all shapes 3. Calculate total 1. Exit Enter your choice => 2 Shape 1 Cerezety center: X Y circles radius 10 Carole'a area 311.15 Shape 2 Rectangle's top left corner: X-20 Y=30 leccargle's bottom right corner X-30-20 Rectangle's Wideh - 10 Tectangle's height -10 Rectangle's area -100 Shapes Circle's center: X-50-50 Carciels radius -50 cerelere -7853.75 Interaction 3. The user chooses option 3 to obtain the total area of all the shapes (MENU) 1. Add a shape 2. Print all shapes 3. Calculate total area 1. Exit Enter your choice => 3 Total Area- B267.9 Interaction 6. The user chooses option 4 to end the program. ========= (MENU)============ 1. Add a shape 2. Print all shapes 3. Calculate total area 4. Exit Enter your choice => 4 Figure 2.4: An example run of the programStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


