Please use this formula worksheet to answer this questions. Thnaks.
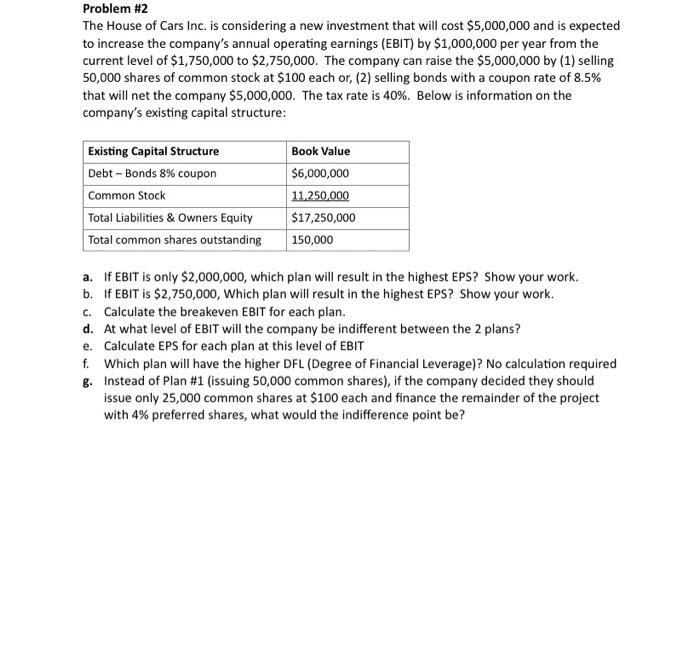
Problem #2 The House of Cars Inc. is considering a new investment that will cost $5,000,000 and is expected to increase the company's annual operating earnings (EBIT) by $1,000,000 per year from the current level of $1,750,000 to $2,750,000. The company can raise the $5,000,000 by (1) selling 50,000 shares of common stock at $100 each or, (2) selling bonds with a coupon rate of 8.5% that will net the company $5,000,000. The tax rate is 40%. Below is information on the company's existing capital structure: Existing Capital Structure Debt-Bonds 8% coupon Common Stock Total Liabilities & Owners Equity Total common shares outstanding Book Value $6,000,000 11.250,000 $17,250,000 150,000 a. If EBIT is only $2,000,000, which plan will result in the highest EPS? Show your work. b. If EBIT is $2,750,000, Which plan will result in the highest EPS? Show your work. C. Calculate the breakeven EBIT for each plan. d. At what level of EBIT will the company be indifferent between the 2 plans? e. Calculate EPS for each plan at this level of EBIT f. Which plan will have the higher DFL (Degree of Financial Leverage)? No calculation required g. Instead of Plan #1 (issuing 50,000 common shares), if the company decided they should issue only 25,000 common shares at $100 each and finance the remainder of the project with 4% preferred shares, what would the indifference point be? Formulas from FINA2360 you may find helpful: FV. PV = = (1+r) C PV =- -S 1 1 - PV = FV, NC (+) C T-9 r-9 w- |--491-4 EAR R=[" APR EAR=1+ m EAR = APR-1 APR 17 EPR= 1+ m FV - MV C + t YTMapprox. FV + MV 2 -12- DA P = -& D Pros 1,011+0.5 r1 [S, dT] 1 PVTS P -g D Ps 1,711+0.571 sarl 1] PV7S = d+r) 1+r +r)(1+r)' Chapter 12: Vari)=(1/(-D)[(R-RY+...+(2, -R] Geometric average retum-[(1+R)(1+R, ) ....*(1+R) - 1 Chapter 13: E(R)-SRXP ' - , - R)] E(R) =W*E(R)+W.XE(R.)+...+WXE(R) g;=Wo+W7g) +2W,w.cov, COV=P(R-E(R)XR, - E(R.)) CORRAPAN COV 00 E(R)=R, +[E(R.)-R, JxB Cov B.-EWB-WA+W.B.+-+W.B. Chapter 14: WACC =W.R.(1-7)+W,RA+W.R. L=W.S+W,S,+W. Amount needed (-XAmount Raised) Pied for 1+(1-TXDIE) Chapter 11 & 16: Financial leverage and capital structure policy EBIT + Fixed Cost Sales-Variable costs_%Change EBIT DOL %Change Sales EBIT EBIT EBIT % Change EPS DFL = EBIT - Interest % Change EBIT % Change EPS DCL = % Change Sales DCL = DOL X DFL General formula for M&M V=E+D No tax case EBIT -= V1 = E,+D. R = R +(R-R,)X(D/E) WACC = W.RE+W.R, RS With taxes case EBIT (1-T) (EBIT-1)(1-T.) V E, R, RE V. =V, +DT. R = R +(R, -R,)X(D/E)x (1-T.) WACC =W.R+W R, (1-T.) With taxes and bankruptcy case V. =V,+DT. - PV of financial distress cost Problem #2 The House of Cars Inc. is considering a new investment that will cost $5,000,000 and is expected to increase the company's annual operating earnings (EBIT) by $1,000,000 per year from the current level of $1,750,000 to $2,750,000. The company can raise the $5,000,000 by (1) selling 50,000 shares of common stock at $100 each or, (2) selling bonds with a coupon rate of 8.5% that will net the company $5,000,000. The tax rate is 40%. Below is information on the company's existing capital structure: Existing Capital Structure Debt-Bonds 8% coupon Common Stock Total Liabilities & Owners Equity Total common shares outstanding Book Value $6,000,000 11.250,000 $17,250,000 150,000 a. If EBIT is only $2,000,000, which plan will result in the highest EPS? Show your work. b. If EBIT is $2,750,000, Which plan will result in the highest EPS? Show your work. C. Calculate the breakeven EBIT for each plan. d. At what level of EBIT will the company be indifferent between the 2 plans? e. Calculate EPS for each plan at this level of EBIT f. Which plan will have the higher DFL (Degree of Financial Leverage)? No calculation required g. Instead of Plan #1 (issuing 50,000 common shares), if the company decided they should issue only 25,000 common shares at $100 each and finance the remainder of the project with 4% preferred shares, what would the indifference point be? Formulas from FINA2360 you may find helpful: FV. PV = = (1+r) C PV =- -S 1 1 - PV = FV, NC (+) C T-9 r-9 w- |--491-4 EAR R=[" APR EAR=1+ m EAR = APR-1 APR 17 EPR= 1+ m FV - MV C + t YTMapprox. FV + MV 2 -12- DA P = -& D Pros 1,011+0.5 r1 [S, dT] 1 PVTS P -g D Ps 1,711+0.571 sarl 1] PV7S = d+r) 1+r +r)(1+r)' Chapter 12: Vari)=(1/(-D)[(R-RY+...+(2, -R] Geometric average retum-[(1+R)(1+R, ) ....*(1+R) - 1 Chapter 13: E(R)-SRXP ' - , - R)] E(R) =W*E(R)+W.XE(R.)+...+WXE(R) g;=Wo+W7g) +2W,w.cov, COV=P(R-E(R)XR, - E(R.)) CORRAPAN COV 00 E(R)=R, +[E(R.)-R, JxB Cov B.-EWB-WA+W.B.+-+W.B. Chapter 14: WACC =W.R.(1-7)+W,RA+W.R. L=W.S+W,S,+W. Amount needed (-XAmount Raised) Pied for 1+(1-TXDIE) Chapter 11 & 16: Financial leverage and capital structure policy EBIT + Fixed Cost Sales-Variable costs_%Change EBIT DOL %Change Sales EBIT EBIT EBIT % Change EPS DFL = EBIT - Interest % Change EBIT % Change EPS DCL = % Change Sales DCL = DOL X DFL General formula for M&M V=E+D No tax case EBIT -= V1 = E,+D. R = R +(R-R,)X(D/E) WACC = W.RE+W.R, RS With taxes case EBIT (1-T) (EBIT-1)(1-T.) V E, R, RE V. =V, +DT. R = R +(R, -R,)X(D/E)x (1-T.) WACC =W.R+W R, (1-T.) With taxes and bankruptcy case V. =V,+DT. - PV of financial distress cost