Question: pls ans correctly...i will thumb up QUESTION 28 when a C programmer uses printf() function, the C program invokes printf() system call. read () system
![defined as: int fd[2]; Such that fd[0] is a read end of](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3a0f4c7a72_48466f3a0f4556a8.jpg)
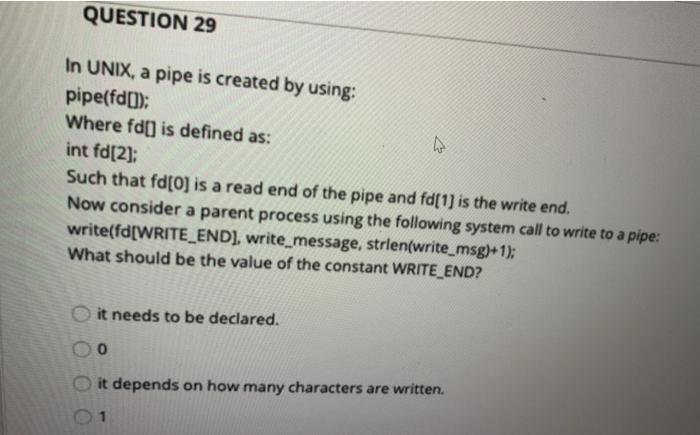
QUESTION 28 when a C programmer uses printf() function, the C program invokes printf() system call. read () system call. write () system call. fprintf() system call. QUESTION 29 In UNIX, a pipe is created by using: pipe(fd()); Where fd) is defined as: int fd[2]; Such that fd[0] is a read end of the pipe and fd[1] is the write end. Now consider a parent process using the following system call write to a pipe: write(fd[WRITE_END], write_message, strlen(write_msg)+1); What should be the value of the constant WRITE_END? it needs to be declared. 0 it depends on how many characters are written. QUESTION 40 One difference between multi-tasking using fork) versus using threads is that inter-process communication between threads is a lot faster than between fork()ed children because context switching is faster inter-processor communications between forked children is not needed. inter-process communication between forked children is a lot faster than between threads because context switching is faster. QUESTION 41 One difference between multi-tasking using fork() versus using threads is that if a parent process in multithreading terminates, all threads terminate automatically. if a parent process in fork() terminates, all children terminate automatically. QUESTION 42 In the following sequence of hello.c execution using the Gnu compiler collection (gcc) 1. gcc-c hello.c 2. gcc-o hello hello.o -Im 3. ./hello Which line number produces the object code for hello.c? 2 3 none
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


