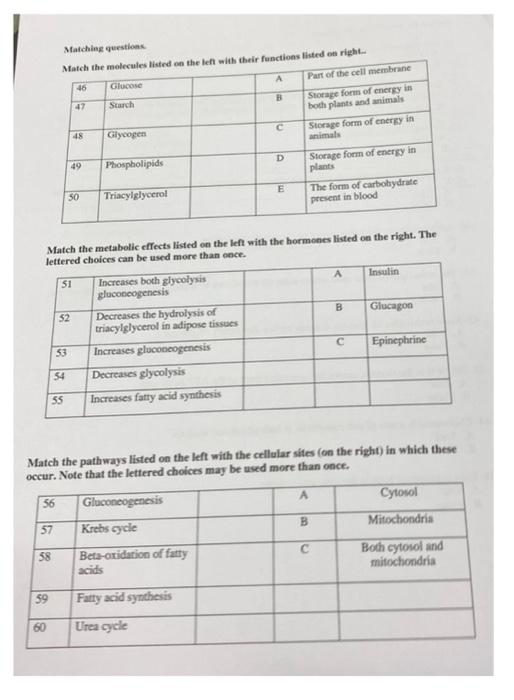
pls anwser frome 1-60

Section I: Multiple Choice questions. Choose the single best answer. 1. The structure shoun below is a A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide D. Dipeptide 2. Which of the following will make the membrane more fluid? A. Low temperature B. Presence of more saturated fatty acids C. Presence of more unsaturated fatty acids D. Presence of cholesterol in membrane at high temperature 3. All of the following are components of cell membrane EXCEPT A. Phospholipids B. Cholesterol C. Proteins D. Triacylglycerol 4. Simple lipids are composed of A. fatty acids and sphingosine B. phospholipids and cholesterol C. fatty acid and ceramide D. fatty acids and glycerol 5. The final three-dimensional structure of the hemoglobin mold. A. primary structure B. secondary structure C. tertiary structure D. quatemary structure 6. Which part of the hemoglobin molecules is responsible for binding with oxygen? A. Histidine of alpha helices B. Iton in the heme molecule C. The amino ierminal end of the all chains D. The carboxy terminal end of all chains 7. -Helix and -pleated sheets are A. primary structure B. secondary structure C. tentiary structure D. quaternary structure 8- Enxymes belong to which of the following class of biomolecules? A. Carbohydrates B. Lipids C. Proteins D. Steroids 9. The Km of an enzyme is the measure of A. inhibition B. total activity C. affinity for the substrate D. covalent modification 10- Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by A. lowering the Km of the reaction B. lowering the activation energy C. increasing the Vman of the reaction D. shifting the equilibrium of the reaction T. Which of the following is required by all enzymes? A. Active site B. Allosteric site C. Co-enzyme D. Inhibitors 12. The regulatory reactions (regulation points) in a pathway are usually catalyzed by A. Coenzymes B. Apoenzymes C. Allosteric enzymes D. Zymogens 13. Glycolysis is the pathway for A. Breakdown of glucose B. Breakdown of glycogen C. Synthesis of glucose D. Synthesis of glycogen 14. Glucose is completely oxidized to CO2 and H2O by the combination of three pathways. These pathways are A. HMP-shunt, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis B. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle C. Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, clectron transport chain D. Gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain 15-Most of the ATP in the cell is produced by A. Substrate level phosphorylation in glycolysis B. Oxidative phosphorylation during electron transport chain C. Substrate level phosphorylation during electron transport chain D. Substrate level phosphorylation in the Krebs cycle 16. Which of the following is produced by MMP - bunt? A NADH B. NADIII C. AcrolCod D. ATP 17. Which of the following pathways compets the inctabolism of cartobydrates, fat and amino peide? oA. glyoolynis B. Krebs cycle C. eluconcogenesis D. hexose mono phosphate shimt. 18. Ammonia (NHu) produced by the degradation of amino acids is toxic. In which of the following form, ammonia is eliminased from the body? A. Urea B. Uric acid C. Glutamine D. NHa+ions in urine 19. Which of the following pathways is responsible for generating energy for red blood cells (Erythrocyes)? A. Krebs cycle B. Glycolysis C. Electron transport chain D. Hexose mono phosphate shunt (HMP-shunt) 20- Ketone bodies are synthesized from A. Pyruvate B. Lactate C. Acetyl CoA D. Cholesterol 21- All of the following can be produced from cholesterol EXCFPT: A. Vitamin D B. Fatty acids C. Bile D. Steroid hormones 22. Acetyl CoA can be produced from the metabolism of which of the following? A. Glucose B. Fatty acids C. Ketogenic amino acids D. All of the above 23- When glycolysis is active, which of the following pathway has to be shut down? A. Krebs cycle B. HMP-shunt C. Gluconeogenesis D. Glycogenolysis 24- In the body glucone is compietely oxidized to CO2 and H,O. HO is produced in which of the following pathways? A. Glycolysis B. Krebs cycle C. HMP-shum D. Electron transport chain 25. The first step in the catabolixm of amino acids for energy is the renyoval of the A. carboxylate groups B. carbon skeleton C. amino group D. side chain 26- If a cell has high levels of AMP (low energy state). which of the following pathways with be inhibited? A. Glycolysis B. Fatty acid synthesis C. Krebs cycle. D. Glycogenolysis 27. Acetyl CoA can be converted into all of the following EXCEMT: A. Fatty acids B. Ketone bodies C. Cholesterol D. Glucose 28- In starvation, which of the following organstissues uses most of the glucose? A. Red blood cells B. Brain C. Skeletal muscles D. Adipose tissues 29. In prolonged starvation ketone bodies are A. produced by kidneys and used by the liver B. produced by muscles and used in the livet C. produced by the liver and used by other tisnues D. produced by the brain and used by muscles 30- During strenuous exercise, when oxygen is in short supply, the muscles cory Art glucose linto which of the following metabolite? A. Pyruvate B. Lactate C. Acetyl CoA D. ketooe bodies 31- Which of the following is the correct sequence of reactions through which lactate is cunverive into glacose by gloconeogencits? 32. Which of the following metabolite of the Krebs cycle is used for gluconeogenesis? A. Oxaloacetate B. Succinyl CoA C. Citrate D. Fumarate 33. Which of the following metabolite plays a key role in the reciprocal regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis? A. Fructose-6-phosphate B. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate C. Fructose-2, 6-bisphosphate D. Glucose-6-phosphate 34. Which of the following amino acids loses its amino group mainly by deamination? A. Glutamine B. Glutamate C. Aspartate D. All amino acids 35- All of the following are required for urea synthesis EXCEPT: A. NADPH B. Ammonia C. ATP D. CO2 36- Camitine helpa transpon acety CeA cet of mitexthendria for fatry acid syntheik. A. Thue B Falve 37. Unsaturated fatty acids produce more ATP than saturated fatry acids of the same chain length. A. Thue B False 38- Hemoglobin is a fibrous protein. A. True B False 39. Being a lipid, eoe gram of cholesterol will produce 9 kcal of energy when oxidized to CO2 and H O. A True - False 40- Amino acids are the major source of glucone during fasting. A True b. False 41. The amino groups from most amino acids are transferred to a-ketoglutarate to make glutamate. A True b. False 42- Since brain relies on glucose, it stores up to a day supply of glycogen. A. True B False 43- NADPH is the electron carrier that generates most of the ATP in the cell. A. True A. False 44- Cholesterol is a part of cell membrane in both plants and animals. A. True B False 5. Urea is produced both in the liver and kidneys. A. True b. False Matching questions. Match the metabolic effects listed on the lef with the hormones listed on the right. The i...-.ed choirens ran be used more than ence. Match the pathways listed on the left with the cellular sites (on the right) in which these occur. Note that the lettered choices may be used more than once. Section I: Multiple Choice questions. Choose the single best answer. 1. The structure shoun below is a A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide D. Dipeptide 2. Which of the following will make the membrane more fluid? A. Low temperature B. Presence of more saturated fatty acids C. Presence of more unsaturated fatty acids D. Presence of cholesterol in membrane at high temperature 3. All of the following are components of cell membrane EXCEPT A. Phospholipids B. Cholesterol C. Proteins D. Triacylglycerol 4. Simple lipids are composed of A. fatty acids and sphingosine B. phospholipids and cholesterol C. fatty acid and ceramide D. fatty acids and glycerol 5. The final three-dimensional structure of the hemoglobin mold. A. primary structure B. secondary structure C. tertiary structure D. quatemary structure 6. Which part of the hemoglobin molecules is responsible for binding with oxygen? A. Histidine of alpha helices B. Iton in the heme molecule C. The amino ierminal end of the all chains D. The carboxy terminal end of all chains 7. -Helix and -pleated sheets are A. primary structure B. secondary structure C. tentiary structure D. quaternary structure 8- Enxymes belong to which of the following class of biomolecules? A. Carbohydrates B. Lipids C. Proteins D. Steroids 9. The Km of an enzyme is the measure of A. inhibition B. total activity C. affinity for the substrate D. covalent modification 10- Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by A. lowering the Km of the reaction B. lowering the activation energy C. increasing the Vman of the reaction D. shifting the equilibrium of the reaction T. Which of the following is required by all enzymes? A. Active site B. Allosteric site C. Co-enzyme D. Inhibitors 12. The regulatory reactions (regulation points) in a pathway are usually catalyzed by A. Coenzymes B. Apoenzymes C. Allosteric enzymes D. Zymogens 13. Glycolysis is the pathway for A. Breakdown of glucose B. Breakdown of glycogen C. Synthesis of glucose D. Synthesis of glycogen 14. Glucose is completely oxidized to CO2 and H2O by the combination of three pathways. These pathways are A. HMP-shunt, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis B. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle C. Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, clectron transport chain D. Gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain 15-Most of the ATP in the cell is produced by A. Substrate level phosphorylation in glycolysis B. Oxidative phosphorylation during electron transport chain C. Substrate level phosphorylation during electron transport chain D. Substrate level phosphorylation in the Krebs cycle 16. Which of the following is produced by MMP - bunt? A NADH B. NADIII C. AcrolCod D. ATP 17. Which of the following pathways compets the inctabolism of cartobydrates, fat and amino peide? oA. glyoolynis B. Krebs cycle C. eluconcogenesis D. hexose mono phosphate shimt. 18. Ammonia (NHu) produced by the degradation of amino acids is toxic. In which of the following form, ammonia is eliminased from the body? A. Urea B. Uric acid C. Glutamine D. NHa+ions in urine 19. Which of the following pathways is responsible for generating energy for red blood cells (Erythrocyes)? A. Krebs cycle B. Glycolysis C. Electron transport chain D. Hexose mono phosphate shunt (HMP-shunt) 20- Ketone bodies are synthesized from A. Pyruvate B. Lactate C. Acetyl CoA D. Cholesterol 21- All of the following can be produced from cholesterol EXCFPT: A. Vitamin D B. Fatty acids C. Bile D. Steroid hormones 22. Acetyl CoA can be produced from the metabolism of which of the following? A. Glucose B. Fatty acids C. Ketogenic amino acids D. All of the above 23- When glycolysis is active, which of the following pathway has to be shut down? A. Krebs cycle B. HMP-shunt C. Gluconeogenesis D. Glycogenolysis 24- In the body glucone is compietely oxidized to CO2 and H,O. HO is produced in which of the following pathways? A. Glycolysis B. Krebs cycle C. HMP-shum D. Electron transport chain 25. The first step in the catabolixm of amino acids for energy is the renyoval of the A. carboxylate groups B. carbon skeleton C. amino group D. side chain 26- If a cell has high levels of AMP (low energy state). which of the following pathways with be inhibited? A. Glycolysis B. Fatty acid synthesis C. Krebs cycle. D. Glycogenolysis 27. Acetyl CoA can be converted into all of the following EXCEMT: A. Fatty acids B. Ketone bodies C. Cholesterol D. Glucose 28- In starvation, which of the following organstissues uses most of the glucose? A. Red blood cells B. Brain C. Skeletal muscles D. Adipose tissues 29. In prolonged starvation ketone bodies are A. produced by kidneys and used by the liver B. produced by muscles and used in the livet C. produced by the liver and used by other tisnues D. produced by the brain and used by muscles 30- During strenuous exercise, when oxygen is in short supply, the muscles cory Art glucose linto which of the following metabolite? A. Pyruvate B. Lactate C. Acetyl CoA D. ketooe bodies 31- Which of the following is the correct sequence of reactions through which lactate is cunverive into glacose by gloconeogencits? 32. Which of the following metabolite of the Krebs cycle is used for gluconeogenesis? A. Oxaloacetate B. Succinyl CoA C. Citrate D. Fumarate 33. Which of the following metabolite plays a key role in the reciprocal regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis? A. Fructose-6-phosphate B. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate C. Fructose-2, 6-bisphosphate D. Glucose-6-phosphate 34. Which of the following amino acids loses its amino group mainly by deamination? A. Glutamine B. Glutamate C. Aspartate D. All amino acids 35- All of the following are required for urea synthesis EXCEPT: A. NADPH B. Ammonia C. ATP D. CO2 36- Camitine helpa transpon acety CeA cet of mitexthendria for fatry acid syntheik. A. Thue B Falve 37. Unsaturated fatty acids produce more ATP than saturated fatry acids of the same chain length. A. Thue B False 38- Hemoglobin is a fibrous protein. A. True B False 39. Being a lipid, eoe gram of cholesterol will produce 9 kcal of energy when oxidized to CO2 and H O. A True - False 40- Amino acids are the major source of glucone during fasting. A True b. False 41. The amino groups from most amino acids are transferred to a-ketoglutarate to make glutamate. A True b. False 42- Since brain relies on glucose, it stores up to a day supply of glycogen. A. True B False 43- NADPH is the electron carrier that generates most of the ATP in the cell. A. True A. False 44- Cholesterol is a part of cell membrane in both plants and animals. A. True B False 5. Urea is produced both in the liver and kidneys. A. True b. False Matching questions. Match the metabolic effects listed on the lef with the hormones listed on the right. The i...-.ed choirens ran be used more than ence. Match the pathways listed on the left with the cellular sites (on the right) in which these occur. Note that the lettered choices may be used more than once