pls help solve this
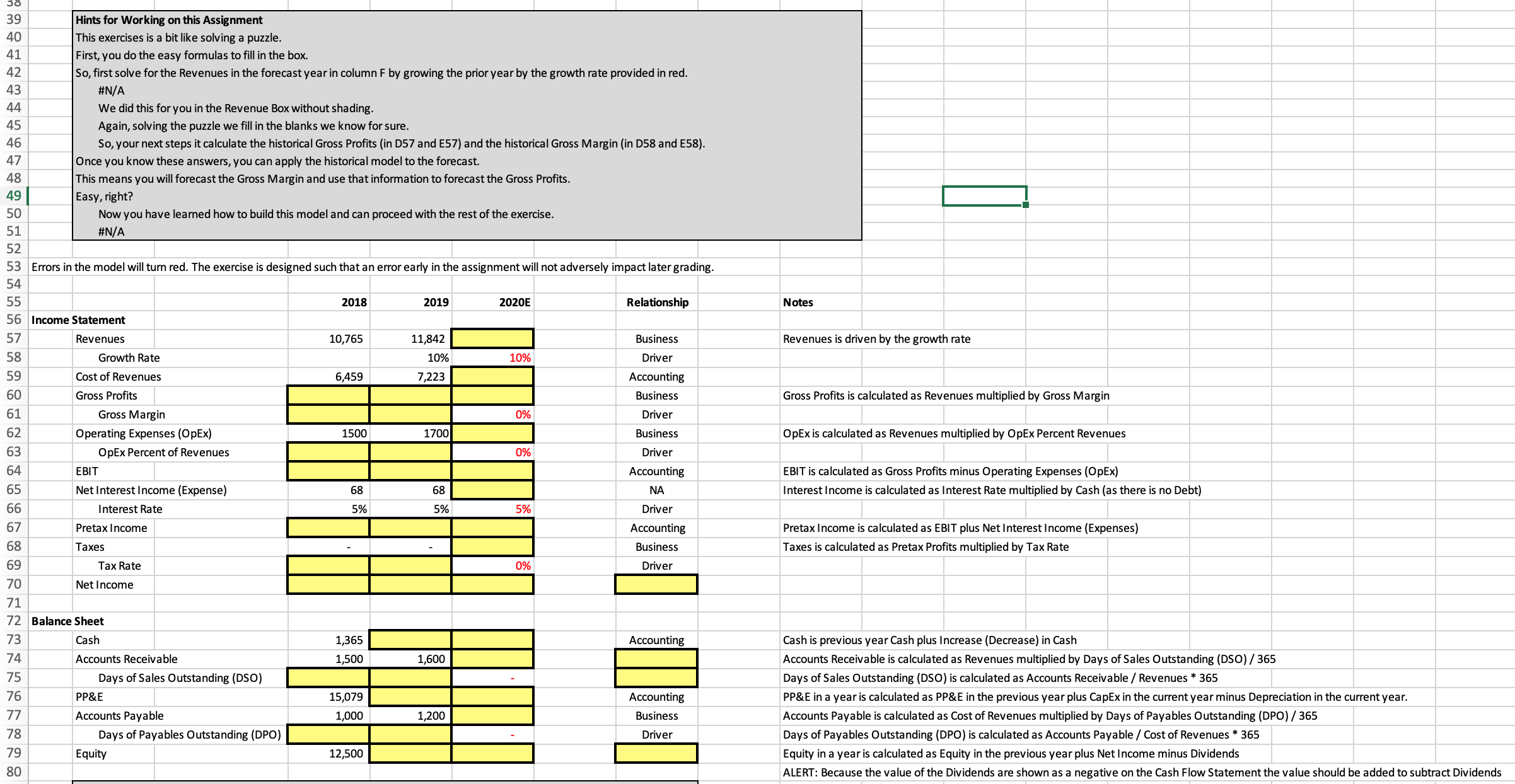
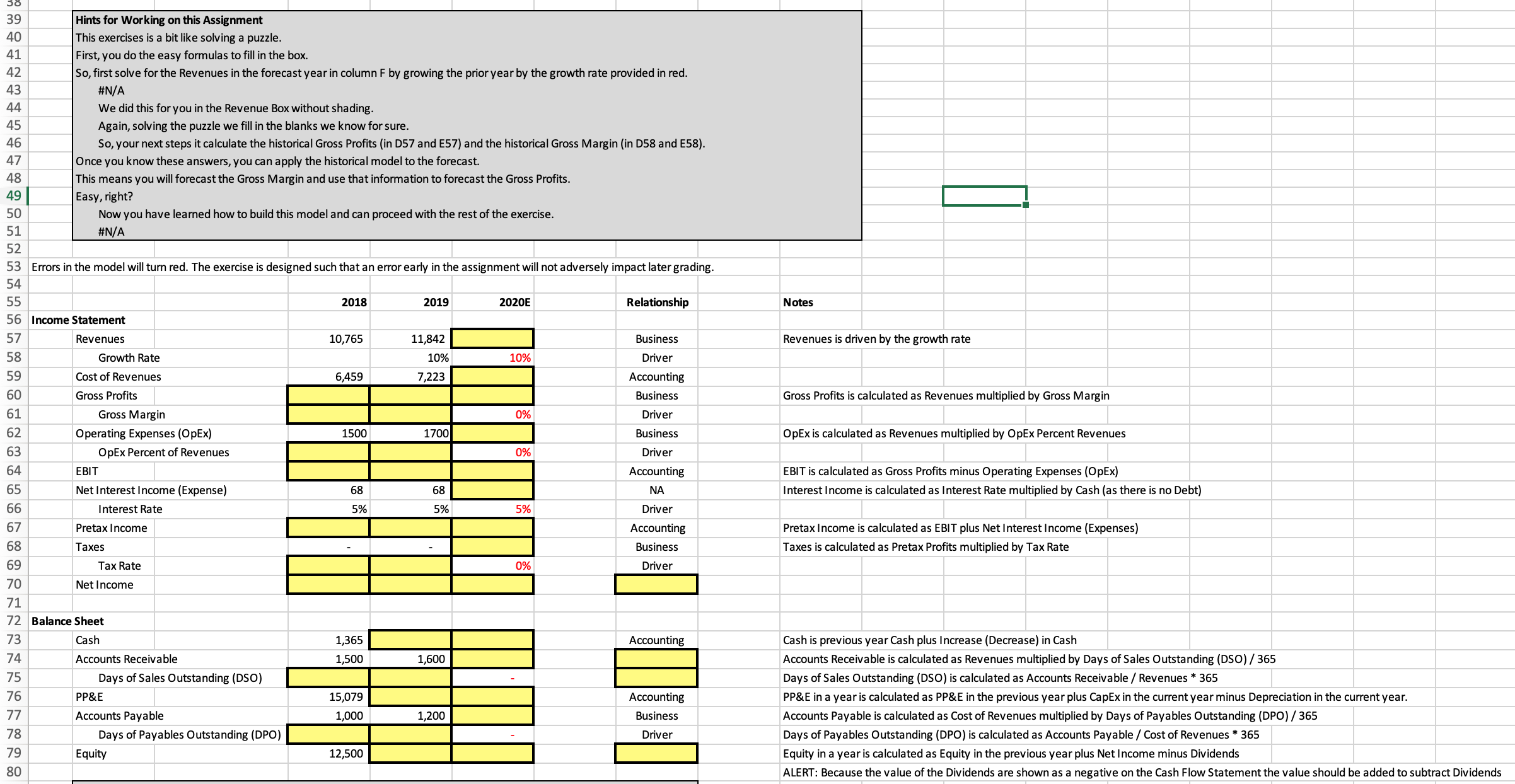
39 Hints for Working on this Assignment 40 This exercises is a bit like solving a puzzle. 41 First, you do the easy formulas to fill in the box. 42 So, first solve for the Revenues in the forecast year in column F by growing the prior year by the growth rate provided in red. 43 #N/A 44 We did this for you in the Revenue Box without shading. 45 Again, solving the puzzle we fill in the blanks we know for sure. 46 So, your next steps it calculate the historical Gross Profits (in D57 and E57) and the historical Gross Margin (in D58 and E58). 47 Once you know these answers, you can apply the historical model to the forecast. 48 This means you will forecast the Gross Margin and use that information to forecast the Gross Profits. 49 Easy, right? 50 Now you have learned how to build this model and can proceed with the rest of the exercise. 51 #N/A 52 53 Errors in the model will turn red. The exercise is designed such that an error early in the assignment will not adversely impact later grading. 54 2018 2020E Notes 55 2019 Relationship 56 Income Statement 57 Revenues 10,765 11,842 Business Revenues is driven by the growth rate 58 Growth Rate 10% 10% Driver 59 Cost of Revenues 6.459 7,223 Accounting Gross Profits is calculated as Revenues multiplied by Gross Margin 60 Gross Profits Business 61 Gross Margin Driver OpEx is calculated as Revenues multiplied by OpEx Percent Revenues 62 Operating Expenses (OpEx) 1500 1700 Business 63 OpEx Percent of Revenues % Driver EBIT is calculated as Gross Profits minus Operating Expenses (OpEx) 64 EBIT Accounting Net Interest Income (Expense) 68 68 NA Interest Income is calculated as Interest Rate multiplied by Cash (as there is no Debt) 65 99 Interest Rate 5% 5% 5% Driver Pretax Income Accounting Pretax Income is calculated as EBIT plus Net Interest Income (Expenses) 67 Taxes is calculated as Pretax Profits multiplied by Tax Rate 68 Taxes Business 69 Tax Rate 0% Driver 70 Net Income 71 72 Balance Sheet 73 Cash 1,365 Accounting Cash is previous year Cash plus Increase (Decrease) in Cash 74 Accounts Receivable 1,500 1.600 Accounts Receivable is calculated as Revenues multiplied by Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) / 365 Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) is calculated as Accounts Receivable / Revenues * 365 75 76 PP&E 15,079 Accounting PP&E in a year is calculated as PP&E in the previous year plus CapEx in the current year minus Depreciation in the current year. Accounts Payable Business Accounts Payable is calculated as Cost of Revenues multiplied by Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) / 365 77 1,000 L,200 78 Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) Driver Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) is calculated as Accounts Payable / Cost of Revenues * 365 12,500 Equity in a year is calculated as Equity in the previous year plus Net Income minus Dividends 79 Equity ALERT: Because the value of the Dividends are shown as a negative on the Cash Flow Statement the value should be added to subtract Dividends 80