Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
plz solve only iv and v asap.Thanks Nitrobenzene is made by the direct nitration of benzene by nitric acid in the presence of strong sulphuric

plz solve only iv and v asap.Thanks
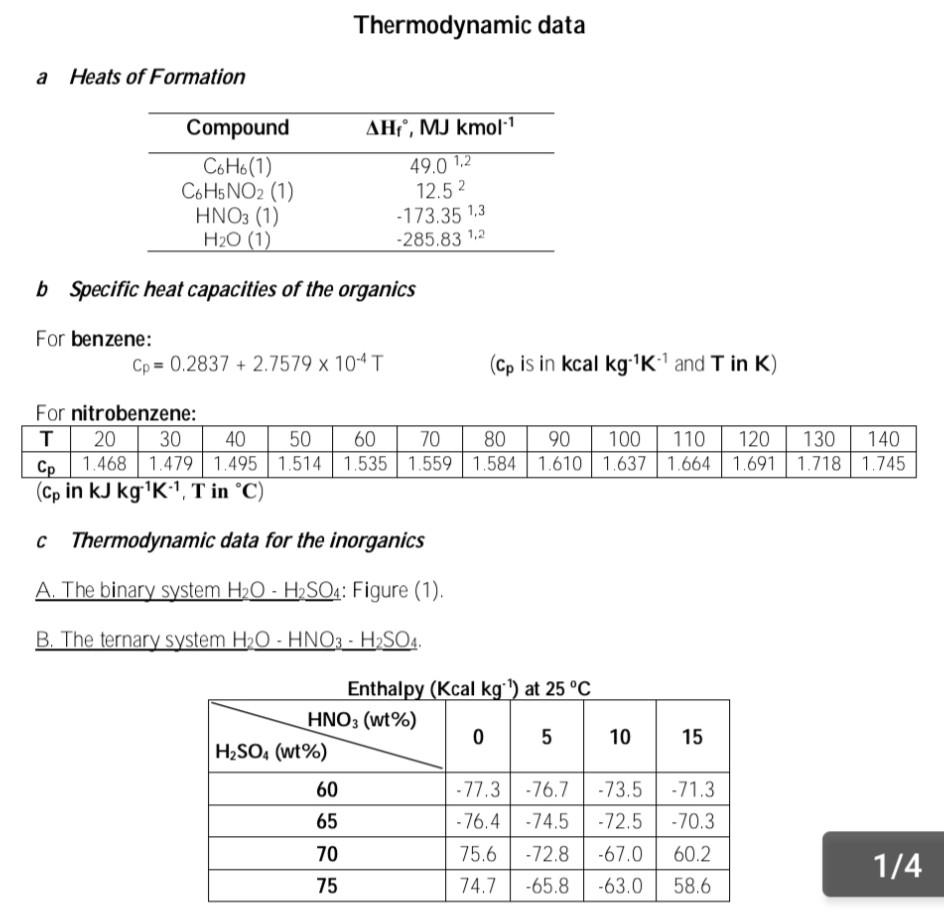
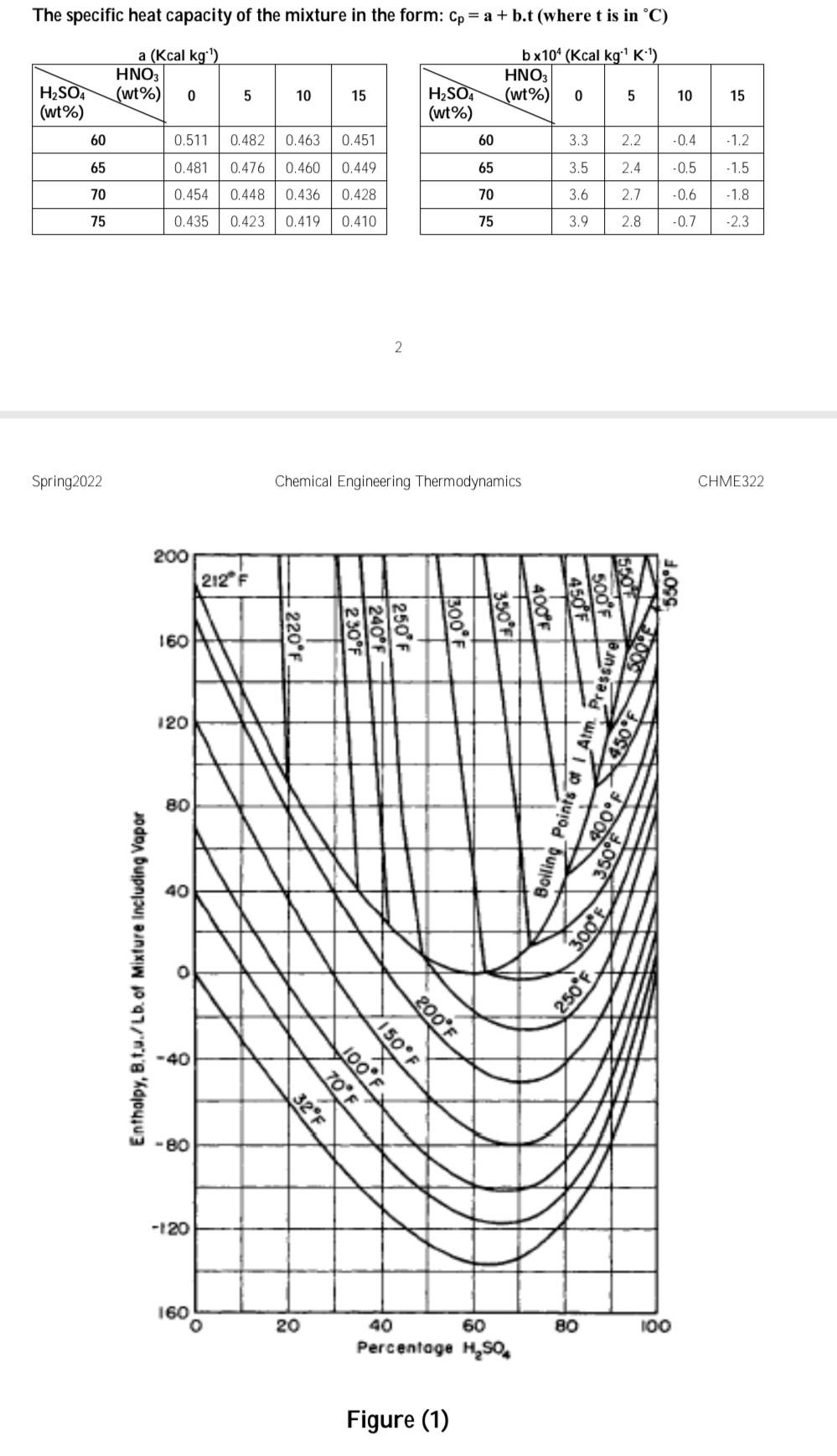
Nitrobenzene is made by the direct nitration of benzene by nitric acid in the presence of strong sulphuric acid solution: CoHo +HNO, CH.NO, +H,0 The actual nitrating agent is the nitronium ion, NO2, and the sulphuric acid is needed to generate this from the nitric acid feed. Reconcentrated sulphuric acid, of strength 74% by weight and XC is mixed with pure nitric acid at 25C to give a nitric acid strength in the mixture of 7.5% by weight. The heat of mixing causes a temperature rise to 95C. The mixed acid is then passed through a heat exchanger to bring its final temperature to 65C and fed to the reactor Liquid benzene at 25C is also fed to the reactor at a rate to give a 10% stoichiometric excess based on the nitric acid flow. The reactor operates adiabatically and gives 100% conversion of the nitric acid. All products leave the reactor as liquids at YC. The sulphuric acid is re-concentrated to 74% and recycled, while the nitrobenzene is sent for purification Using the attached thermodynamic data, you are asked to calculate: (0) e (iii) (iv) (v) the temperature, XC of the reconcentrated sulphuric acid the amount of water removed to bring the concentration of the sulphuric acid solution back to 74% the temperature, Yc, at the exit of the reactor the heat load on the heat exchanger per kg of nitrobenzene produced. Discussions of the overall results and what you have learnt. You may assume that the organics benzene and nitrobenzene form an ideal liquid mixture, and there is complete immiscibility between organics and inorganics. Thermodynamic data a Heats of Formation Compound C6H6(1) Co H5NO2 (1) HNO3 (1) H20 (1) AH, MJ kmol. 49.0 1,2 12.52 - 173.35 1,3 -285,83 1,2 b Specific heat capacities of the organics For benzene: Cp = 0.2837 + 2.7579 x 10^T (Cp is in kcal kg 'K and T in K) For nitrobenzene: T 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 Cp 1.468 1.479 1.495 1.514 1.535 1.559 1.584 1.610 1.637 1.664 1.691 1.718 1.745 (Cp in kJ kg'K1, T in C) C Thermodynamic data for the inorganics A. The binary system H2O - H2SO4: Figure (1). B. The ternary system H2O - HNO3 - H2SO4. 15 Enthalpy (Kcal kg:") at 25C HNO3 (wt%) 0 5 10 H2SO4 (wt%) 60 - 77.3 -76.7 -73.5 65 -76.4 -74.5-72.5 70 75.6 -72.8 -67.0 75 74.7 -65.8 -63.0 -71.3 -70.3 60.2 1/4 58.6 The specific heat capacity of the mixture in the form: Cp = a + b.t (where t is in C) a (Kcal kg ) HNO3 (wt%) 0 bx10^ (Kcal kg K:) HNO3 (wt%) 15 0 10 H2SO4 (wt%) 15 H2SO4 (wt%) 60 60 0.511 0.482 0.463 0.451 3.3 2.2. -0.4 -1.2 65 0.481 0.476 0.460 0.449 65 3.5 2.4 -0.5 -1.5 | | | 70 0.454 0.448 0.436 0.428 70 3.6 NININ 2.7 -0.6 -1.8 75 0.435 0.423 0.419 0.410 75 3.9 2.8 -0.7 -2.3 2 Spring2022 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics CHME322 200 212 F 550F 160 220*F boos 120 ressure Bolling Points of Am. Press 80 SON 5000 550 40 Enthalpy, B.tu./Lb. of Mixture including Vapor 300F 250F -40 150F 200F 32F 70F 100F -80 -120 160 20 60 80 100 40 Percentage H, SO Figure (1)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


