
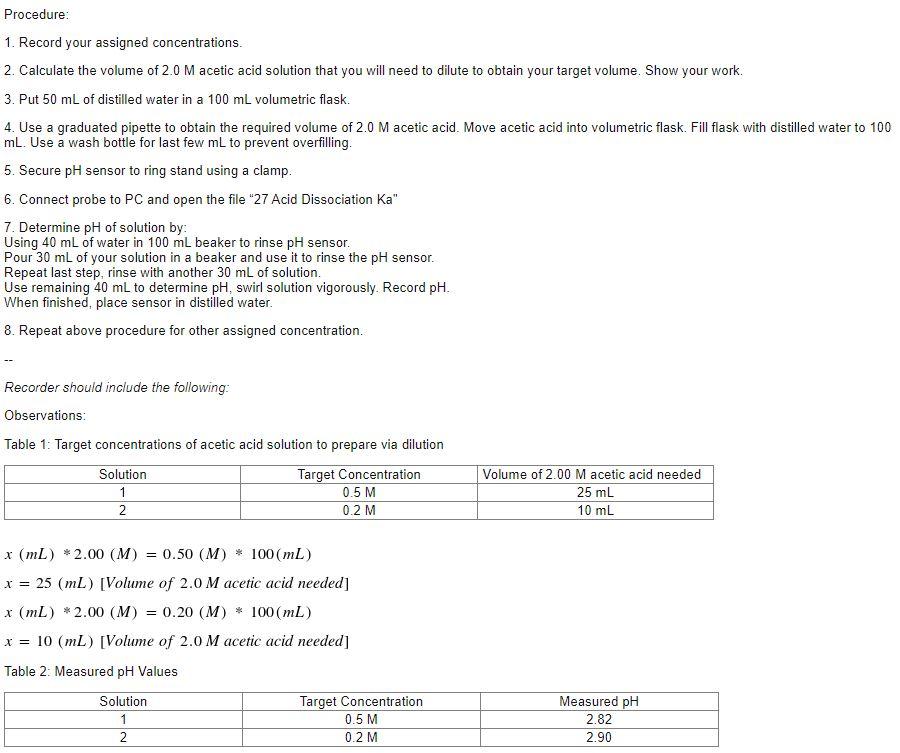
Post-Lab: Complete the following in the Post-lab assignment in the lab folder on BlackBoard. You can write your answer in the BlackBoard text editor or upload a file. Your response should be in complete sentences. All work for any calculations must be included. 1. (4 points) For both solutions studied, compute [H3O+]. 2. (6 points) For both solutions studied, determine the value of Ka. NOTE: You will need to use an ICE Table to set up the problem. The answers from #1 and the concentration of each solution will be needed for this calculation. 3. (3 points) Are the values you calculated in #2 consistent with the characterization of CH3COOH as a weak acid? Explain you answer. 4. (3 points) How do the values you calculated in #2 compare to each other? Would you expect the answers to be the same or different? Should the initial concentration of acid affect the value of Ka? Why? 5. (4 points) Look up the reference value of Ka for acetic acid. Average your two calculated values. Calculate the percent error of your calculations using the follow formula. Experimental Value - Reference Value % Error = X 100 Reference Value Procedure: 1. Record your assigned concentrations. 2. Calculate the volume of 2.0 M acetic acid solution that you will need to dilute to obtain your target volume. Show your work. 3. Put 50 mL of distilled water in a 100 mL volumetric flask. 4. Use a graduated pipette to obtain the required volume of 2.0 M acetic acid. Move acetic acid into volumetric flask. Fill flask with distilled water to 100 mL. Use a wash bottle for last few mL to prevent overfilling, 5. Secure pH sensor to ring stand using a clamp. 6. Connect probe to PC and open the file "27 Acid Dissociation Ka" 7. Determine pH of solution by: Using 40 mL of water in 100 ml beaker to rinse pH sensor. Pour 30 mL of your solution in a beaker and use it to rinse the pH sensor. Repeat last step, rinse with another 30 mL of solution. Use remaining 40 mL to determine pH, swirl solution vigorously. Record pH. When finished, place sensor in distilled water. 8. Repeat above procedure for other assigned concentration. Recorder should include the following: Observations: Table 1: Target concentrations of acetic acid solution to prepare via dilution Solution Target Concentration 1 0.5 M 2 0.2 M Volume of 2.00 Macetic acid needed 25 mL 10 mL x (mL) *2.00 (M) = 0.50 (M) * 100 (mL) x = 25 (mL) [Volume of 2.0 M acetic acid needed] x (L) *2.00 (M) 0.20 (M) * 100mL) x = 10 (mL) [Volume of 2.0 M acetic acid needed] = Table 2: Measured pH Values Solution Target Concentration 0.5 M 0.2 M Measured pH 2.82 2.90 2








