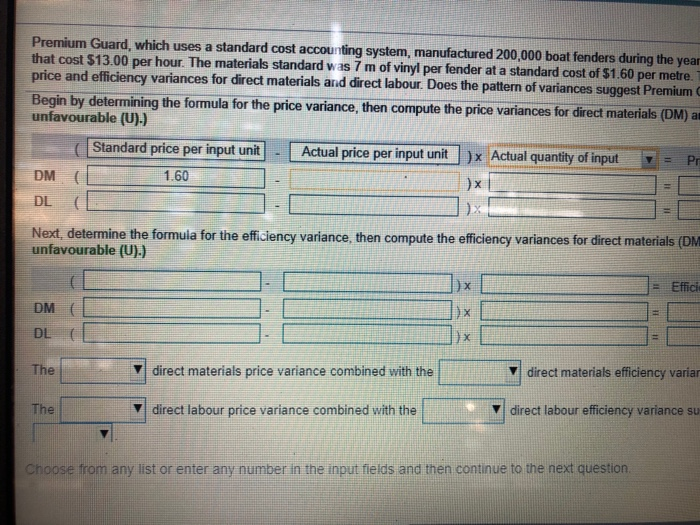
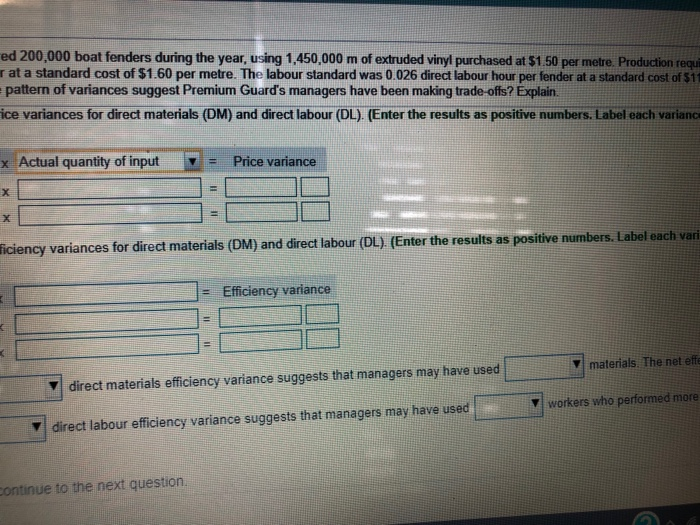
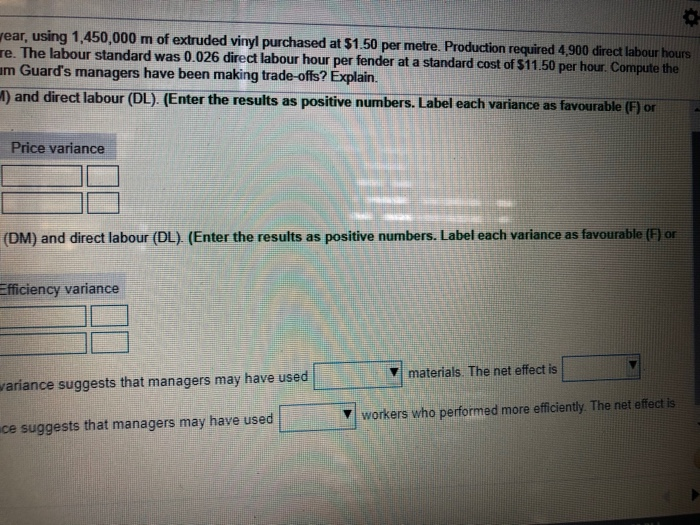
Premium Guard, which uses a standard cost accounting system, manufactured 200,000 boat fenders during the year that cost $13.00 per hour. The materials standard was 7 m of vinyl per fender at a standard cost of $1.60 per metre. price and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labour. Does the pattern of variances suggest Premium Begin by determining the formula for the price variance, then compute the price variances for direct materials (DM) an unfavourable (U).) Standard price per input unit - Actual price per input unit ) Actual quantity of input = Pr DM ( 1.60 . DE O Next, determine the formula for the efficiency variance, then compute the efficiency variances for direct materials (DM unfavourable (U).) - L ) = Effici DM DL . direct materials price variance combined with the v direct materials efficiency variar direct labour price variance combined with the direct labour efficiency variance su Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then continue to the next question. ed 200,000 boat fenders during the year, using 1,450,000 m of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.50 per metre. Production requ. rat a standard cost of $1.60 per metre. The labour standard was 0.026 direct labour hour per fender at a standard cost of S11 pattern of variances suggest Premium Guard's managers have been making trade offs? Explain. ice variances for direct materials (DM) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each varianc x Actual quantity of input v = Price variance ficiency variances for direct materials (DM) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each vari = Efficiency variance materials. The net effe direct materials efficiency variance suggests that managers may have used workers who performed more direct labour efficiency variance suggests that managers may have used continue to the next question. wear, using 1,450,000 m of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.50 per metre. Production required 4,900 direct labour hours re. The labour standard was 0.026 direct labour hour per fender at a standard cost of $11.50 per hour. Compute the um Guard's managers have been making trade-offs? Explain. M) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each variance as favourable (F) or Price variance (DM) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each variance as favourable (F) or Efficiency variance materials. The net effect is variance suggests that managers may have used workers who performed more efficiently. The net effect is ce suggests that managers may have used Premium Guard, which uses a standard cost accounting system, manufactured 200,000 boat fenders during the year that cost $13.00 per hour. The materials standard was 7 m of vinyl per fender at a standard cost of $1.60 per metre. price and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labour. Does the pattern of variances suggest Premium Begin by determining the formula for the price variance, then compute the price variances for direct materials (DM) an unfavourable (U).) Standard price per input unit - Actual price per input unit ) Actual quantity of input = Pr DM ( 1.60 . DE O Next, determine the formula for the efficiency variance, then compute the efficiency variances for direct materials (DM unfavourable (U).) - L ) = Effici DM DL . direct materials price variance combined with the v direct materials efficiency variar direct labour price variance combined with the direct labour efficiency variance su Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then continue to the next question. ed 200,000 boat fenders during the year, using 1,450,000 m of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.50 per metre. Production requ. rat a standard cost of $1.60 per metre. The labour standard was 0.026 direct labour hour per fender at a standard cost of S11 pattern of variances suggest Premium Guard's managers have been making trade offs? Explain. ice variances for direct materials (DM) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each varianc x Actual quantity of input v = Price variance ficiency variances for direct materials (DM) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each vari = Efficiency variance materials. The net effe direct materials efficiency variance suggests that managers may have used workers who performed more direct labour efficiency variance suggests that managers may have used continue to the next question. wear, using 1,450,000 m of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.50 per metre. Production required 4,900 direct labour hours re. The labour standard was 0.026 direct labour hour per fender at a standard cost of $11.50 per hour. Compute the um Guard's managers have been making trade-offs? Explain. M) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each variance as favourable (F) or Price variance (DM) and direct labour (DL). (Enter the results as positive numbers. Label each variance as favourable (F) or Efficiency variance materials. The net effect is variance suggests that managers may have used workers who performed more efficiently. The net effect is ce suggests that managers may have used