Question: Problem 1 Velocity (m/s) 5 3 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.2 1.4 1.6 1 .8 Time (s) -2 -4 A light sphere is thrown upwards
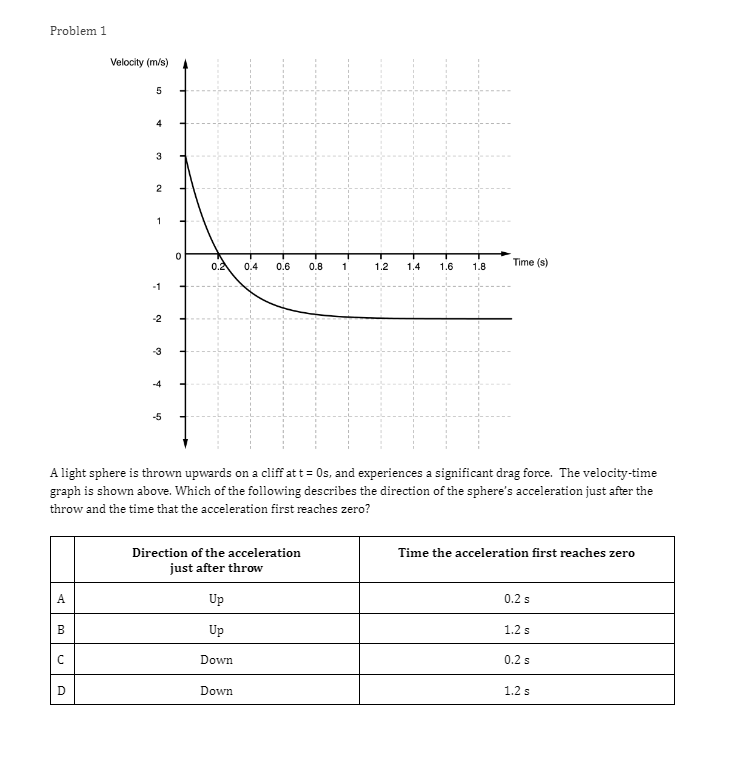
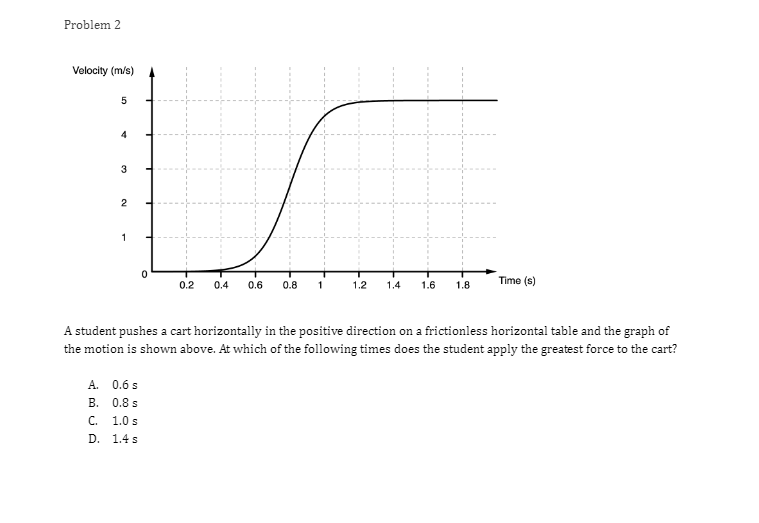
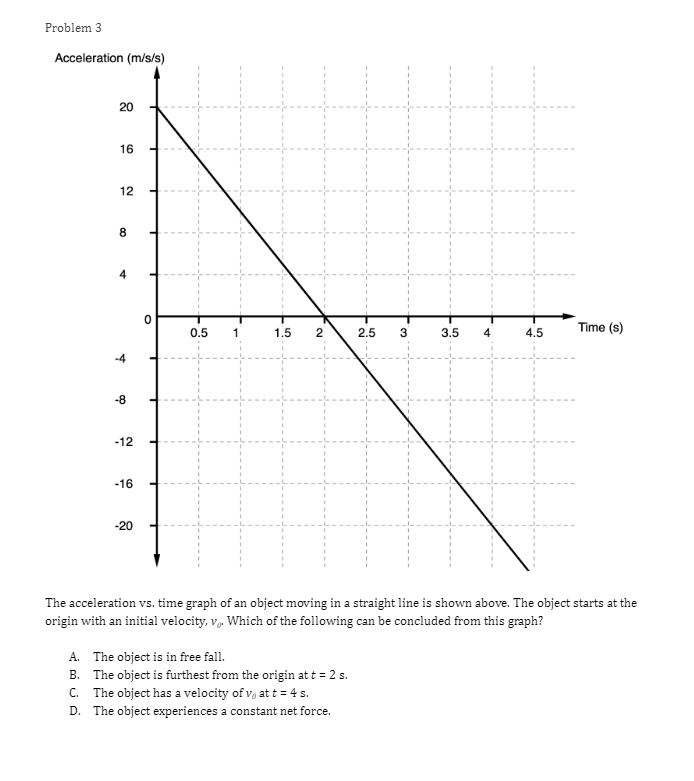

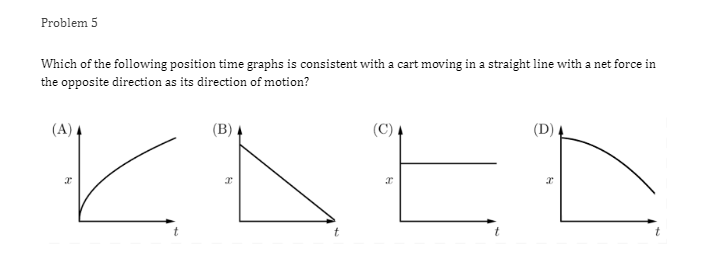
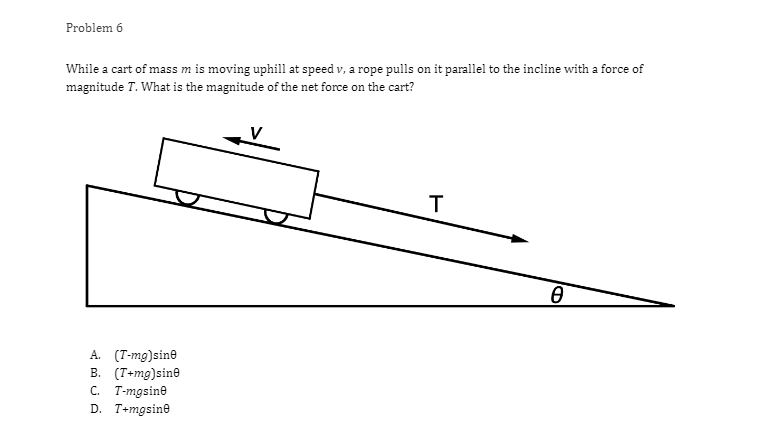
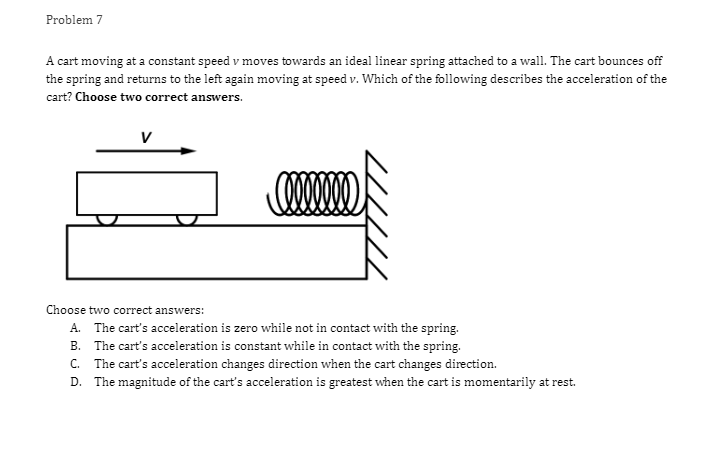
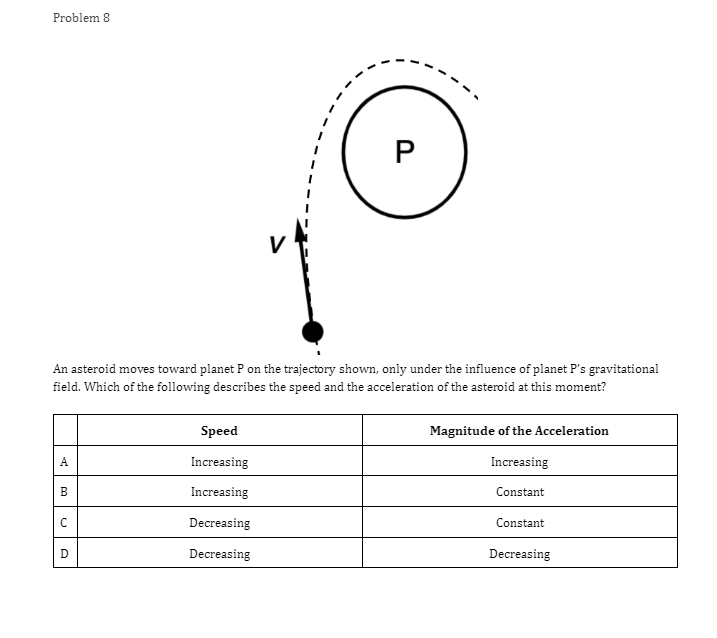
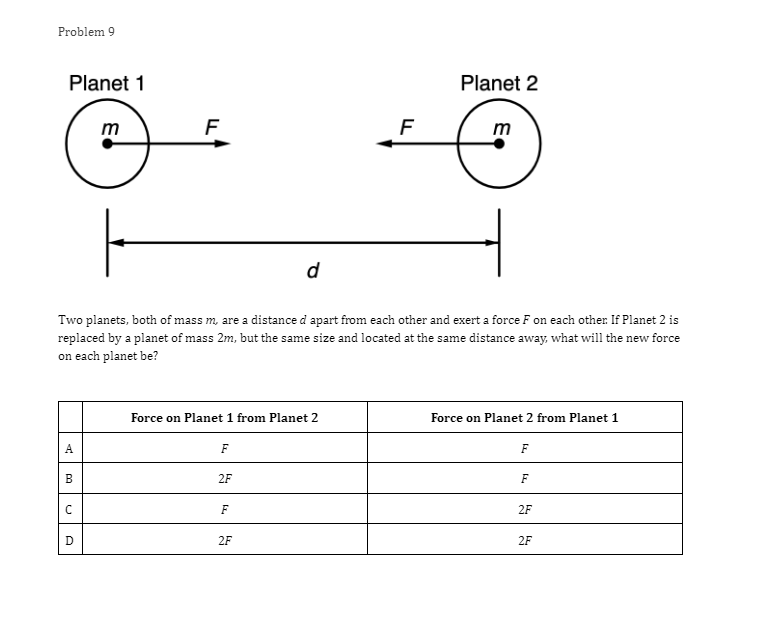


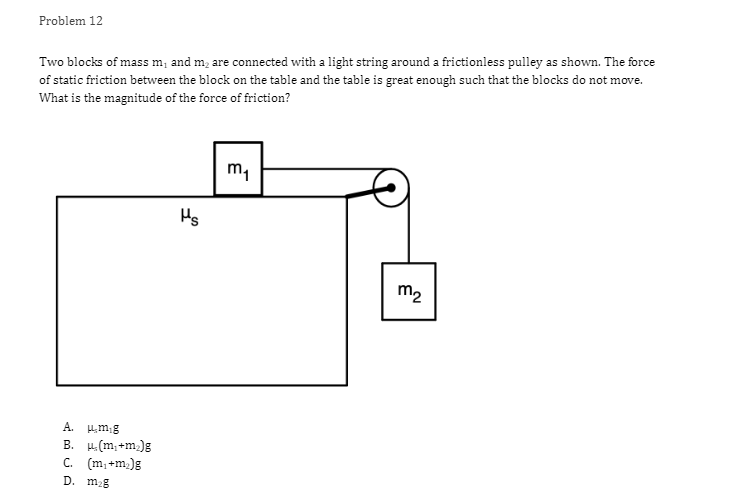
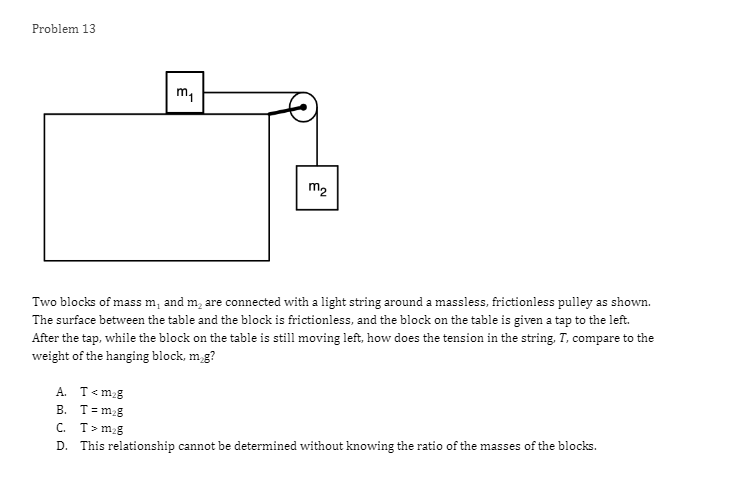
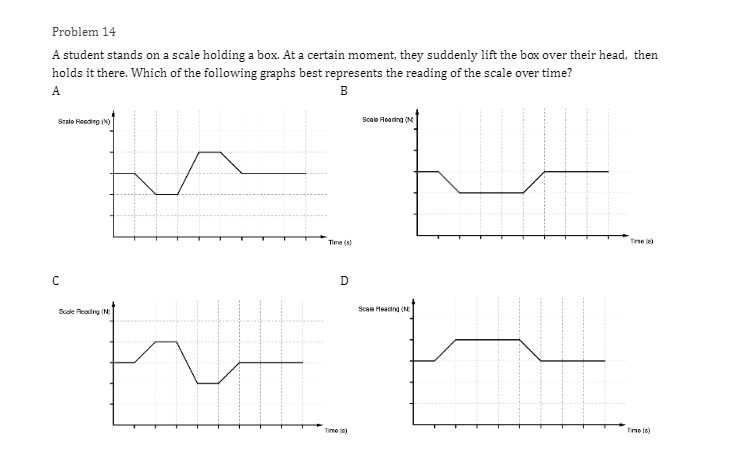


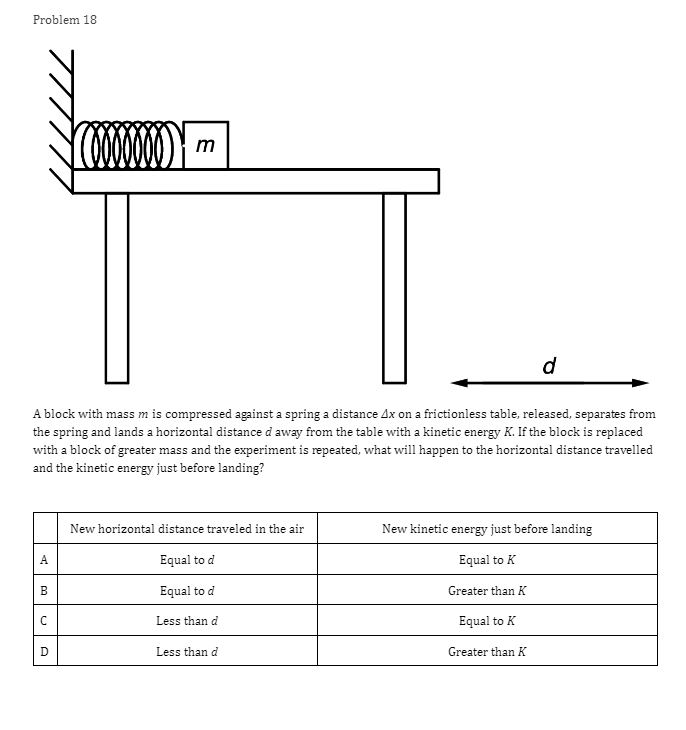
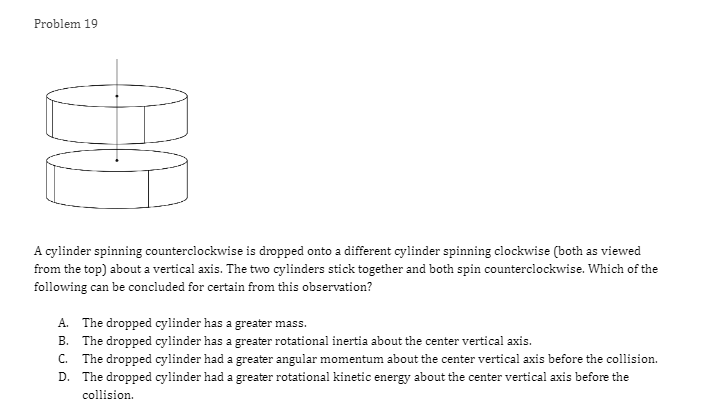
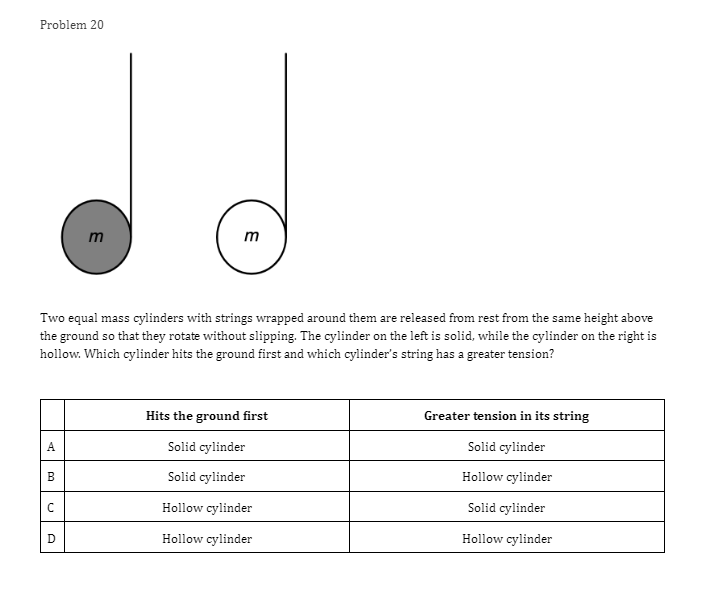
Problem 1 Velocity (m/s) 5 3 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.2 1.4 1.6 1 .8 Time (s) -2 -4 A light sphere is thrown upwards on a cliff at t = 0s, and experiences a significant drag force. The velocity-time graph is shown above. Which of the following describes the direction of the sphere's acceleration just after the throw and the time that the acceleration first reaches zero? Direction of the acceleration Time the acceleration first reaches zero just after throw UP 0.2 s Up 1.2 s Down 0.2 s Down 1.2 sProblem 2 Velocity (m/s) - - -- 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 Time (s) A student pushes a cart horizontally in the positive direction on a frictionless horizontal table and the graph of the motion is shown above. At which of the following times does the student apply the greatest force to the cart? A. 0.65 B. 0.8s C. 1.0 s D. 1.45Problem 3 Acceleration (m/s/s) 20 16 12 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3' 3.5 4 4.5 Time (s) -8 -12 -16 -20 The acceleration vs. time graph of an object moving in a straight line is shown above. The object starts at the origin with an initial velocity, vo Which of the following can be concluded from this graph? A. The object is in free fall. B. The object is furthest from the origin at t = 2 s. C. The object has a velocity of vo at t = 4 s. D. The object experiences a constant net force.Problem 4 A block slides without friction at speed v off a horizontal table and lands on the floor. Which of the following pairs of measurements would allow one to estimate v? Choose two correct answers. A. The horizontal distance from the table the block landed and the time in the air. B. The time in the air and the height of the table. C. The horizontal distance from the table the block landed and the height of the table. D. The vertical velocity just before reaching the ground and the time in the air.Problem 5 Which of the following position time graphs is consistent with a cart moving in a straight line with a net force in the opposite direction as its direction of motion? (A) (B) (C) (D)Problem 6 While a cart of mass m is moving uphill at speed v, a rope pulls on it parallel to the incline with a force of magnitude 7. What is the magnitude of the net force on the cart? V T A. (T-mg)sine B. (T+mg)sine C. T-mgsine D. T+mgsineProblem T A cart moving at a constant speed 1* moves inwards an ideal linear spring attached to a wall. The cart bounces off the spring and returns to the left again moving at speed 1!. Which of the following describes the acceleration of the cart? Choose two correct answers. If - Choose two correct answers: A The cart's acceleration is zero while not in contact with the spring. The cart's acceleration is oonstant while in oontact with the spring. E. C. The cart's acceleration changes direction when the cart changes direction. D. The magnitude of the carts acceleration is greatest when the cart is momentarily at rest. Problem 8 P V An asteroid moves toward planet P on the trajectory shown, only under the influence of planet P's gravitational field. Which of the following describes the speed and the acceleration of the asteroid at this moment? Speed Magnitude of the Acceleration A Increasing Increasing Increasing Constant B Constant Decreasing Decreasing DecreasingProblem 9 Planet 1 Planet 2 m F F m d Two planets, both of mass m, are a distance d apart from each other and exert a force F on each other. If Planet 2 is replaced by a planet of mass 2m, but the same size and located at the same distance away, what will the new force on each planet be? Force on Planet 1 from Planet 2 Force on Planet 2 from Planet 1 A F F 2F F F 2F 2F 2FProblem 10 wall 3 clay balls, labeled A, B, and Care launched from the same height at the same speed. A is launched at 30# above horizontal, B is launched horizontally, and C is launched 30" below the horizontal. They all hit the wall (before reaching the ground) in times to, to, and to respectively. Rank these times from least to greatest. . t= = t B. to
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


