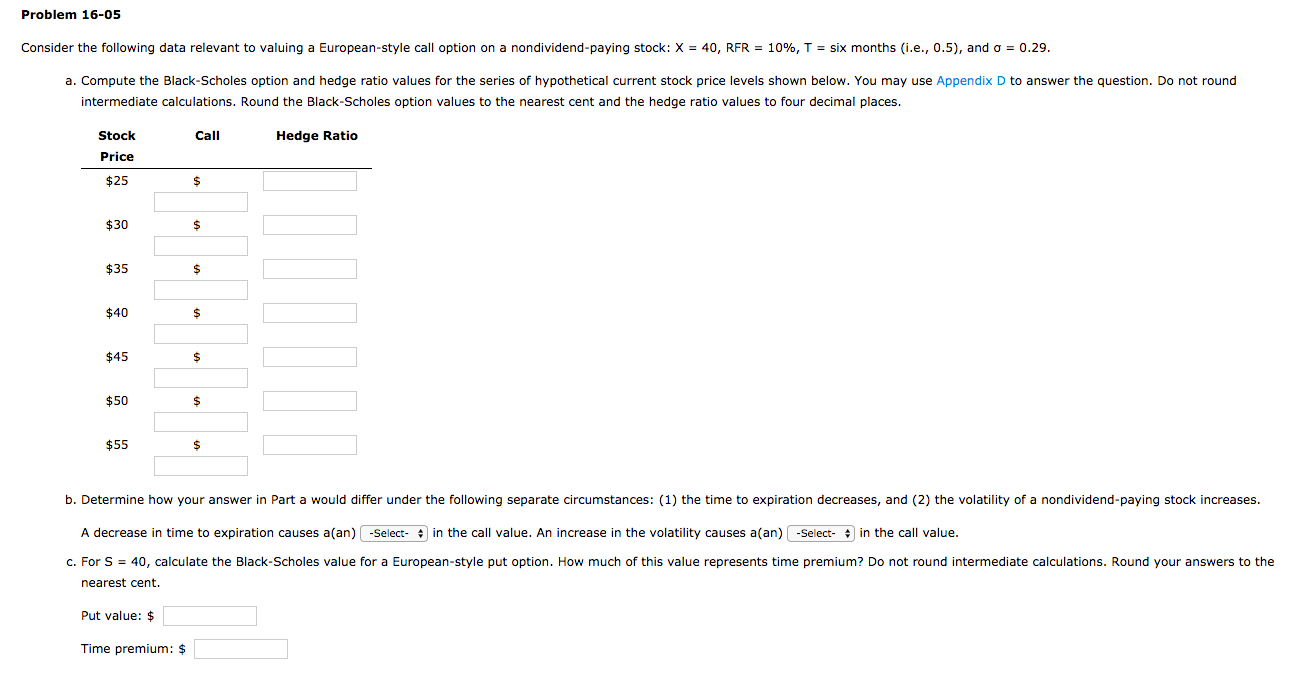
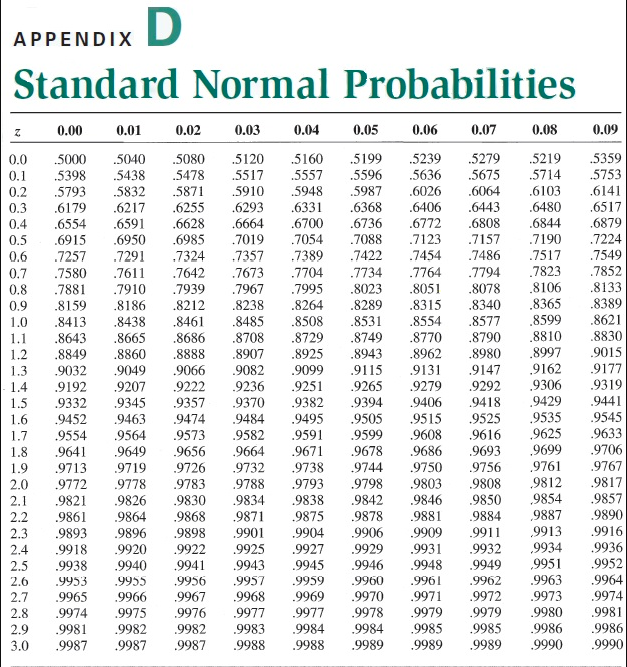
Problem 16-05 Consider the following data relevant to valuing a European-style call option on a nondividend-paying stock: X = 40, RFR = 10%, T = six months (i.e., 0.5), and a = 0.29. a. Compute the Black-Scholes option and hedge ratio values for the series of hypothetical current stock price levels shown below. You may use Appendix D to answer the question. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round the Black-Scholes option values to the nearest cent and the hedge ratio values to four decimal places. Call Hedge Ratio Stock Price b. Determine how your answer in Part a would differ under the following separate circumstances: (1) the time to expiration decreases, and (2) the volatility of a nondividend-paying stock increases. A decrease in time to expiration causes a(an) -Select- in the call value. An increase in the volatility causes a(an) -Select- in the call value. c. For S = 40, calculate the Black-Scholes value for a European-style put option. How much of this value represents time premium? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Put value: $ Time premium: $ APPENDIX Standard Normal Probabilities 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.09 0.0 0.1 0.2 .5359 .5753 .6141 0.3 .6517 .6879 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 .5000 .5398 .5793 .6179 .6554 .6915 .7257 .7580 .7881 .8159 .8413 .8643 .8849 .9032 .9192 .7224 .7549 .7852 .8133 .7967 .8389 1.1 .8621 .8830 .9015 .9177 1.2 1.3 1.4 .9319 1.5 .9332 5040 .5438 .5832 .6217 .6591 .6950 .7291 .7611 .7910 .8186 .8438 .8665 .8860 .9049 9207 9345 9463 9564 9649 9719 .9778 .9826 9864 .9896 .9920 .9940 9955 9966 .9975 .9982 .9987 5080 .5120 .5478 5517 .5871 .5910 .6255 .6293 .6628 .6664 .6985 .7019 .7324 .7357 .7642 .7673 .7939 .8212 .8238 .8461 .8485 .8686 .8708 .8888 .8907 .9066 .9082 .9222 .9236 9357 9370 9474 9484 9573 .9582 .9656 9664 9726 .9732 9783 9788 .9830 9834 .9868 9871 9898 9901 .9922 9925 9943 .9956 .9957 9967 9968 9976 .9977 9982 9983 99879988 5160 5557 5948 .6331 6700 7054 .7389 .7704 .7995 .8264 .8508 .8729 .8925 9099 .9251 .9382 .9495 .9591 .9671 .9738 9793 9838 .9875 .9904 9927 .9945 .9959 .9969 .9977 .9984 .9988 .5199 .5596 5987 .6368 .6736 .7088 .7422 .7734 .8023 .8289 .8531 .8749 .8943 .9115 9265 .9394 .9505 .9599 .9678 .9744 .9798 9842 .9878 .9906 .9929 .9946 .9960 .9970 .9978 9984 9989 5239 .5279 .5636 .5675 .6026 .6064 .6406 6443 .6772 .6808 .7123 .7157 .7454 .7486 .7764 .7794 .8051 .8078 .8315 .8340 .8554 .8577 .8770 .8790 .8962 .8980 .9131 9147 9279 9292 9406 9418 9515 9525 .9608 9616 .9686 9693 .9750 9756 9803 9808 .9846 .9850 .9881 .9884 .9909 .9911 .9931 .9932 .9948 .9949 .9961 9962 .9971 .9972 .9979 .9979 9985 .9985 99899989 .5219 .5714 .6103 .6480 .6844 .7190 .7517 7823 .8106 .8365 .8599 .8810 .8997 9162 9306 9429 .9535 9625 .9699 .9761 9812 9854 9887 9913 ,9934 ,9951 .9963 .9973 .9980 .9986 .9990 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 9441 .9545 .9633 .9706 .9767 .9817 9857 .9890 .9916 .9936 .9952 .9964 9974 9981 9986 9990 .9452 9554 .9641 .9713 .9772 .9821 .9861 .9893 .9918 .9938 .9953 .9965 .9974 .9981 .9987 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 3.0 .9941 Problem 16-05 Consider the following data relevant to valuing a European-style call option on a nondividend-paying stock: X = 40, RFR = 10%, T = six months (i.e., 0.5), and a = 0.29. a. Compute the Black-Scholes option and hedge ratio values for the series of hypothetical current stock price levels shown below. You may use Appendix D to answer the question. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round the Black-Scholes option values to the nearest cent and the hedge ratio values to four decimal places. Call Hedge Ratio Stock Price b. Determine how your answer in Part a would differ under the following separate circumstances: (1) the time to expiration decreases, and (2) the volatility of a nondividend-paying stock increases. A decrease in time to expiration causes a(an) -Select- in the call value. An increase in the volatility causes a(an) -Select- in the call value. c. For S = 40, calculate the Black-Scholes value for a European-style put option. How much of this value represents time premium? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Put value: $ Time premium: $ APPENDIX Standard Normal Probabilities 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.09 0.0 0.1 0.2 .5359 .5753 .6141 0.3 .6517 .6879 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 .5000 .5398 .5793 .6179 .6554 .6915 .7257 .7580 .7881 .8159 .8413 .8643 .8849 .9032 .9192 .7224 .7549 .7852 .8133 .7967 .8389 1.1 .8621 .8830 .9015 .9177 1.2 1.3 1.4 .9319 1.5 .9332 5040 .5438 .5832 .6217 .6591 .6950 .7291 .7611 .7910 .8186 .8438 .8665 .8860 .9049 9207 9345 9463 9564 9649 9719 .9778 .9826 9864 .9896 .9920 .9940 9955 9966 .9975 .9982 .9987 5080 .5120 .5478 5517 .5871 .5910 .6255 .6293 .6628 .6664 .6985 .7019 .7324 .7357 .7642 .7673 .7939 .8212 .8238 .8461 .8485 .8686 .8708 .8888 .8907 .9066 .9082 .9222 .9236 9357 9370 9474 9484 9573 .9582 .9656 9664 9726 .9732 9783 9788 .9830 9834 .9868 9871 9898 9901 .9922 9925 9943 .9956 .9957 9967 9968 9976 .9977 9982 9983 99879988 5160 5557 5948 .6331 6700 7054 .7389 .7704 .7995 .8264 .8508 .8729 .8925 9099 .9251 .9382 .9495 .9591 .9671 .9738 9793 9838 .9875 .9904 9927 .9945 .9959 .9969 .9977 .9984 .9988 .5199 .5596 5987 .6368 .6736 .7088 .7422 .7734 .8023 .8289 .8531 .8749 .8943 .9115 9265 .9394 .9505 .9599 .9678 .9744 .9798 9842 .9878 .9906 .9929 .9946 .9960 .9970 .9978 9984 9989 5239 .5279 .5636 .5675 .6026 .6064 .6406 6443 .6772 .6808 .7123 .7157 .7454 .7486 .7764 .7794 .8051 .8078 .8315 .8340 .8554 .8577 .8770 .8790 .8962 .8980 .9131 9147 9279 9292 9406 9418 9515 9525 .9608 9616 .9686 9693 .9750 9756 9803 9808 .9846 .9850 .9881 .9884 .9909 .9911 .9931 .9932 .9948 .9949 .9961 9962 .9971 .9972 .9979 .9979 9985 .9985 99899989 .5219 .5714 .6103 .6480 .6844 .7190 .7517 7823 .8106 .8365 .8599 .8810 .8997 9162 9306 9429 .9535 9625 .9699 .9761 9812 9854 9887 9913 ,9934 ,9951 .9963 .9973 .9980 .9986 .9990 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 9441 .9545 .9633 .9706 .9767 .9817 9857 .9890 .9916 .9936 .9952 .9964 9974 9981 9986 9990 .9452 9554 .9641 .9713 .9772 .9821 .9861 .9893 .9918 .9938 .9953 .9965 .9974 .9981 .9987 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 3.0 .9941








