Question: PROBLEM 3 Consider the reaction carried out by the Haber Process: N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(0) (a) Determine the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction,

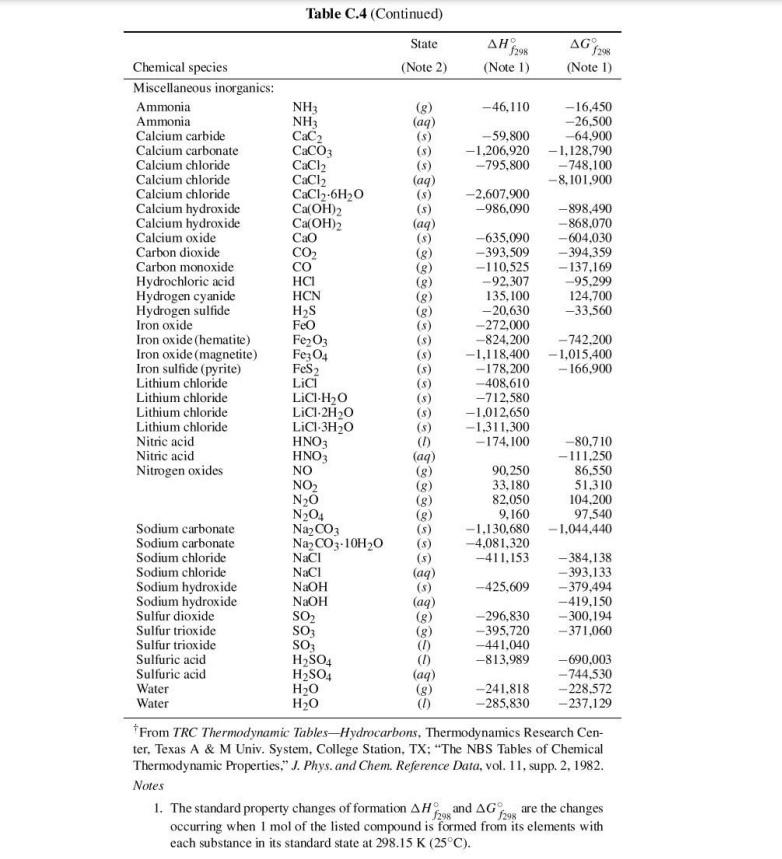
PROBLEM 3 Consider the reaction carried out by the Haber Process: N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(0) (a) Determine the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction, 4, G, the standard enthalpy of reaction, 4, H, and the standard heat capacity change of reaction, 4,Cat 298.15 K. Use the data in Table C.4 of SVNA (see next page). Heat capacity data: CNH/R = 3.578 + (3.020 x 10-3K-1)7+(-0.186 x 105 K2)7-2 C.nz/R = 3.280 + (0.593 x 10-3K-')T + (0.040 x 105 K2)7-2 CH_/R = 3.249 +(0.422 x 10-3K-4)T + (0.083 x 105 k)-2 (b) At a pressure of 1 bar and for a stoichiometric feed (1 mole of N2 mixed with 3 moles of Hz), calculate the temperature at which the equilibrium conversion, defined as the fraction of H2 consumed, reaches 50%. (c) Unfortunately, the reaction is extremely slow at that temperature. Haber discovered a catalyst to speed up the reaction, but even with the catalyst, the temperature must be increased to 700 K to attain a practical reaction rate. For the same feed, calculate the pressure needed to keep the equilibrium conversion at 50%, if the temperature is set at 700 K. You may assume that at such elevated pressure, the gaseous mixture in the reactor is not an ideal gas mixture, but still obeys the Lewis-Randall Rule. The pure components can be described by the virial equation of state, which yields fugacity coefficients of the following form: = exp RT () = where the second virial coefficients are constants: BN2 = 18 cmmol, BH, = 2 cmmol! and Bnh, = 20 cm mol? Table C.4 (Continued) . (aq) Cao State f298 298 Chemical species (Note 2) (Note 1) (Note 1) Miscellaneous inorganics: Ammonia NH3 -46,110 - 16,450 Ammonia NH3 (aq) -26,500 Calcium carbide CaC2 -59,800 -64,900 Calcium carbonate CaCO3 -1,206,920 -1,128.790 Calcium chloride CaCl2 -795,800 - 748,100 Calcium chloride CaCl2 (aq) -8.101.900 Calcium chloride CaCl2-6H2O -2,607,900 Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 (5) -986,090 -898,490 Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 -868,070 Calcium oxide -635,090 -604.030 Carbon dioxide CO2 (8) -393,509 -394,359 Carbon monoxide (8) -110,525 - 137.169 Hydrochloric acid HCI -92,307 --95.299 Hydrogen cyanide HCN (8) 135,100 124,700 Hydrogen sulfide Hys (8) -20,630 -33,560 Iron oxide Feo - 272,000 Iron oxide (hematite) Fe2O3 --824,200 - 742.200 Iron oxide (magnetite) Fez 04 -1,118,400 -1,015,400 Iron sulfide (pyrite) FeS 2 -178,200 - 166,900 Lithium chloride Lici -408,610 Lithium chloride LICI.H2O -712,580 Lithium chloride LiCI.2H2O -1,012,650 Lithium chloride LiCI-3H20 -1.311.300 Nitric acid HNO3 - 174,100 -80,710 Nitric acid HNO3 (aq) --111.250 Nitrogen oxides NO 90,250 86,550 NO2 (8) 33,180 51.310 N20 82,050 104.200 N204 (8) 9,160 97.540 Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 -1.130,680 - 1,044,440 Sodium carbonate Na2CO3.10H20 (5) -4.081,320 Sodium chloride NaCl (5) -411,153 -384.138 Sodium chloride Naci (aq) -- 393,133 Sodium hydroxide NaOH -425,609 -379.494 Sodium hydroxide NaOH (aq) -419,150 Sulfur dioxide SO2 -296,830 -300,194 Sulfur trioxide SO3 --395,720 - 371,060 Sulfur trioxide SO3 --441,040 Sulfuric acid H2SO4 -813.989 -690.003 Sulfuric acid H2SO4 (aq) - 744,530 Water -241.818 - 228.572 Water H2O -285,830 - 237.129 From TRC Thermodynamic Tables-Hydrocarbons, Thermodynamics Research Cen- ter, Texas A&M Univ. System, College Station, TX; "The NBS Tables of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties," J. Phys. and Chem. Reference Data, vol. 11, supp. 2. 1982. Notes 1. The standard property changes of formation AH and AG are the changes 1296 occurring when I mol of the listed compound is formed from its elements with each substance in its standard state at 298.15 K (25C). SETSSTELE H20
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


