Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problems: (A) Understanding Receivables: ABC sells on credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Daily sales average 200 units at P2,500 each throughout the 365-day year. All
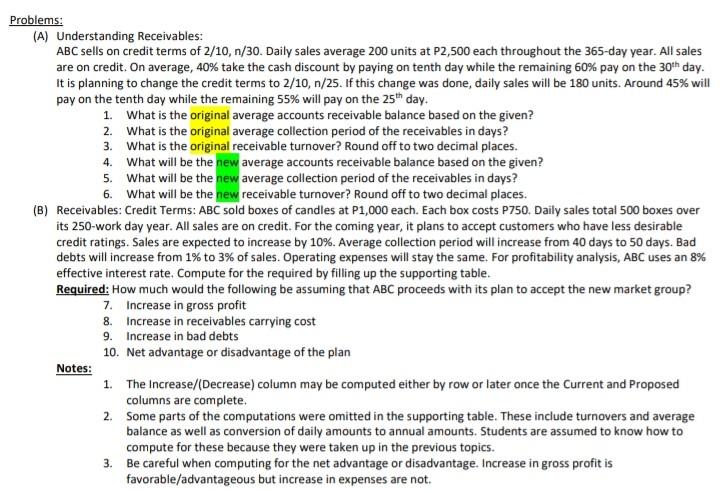
Problems: (A) Understanding Receivables: ABC sells on credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Daily sales average 200 units at P2,500 each throughout the 365-day year. All sales are on credit. On average, 40% take the cash discount by paying on tenth day while the remaining 60% pay on the 30th day. It is planning to change the credit terms to 2/10, n/25. If this change was done, daily sales will be 180 units. Around 45% will pay on the tenth day while the remaining 55% will pay on the 25th day. 1. What is the original average accounts receivable balance based on the given? 2. What is the original average collection period of the receivables in days? 3. What is the original receivable turnover? Round off to two decimal places. 4. What will be the new average accounts receivable balance based on the given? 5. What will be the new average collection period of the receivables in days? 6. What will be the new receivable turnover? Round off to two decimal places. (B) Receivables: Credit Terms: ABC sold boxes of candles at P1,000 each. Each box costs P750. Daily sales total 500 boxes over its 250-work day year. All sales are on credit. For the coming year, it plans to accept customers who have less desirable credit ratings. Sales are expected to increase by 10%. Average collection period will increase from 40 days to 50 days. Bad debts will increase from 1% to 3% of sales. Operating expenses will stay the same. For profitability analysis, ABC uses an 8% effective interest rate. Compute for the required by filling up the supporting table. Required: How much would the following be assuming that ABC proceeds with its plan to accept the new market group? 7. Increase in gross profit 8. Increase in receivables carrying cost 9. Increase in bad debts 10. Net advantage or disadvantage of the plan Notes: 1. The Increase/(Decrease) column may be computed either by row or later once the Current and Proposed columns are complete. 2. Some parts of the computations were omitted in the supporting table. These include turnovers and average balance as well as conversion of daily amounts to annual amounts. Students are assumed to know how to compute for these because they were taken up in the previous topics. 3. Be careful when computing for the net advantage or disadvantage. Increase in gross profit is favorable/advantageous but increase in expenses are not
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


