Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
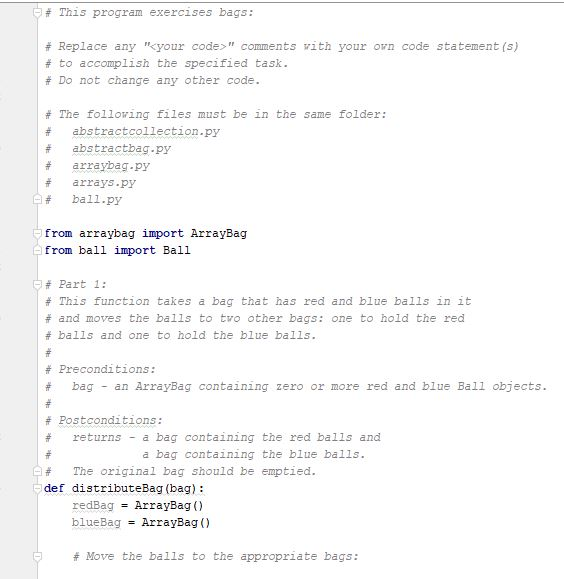
Programming Activity 3 - Guidance ================================= Part 1 ====== distributeBag() function ------------------------ Read the function header to understand what this function does. Pay particular attention
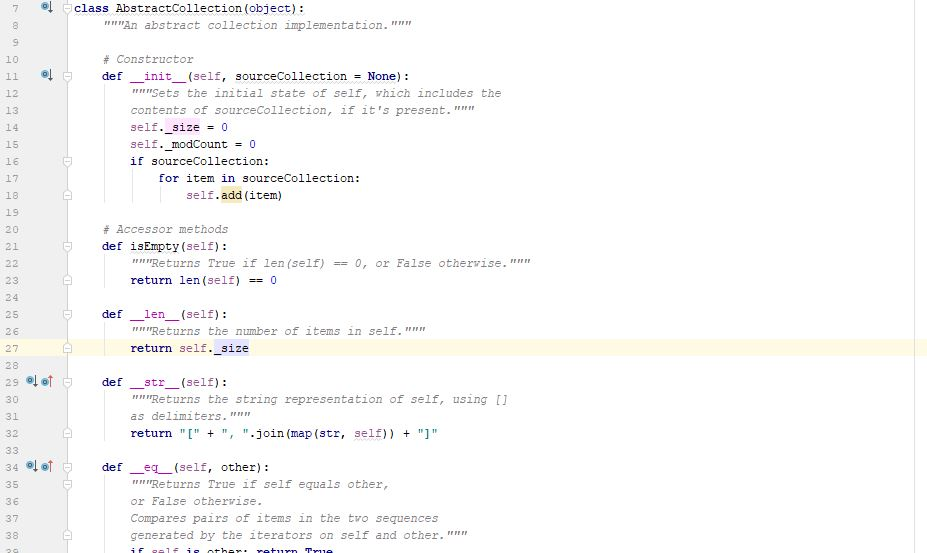
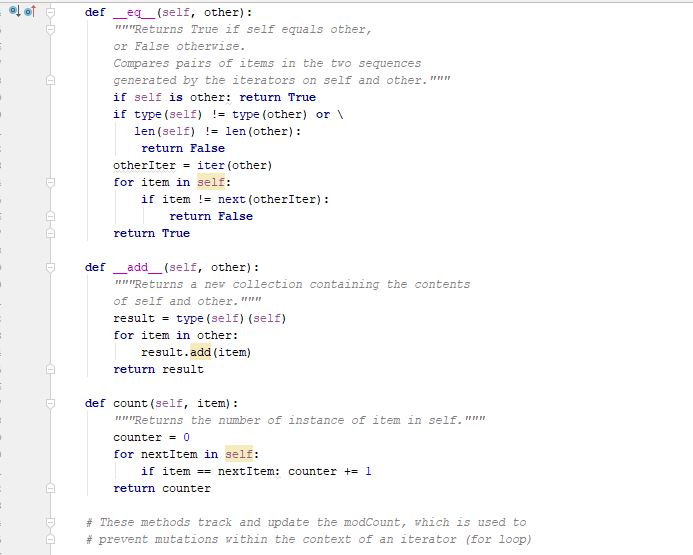
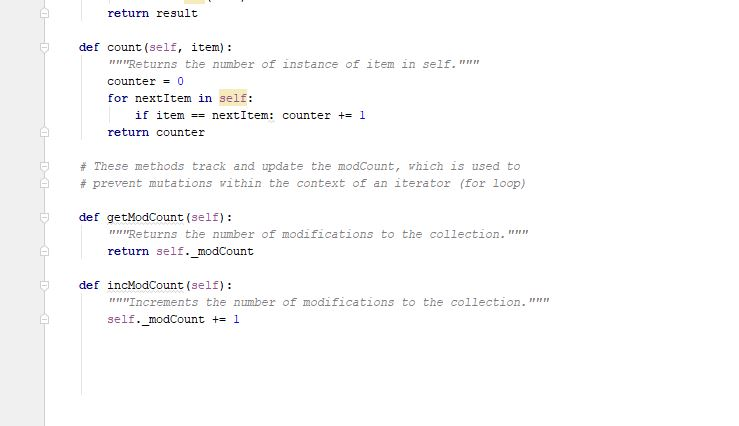
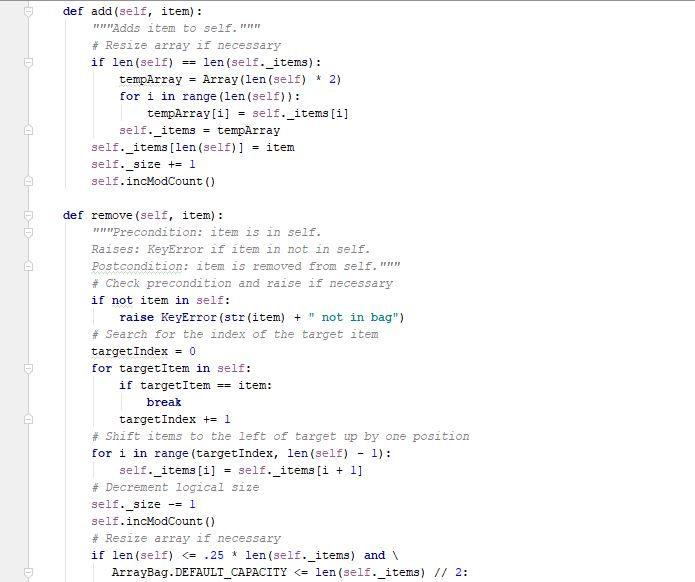
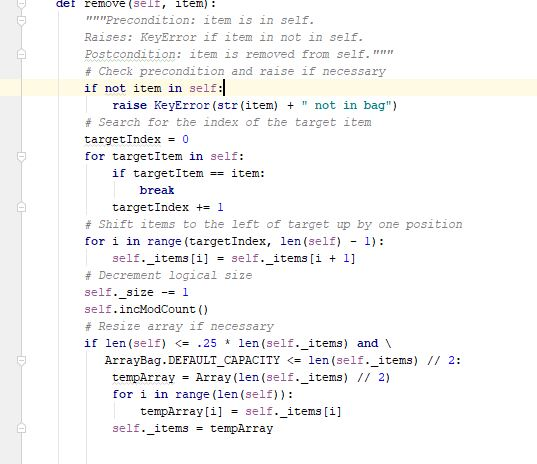
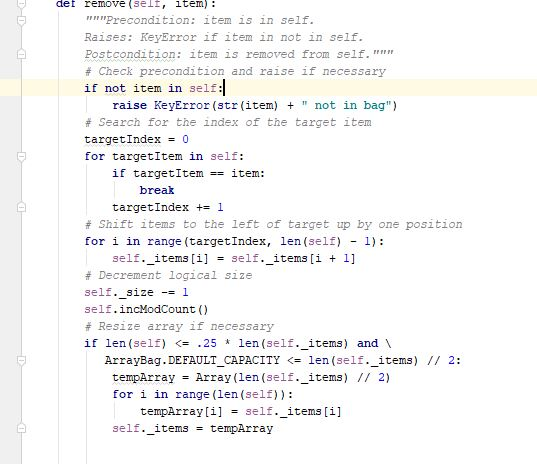
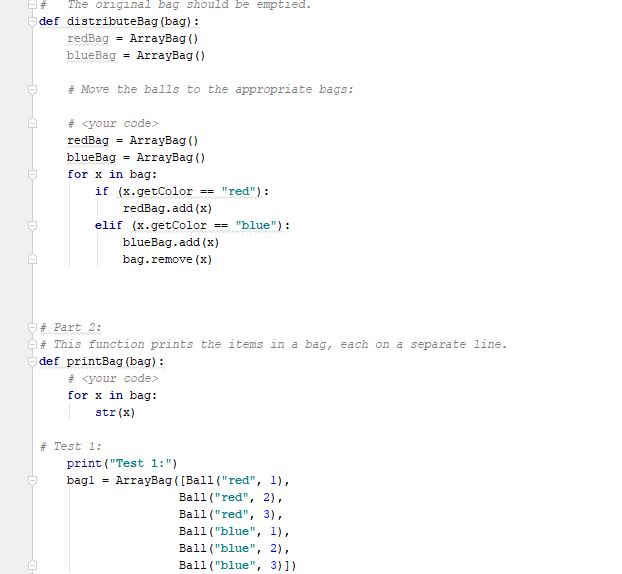
Programming Activity 3 - Guidance ================================= Part 1 ====== distributeBag() function ------------------------ Read the function header to understand what this function does. Pay particular attention to its preconditions and postconditions. You need to add your code to this function where indicated. Do not change any of its existing code. Note that this function's return statement returns 2 objects: The red bag and the blue bag objects. Returning multiple objects in a single return statement is a unique Python feature. The balls --------- The balls in the bags are objects of class Ball. This class is provided under the assignment in the course web page. Also provided there is a ball tester, which makes it easy to see how to use a ball. A red ball's color is the string "red". A blue ball's color is the string "blue". Moving the balls ---------------- Moving the balls means they need to end up in the right bag. It also means they should not be in the starting bag after your code completes. For each test case, a reference to the starting bag is passed in as a function parameter. Changes you make to this bag parameter result in changes to the bag used at the point of call. This is because parameters in Python are passed by reference, rather than by copied value. Your code should be general enough to handle all 3 sets of test data. Do NOT write 3 separate blocks of code, one for each specific test set. Instead, your single solution should work for any of these test cases. You should use a for loop on the original mixed bag. You do NOT need to remove the balls from the mixed bag as you see them. You can wait until after all the ball references have been added to the unicolor bags. Using references is a shallow copy of the balls. This is OK here because you will be removing the ball references from the mixed bag. This means there will not be any duplicate references in differebt bags to worry about. Keep it simple -------------- Do not overthink/overcomplicate this. Solutions are simple and easy to understand. There is more than one possible coding solution. Part 2 ====== printBag() function ------------------- This function takes a bag as a paramater. Look at the expected output document to see what it is supposed to print. It must iterate through the given bag. Each item must be printed on a separate line. To get a string version of a ball item, just use str(item). Notice that it must print "empty" if the bag is empty. Notice that it must print a blank line after the bag output.

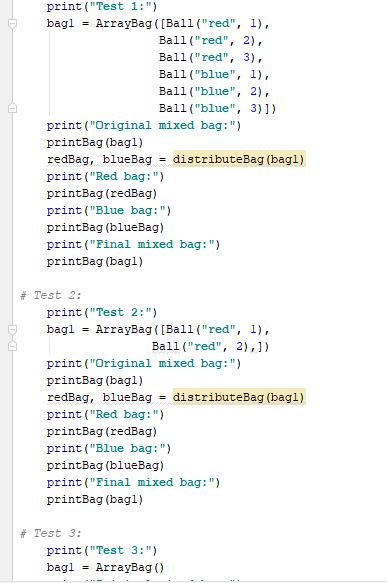
Test 1: Original mixed bag: red ball, radius 1 red ball, radius 2 red ball, radius 3 blue ball, radius 1 blue ball, radius 2 blue ball, radius 3 Red bag: red ball, radius 1 red ball, radius 2 red ball, radius 3 Blue bag: blue ball, radius 1 blue ball, radius 2 blue ball, radius 3 Final mixed bag: empty Test 2: Original mixed bag: red ball, radius 1 red ball, radius 2 Red bag: red ball, radius 1 red ball, radius 2 Blue bag: empty Final mixed bag: empty Test 3: Original mixed bag: empty Red bag: empty Blue bag: empty Final mixed bag: empty
0
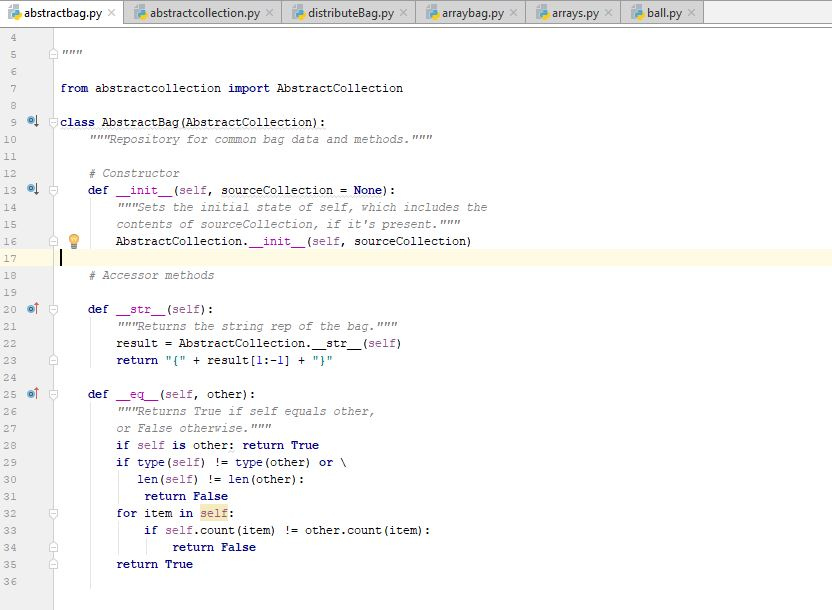
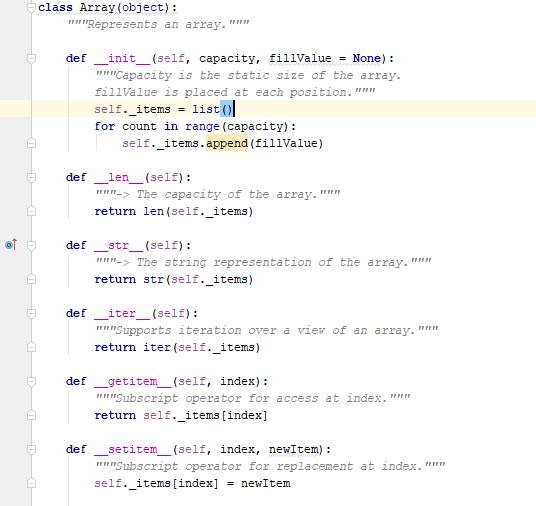
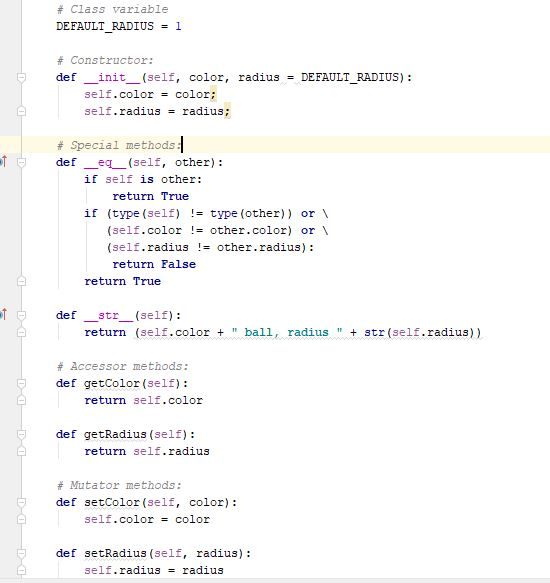
abstractbag.pyx abstractcollection.py |redistributeBag.py rearraybag.pyxl?narrays.py, eball.py from abstractcollection import AbstractCollection AbstractBag(AbstractCollection) : """Repository for common bag data and methods. " class 9 10 # Constructor def init (self, sourceCollection= None) : 12 13 14 15 Sets the initial state of self, which includes the contents of sourceCollection, if it's present." AbstractCollection.--init--(self, sourceCollection) 17 18 19 20 ot 21 # Accessor methods def tr (self): "Returns the string rep of the bag.""" result AbstractCollection. str (self) return "result [1:-1"" 24 25 o 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 def _ecg (self, other): """Returns True if self equals other, or False otherwise. if self is other: return True if type (self) != type (other) or \ len (self) len (other) return False for item in self: if self.count (1tem) return False != other.count (1tem): 34 35 3 6 return TrueStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


