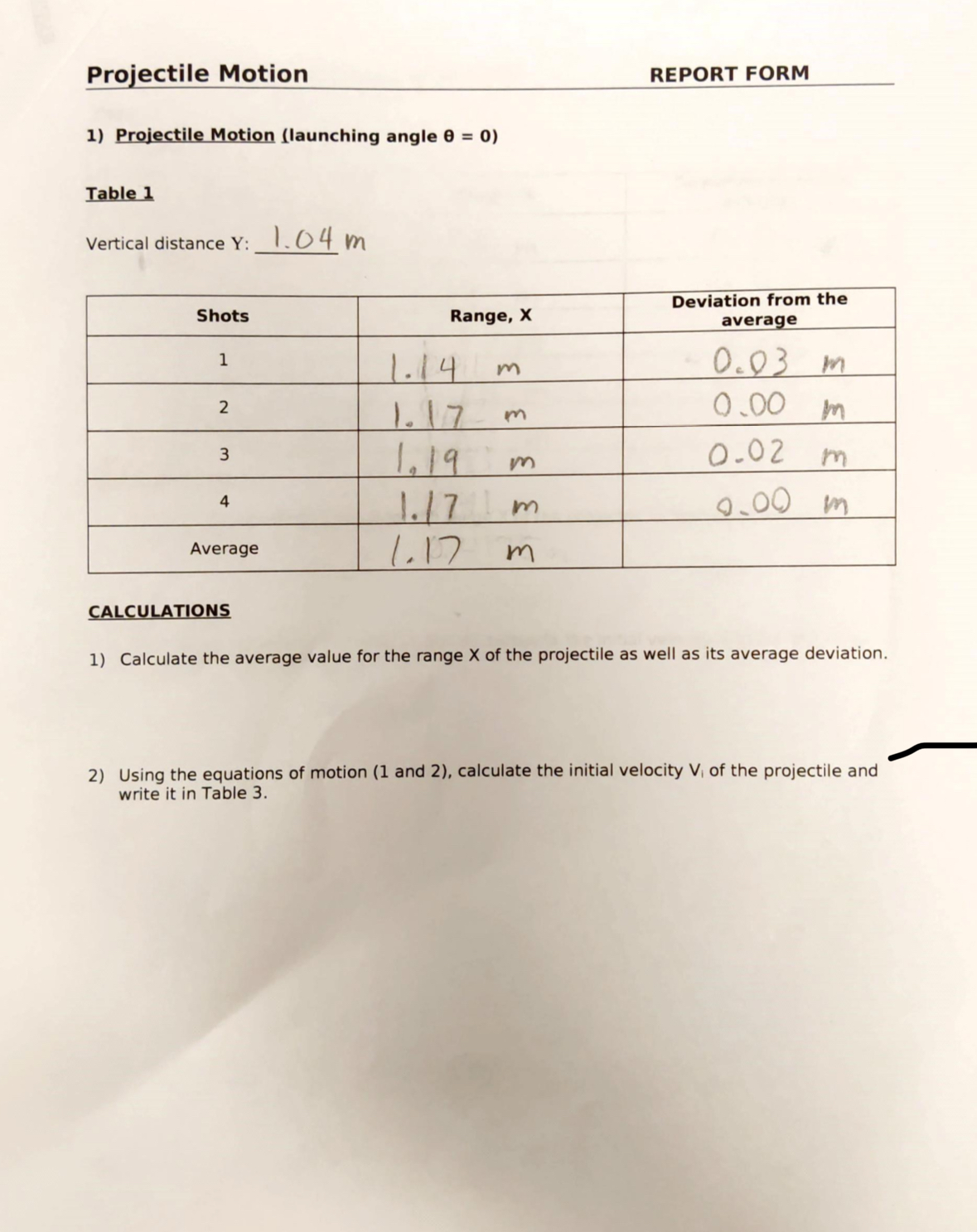
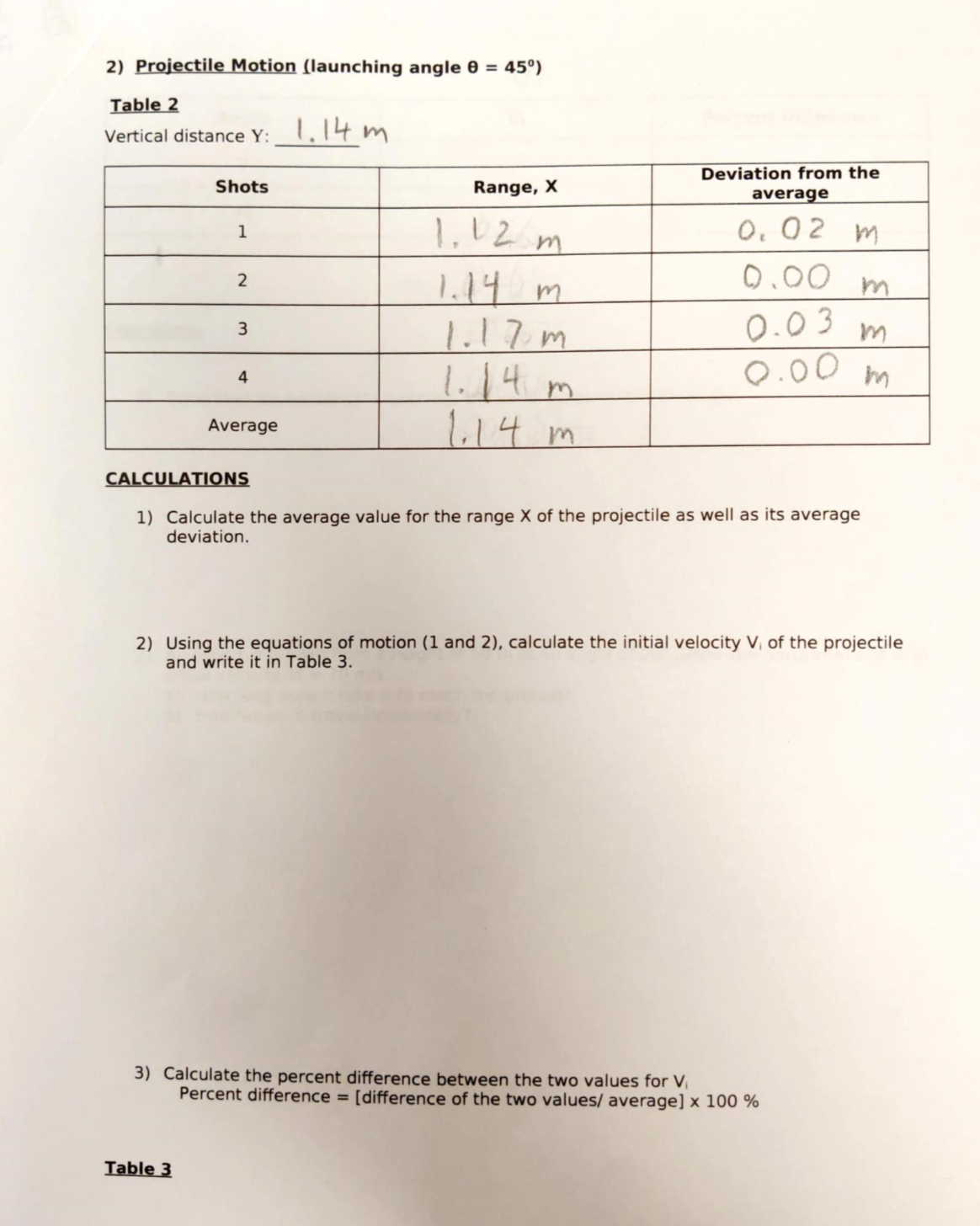
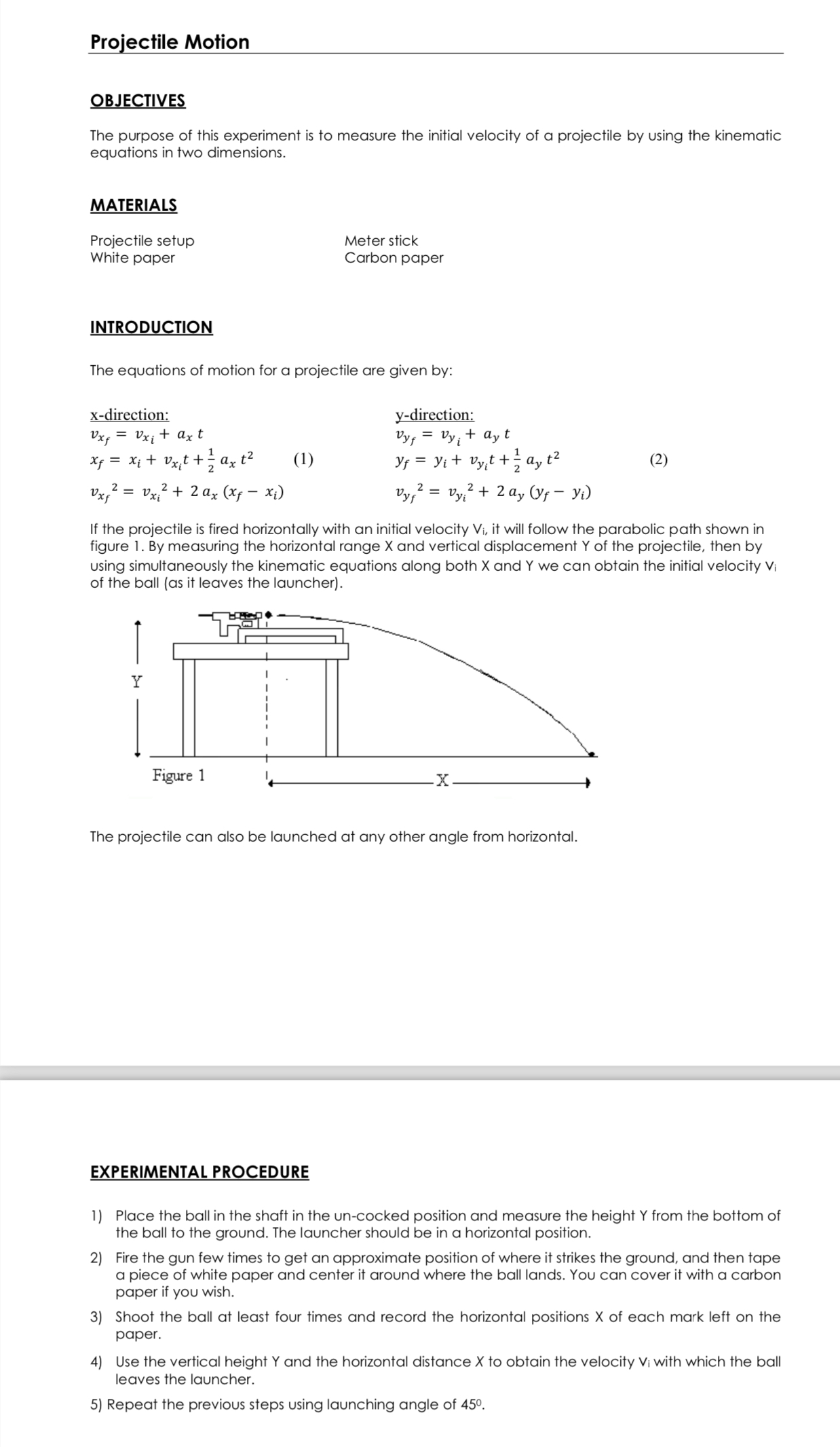
Projectile Motion REPORT FORM 1) Projectile Motion (launching angle 0 = 0) Table 1 Vertical distance Y: 1 04 m Deviation from the Shots Range, X average 1 1. 14 m 0.03 m N 1. 17 m 0.00 m 3 1 19 0-02 m A 1. 1 7 Im 0.00 m Average 1. 17 m CALCULATIONS 1) Calculate the average value for the range X of the projectile as well as its average deviation. 2) Using the equations of motion (1 and 2), calculate the initial velocity V, of the projectile and write it in Table 3.2) Projectile Motion (launching angle 0 = 45) Table 2 Vertical distance Y: 1. 14 m Deviation from the Shots Range, X average 1 1. 1 2 m 0. 02 m N 1. 14 m 0.00 m 3 1. 1 7 m 0.03 m 1. 14 m 0.00 m Average 1. 14 m CALCULATIONS 1) Calculate the average value for the range X of the projectile as well as its average deviation. 2) Using the equations of motion (1 and 2), calculate the initial velocity V, of the projectile and write it in Table 3. 3) Calculate the percent difference between the two values for V. Percent difference = [difference of the two values/ average] x 100 % Table 3Projectile Motion BE IVE The purpose of this experiment is to measure the initial velocity of a projectile by using the kinematic equations in two dimensions. MATERIAL Projectile setup Meter stick White paper Carbon paper INTR D Tl N The equations of motion for a projectile are given by: xdirection: x-direction: \"if: vxi+axt vyf=vyi+ayt 1 1 xf= xi+ int'l'gax :2 (1) yr: yi+ vyit+gay :2 (2) 11472: vxlz+ 2a,: (x; xi) ny: vyi2+ 211}, (yf Jr'i) If the projectile is fired horizontally with an initial velocity Vi. it will follow the parabolic path shown in figure 1. By measuring the horizontal range X and vertical displacement Y of the projectile. then by using simultaneously the kinematic equations along both X and Y we can obtain the initial velocity vi of the ball [as it leaves the launcher]. The projectile can also be launched at any other angle from horizontal. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE 1] Place the ball in the shaft in the uncocked position and measure the height Y from the bottom of the ball to the ground. The launcher should be in a horizontal position. 2] Fire the gun few times to get an approximate position of where it strikes the ground, and then tape a piece of white paper and center it around where the ball lands. You can cover it with a carbon paper if you wish. 3] Shoot the ball at least four times and record the horizontal positions X of each mark left on the papeL 4] Use the vertical height Y and the horizontal distance X to obtain the velocity Vi with which the ball leaves the launcher. 5] Repeat the previous steps using launching angle of 45. 9:11 97 05_Projectile Motion.pdf V Done 3) Calculate the percent difference between the two values for Vi Percent difference = [difference of the two values/ average] x 100 % Table 3 Angle Vi Percent Difference 0 45 Questions 1) Show that for horizontal launching, the initial velocity Vi is given by: Vi = X g/2Y An object is thrown from a height of 50 m at an angle of 20 below the horizontal and with initial velocity Vi = 70 m/s. a) How long does it take it to reach the ground? b) How far did it travel horizontally