



Provide the correct answer as well as explanation for each of the following:
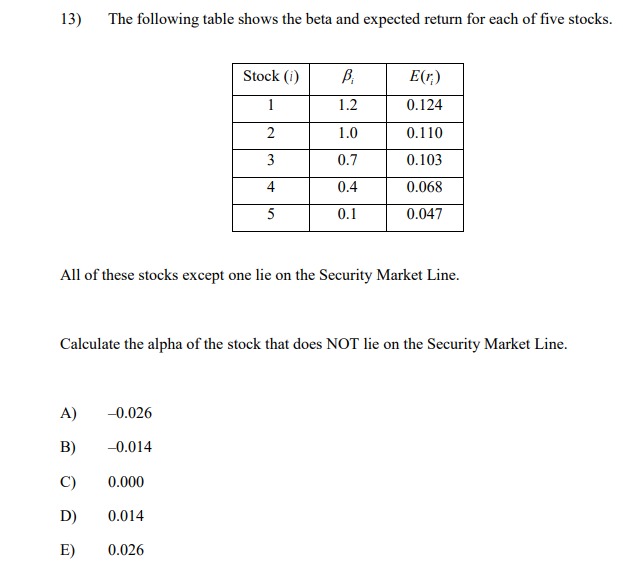
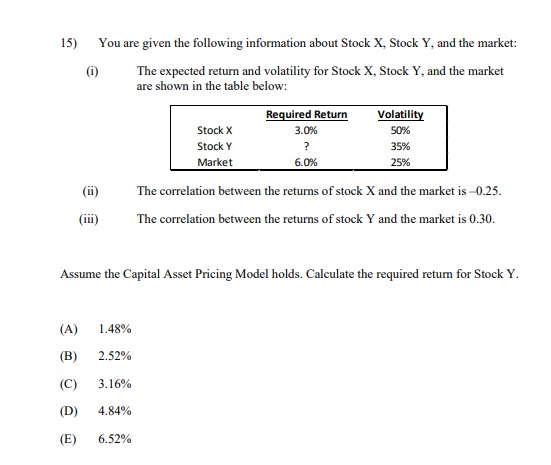
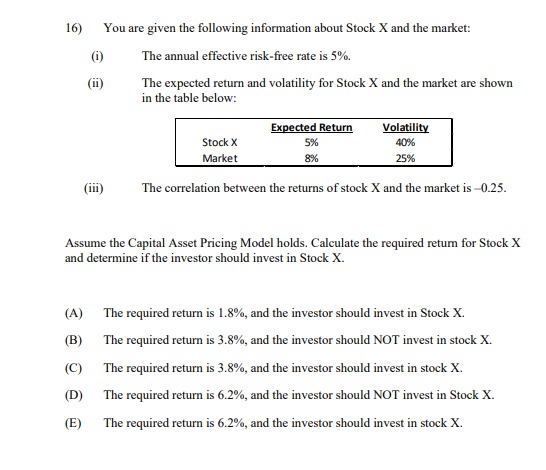
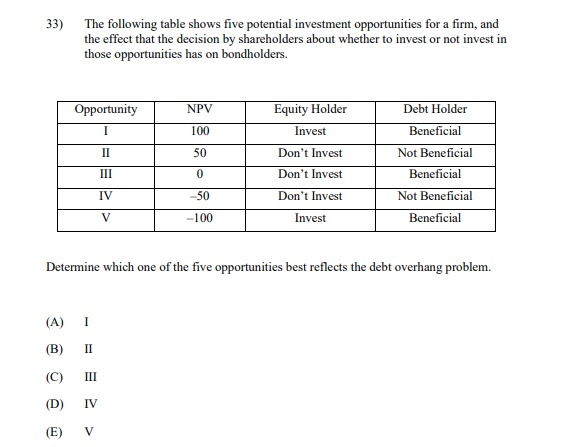
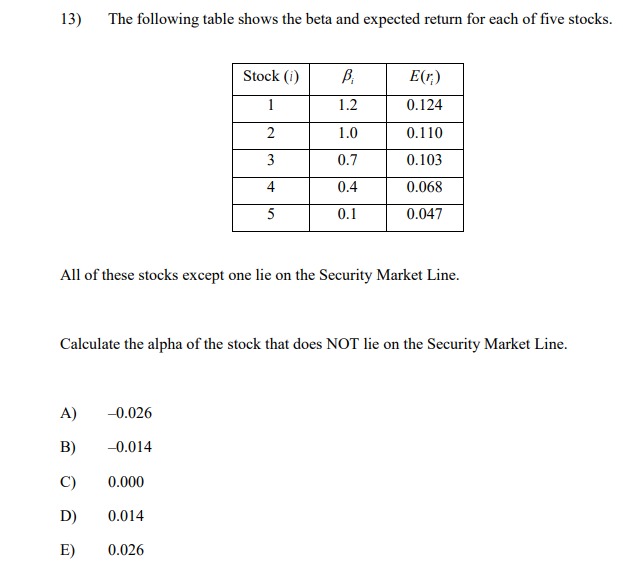
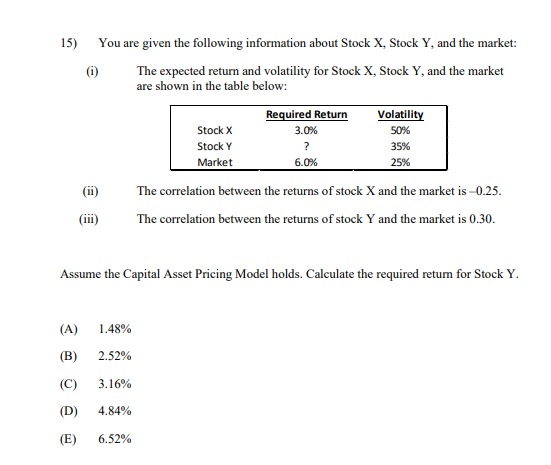
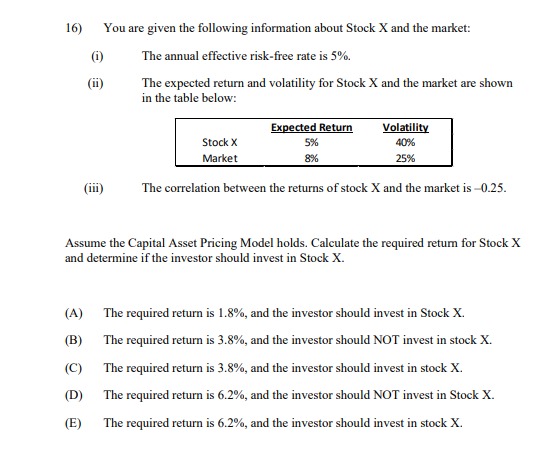
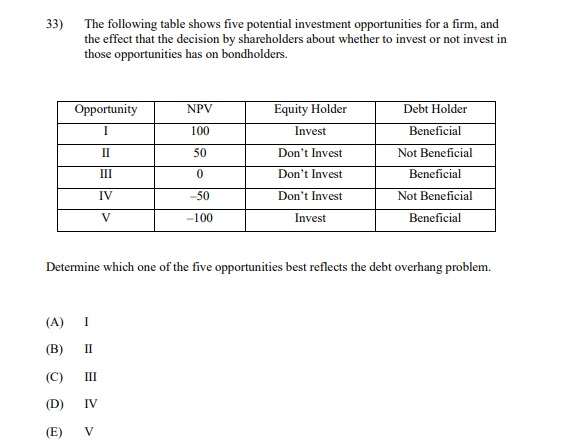
13) The following table shows the beta and expected return for each of five stocks. Stock (i) E(r) 1.2 0.124 2 1.0 0.110 0.7 0.103 0.4 0.068 5 0.1 0.047 All of these stocks except one lie on the Security Market Line. Calculate the alpha of the stock that does NOT lie on the Security Market Line. A) -0.026 -0.014 C) 0.000 D) 0.014 E) 0.02614) You are given the following information about Stock X, Stock Y, and the market: (i) The annual effective risk-free rate is 4%. (i) The expected return and volatility for Stock X, Stock Y, and the market are shown in the table below: Expected Return Volatility Stock X 5.5% 40% Stock Y 4.5% 35% Market 6.0%% 25% (iii) The correlation between the returns of stock X and the market is -0.25. (iv) The correlation between the returns of stock Y and the market is 0.30. Assume the Capital Asset Pricing Model holds. Calculate the required returns for Stock X and Stock Y, and determine which of the two stocks an investor should choose. (A) The required return for Stock X is 3.20%, the required return for Stock Y is 4.84%, and the investor should choose Stock X. (B) The required return for Stock X is 3.20%, the required return for Stock Y is 4.84%, and the investor should choose Stock Y. (C) The required return for Stock X is 4.80%, the required return for Stock Y is 4.84%, and the investor should choose Stock X. (D) The required return for Stock X is 6.40%, the required return for Stock Y is 3.16%, and the investor should choose Stock Y. (E) The required return for Stock X is 3.50%, the required return for Stock Y is 3.16%, and the investor should choose both Stock X and Stock Y.15) You are given the following information about Stock X, Stock Y, and the market: (1) The expected return and volatility for Stock X, Stock Y, and the market are shown in the table below: Required Return Volatility Stock X 3.0%% 50% Stock Y ? 35% Market 6.0% 25% (ii) The correlation between the returns of stock X and the market is -0.25. (iii) The correlation between the returns of stock Y and the market is 0.30. Assume the Capital Asset Pricing Model holds. Calculate the required return for Stock Y. (A) 1.48% (B) 2.52% (C) 3.16% (D) 4.84% (E) 6.52%[6} You are given the following information about Stock I and the market: {i} The annual effective risk-free rate is 5%. (ii) The expected return and volatility ar Stock I and the market are shown in the table below: {iii} The correlation between the returns of stock I and the market is 4125- Assume the Capital Asset Pricing Model holds. Calculate the required retunt for Stock K and determine if'the investor should invest in Stuck "X. {A} The required return is 1.8%, and the investor should invest in Stock K. {B} The required return is 3.3%, and the investor should NUT invest in stock X. {C} The required return is 3.3%, and the investor should invest in stock K. {D} The required return is 6.2%, and the investor should HUT invest in Stock \"K. {E} The required return is 15.2%, and the investor should invest in stock K. 26) Consider the following four behavioral patterns of investors. I: Familiarity Bias II: Disposition Effect III: Overconfidence Bias IV: Herd Behavior Determine which two of these behavioral patterns are NOT systematic trading biases, and are thus LESS likely to cause stock prices to deviate from their fundamental values. (A) I and II (B) I and III (C) II and III (D) II and IV (E) III and IV33) The following table shows five potential investment opportunities for a firm, and the effect that the decision by shareholders about whether to invest or not invest in those opportunities has on bondholders. Opportunity NPV Equity Holder Debt Holder I 100 Invest Beneficial II 50 Don't Invest Not Beneficial III 0 Don't Invest Beneficial IV -50 Don't Invest Not Beneficial V -100 Invest Beneficial Determine which one of the five opportunities best reflects the debt overhang problem. (A) I (B) II (C) III (D) IV (E) V34) Let X be the random gain from operations of a company. You are given: (i) X is normally distributed with mean 42 and variance 6400. (ii) p is the probability that X is negative. (iii) K is the amount of capital such that the Value-at-Risk (VaR) at the 5th percentile for X' + K is zero. Calculate p and K. (A) p=0.7; K = 157 (B) p=0.7; K = 131 (C) p=0.5; K = 115 (D) p=0.3; K= 115 (E) p= 0.3; K= 9035) You own a share of a nondividend-paying stock and will hold it for a period of time. You want to set aside an amount of capital as a percentage of the initial stock price to reduce the risk of loss at the end of the holding period. You are given: The stock price follows a lognormal distribution. ii) The annualized expected rate of return on the stock is 15%. The annualized stock volatility is 40%. iv) The investment period is 4 years. v ) The Value-at Risk (VaR) at the 3rd percentile for the capital plus the ending stock value equals the initial stock price. Calculate the capital amount as a percentage of initial stock price. (A) 57% (B) 63% (C) 71% (D) 82% (E) 91%