
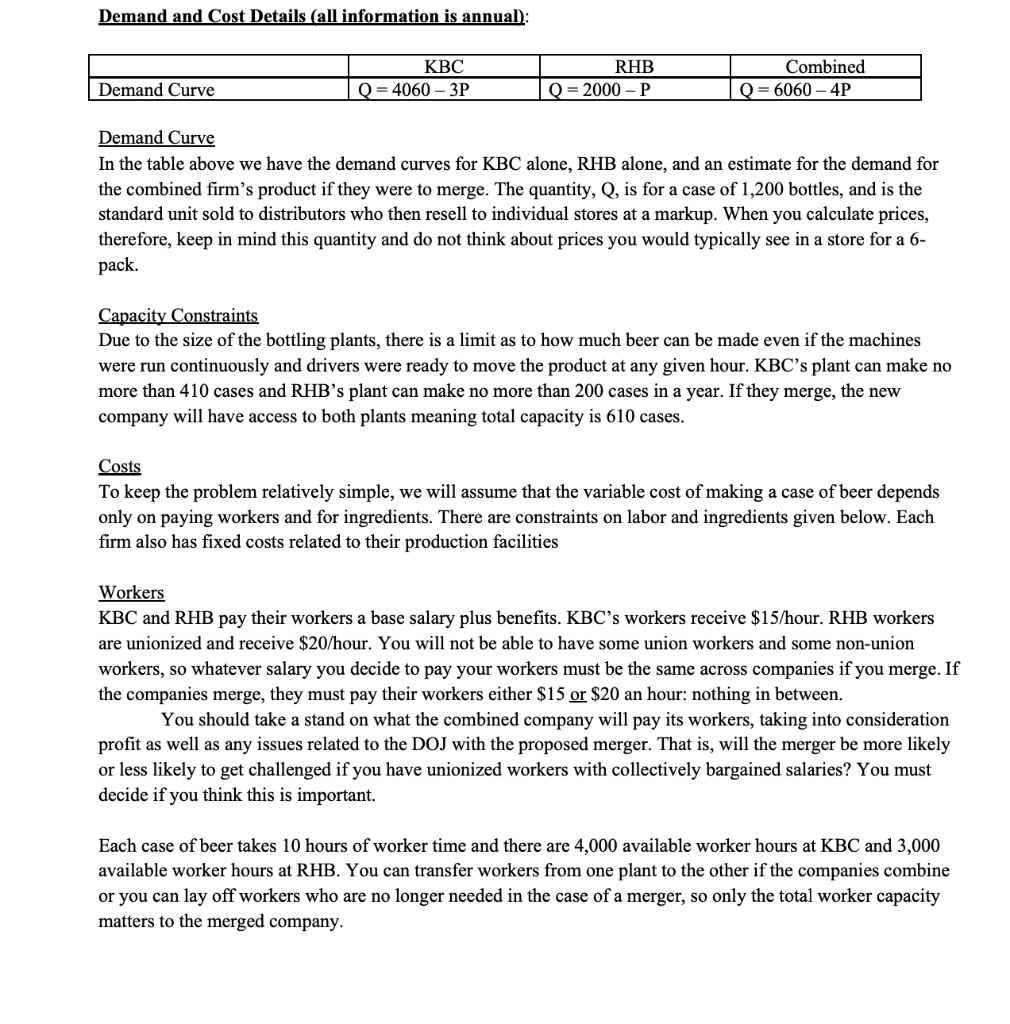

Purpose: This project is the second of two deliverables for the large project for your client, Kalamazoo Brewing Company (KBC). As a reminder, this project has been designed to mock actual tasks you might very well be assigned to if you were to take a position with an economic consulting firm. You should therefore view your work as a "mini-internship, where the project deliverable will be evaluated by your boss and will be used to assess your performance and to determine your raise. Objectives: Apply business economics concepts and theories to "real world" business scenarios; Use the Solver function in Microsoft Excel to evaluate profitability; Effectively communicate economic concepts and results using clearly labeled tables; Produce a professional" product. In this project there are a few times where you will need to make a judgement call about the best way to do something (either for the firm or for your analysis). You are smart: think about the pros & cons of each, and make an informed decision. Part of your informed decision should probably be seeing what it looks like under each alternative so that you know what you are comparing. The deliverable guidelines: KBC is considering purchasing a rival brewery in Oxford, Ohio, Red Hawk Brewing (RHB). You are to address whether the acquisition is worth pursuing from a profit standpoint, as well as any considerations with regards to the Department of Justice (DOJ). Information about the demand curves for each company and specific cost information was conducted by other analysts and is provided below. You have been asked to do the following analyses and report the results: (1) Calculate the current revenue, cost and profit of KBC and RHB assuming that they are currently maximizing profit. (2) Find how much KBC's profit would change if the company goes through with the merger. Summarize all of the profit calculations and assumptions using tables (I do not need to see your Excel file, just the results your boss would want to see.) (3) Advise KBC on the most they should be willing to pay for RHB, or advise against the acquisition. You should consider how much profit changes, the price that it would likely take to acquire RHB, and the likelihood that the DOJ will contest the merger. If it is likely to be contentious then there will be additional (unpredictable) costs for attorney fees and costs of defending the merger to the DOJ. You must detail specific reasons for why the DOJ might challenge the merger based on an HHI calculation (market shares are found below) in addition to other considerations for how consumers and workers will be affected that the DOJ might care about. Note that the demands, costs, and profit below are annual. If KBC and RHB are currently profitable, then they will probably be in business and earning annual profit) for a long time. You will need to consider this when deciding whether you should pursue a merger and how much it will take to get RHB to accept the offer. We have not discussed how to value a long stream of annual profits, so you can do this in any way you want, but however you value future profits you must do it consistently for both companies, including the value to the current owners of RHB of the company they own. One simple way to value a stream of income is the sum of 5 years of profits. Demand and Cost Details (all information is annual): KBC Q = 4060 - 3P RHB Q = 2000-P Combined Q = 6060-4P Demand Curve Demand Curve In the table above we have the demand curves for KBC alone, RHB alone, and an estimate for the demand for the combined firm's product if they were to merge. The quantity, Q, is for a case of 1,200 bottles, and is the standard unit sold to distributors who then resell to individual stores at a markup. When you calculate prices, therefore, keep in mind this quantity and do not think about prices you would typically see in a store for a 6- pack. Capacity Constraints Due to the size of the bottling plants, there is a limit as to how much beer can be made even if the machines were run continuously and drivers were ready to move the product at any given hour. KBC's plant can make no more than 410 cases and RHBs plant can make no more than 200 cases in a year. If they merge, the new company will have access to both plants meaning total capacity is 610 cases. Costs To keep the problem relatively simple, we will assume that the variable cost of making a case of beer depends only on paying workers and for ingredients. There are constraints on labor and ingredients given below. Each firm also has fixed costs related to their production facilities Workers KBC and RHB pay their workers a base salary plus benefits. KBC's workers receive $15/hour. RHB workers are unionized and receive $20/hour. You will not be able to have some union workers and some non-union workers, so whatever salary you decide to pay your workers must be the same across companies if you merge. If the companies merge, they must pay their workers either $15 or $20 an hour: nothing in between. You should take a stand on what the combined company will pay its workers, taking into consideration profit as well as any issues related to the DOJ with the proposed merger. That is, will the merger be more likely or less likely to get challenged if you have unionized workers with collectively bargained salaries? You must decide if you think this is important. Each case of beer takes 10 hours of worker time and there are 4,000 available worker hours at KBC and 3,000 available worker hours at RHB. You can transfer workers from one plant to the other if the companies combine or you can lay off workers who are no longer needed in the case of a merger, so only the total worker capacity matters to the merged company. Ingredients All beer uses water, barley, hops and yeast. We will assume that each case costs $100 to produce in terms of ingredients. KBC can access $50,000 worth of ingredients from local suppliers. RHB has access to $40,000 of ingredients. A merged company would have access to both supplies: $90,000 of ingredients. Hint: Pay attention to whether the numbers you are working with are total costs, or costs per case. Some things, like workers, I have given as a total. Some, like ingredients, I have given per case. You may have to do some math to make everything fit together, so label your values clearly. Fixed Costs KBC has fixed costs of $800 per year related to its production facility. RHB has similar fixed costs of $500/year. Since a combined firm would operate both facilities, they still have to pay both fixed costs. Set Up You now have all of the information you need to solve the profit maximization problems. First, find the profit maximizing price per case and quantity of cases for KBC given their demand, cost and constraint information. Then do the same calculation for RHB, to determine how profitable they are on their own. Then redo the problem with the joint demand curve and combined constraints to see how profitable a combined firm would be if they merge. State your decision about uniononunion workers clearly. Market Concentration In addition to make calculations related to maximizing profit, you are asked to provide information on whether the DOJ is likely to challenge the merger. The DOJ factors in market concentration (HHI) as well as how this will affect customers, workers, and rival businesses. In order to make an HHI calculation the market shares for the entire beer industry in the four states that KBC operates are given below, in addition to whether the particular company is a "craft beer" or "big beer" specialist. Use this information in a way that makes sense to your analysis, but if you separate them into 2 markets, you will have to do math in order to figure out each firm's market share in that market. There is no "right" or "wrong" way here: do what makes sense to you and briefly explain why. Market Share 0.47 Company AN-Beach Cantina Fedora SBC National KBC RHB Brew Time Buckeye Western Diplomat Top Notch Free Bird 0.14 0.11 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Company Type Big Beer Big Beer Big Beer Craft Beer Big Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Purpose: This project is the second of two deliverables for the large project for your client, Kalamazoo Brewing Company (KBC). As a reminder, this project has been designed to mock actual tasks you might very well be assigned to if you were to take a position with an economic consulting firm. You should therefore view your work as a "mini-internship, where the project deliverable will be evaluated by your boss and will be used to assess your performance and to determine your raise. Objectives: Apply business economics concepts and theories to "real world" business scenarios; Use the Solver function in Microsoft Excel to evaluate profitability; Effectively communicate economic concepts and results using clearly labeled tables; Produce a professional" product. In this project there are a few times where you will need to make a judgement call about the best way to do something (either for the firm or for your analysis). You are smart: think about the pros & cons of each, and make an informed decision. Part of your informed decision should probably be seeing what it looks like under each alternative so that you know what you are comparing. The deliverable guidelines: KBC is considering purchasing a rival brewery in Oxford, Ohio, Red Hawk Brewing (RHB). You are to address whether the acquisition is worth pursuing from a profit standpoint, as well as any considerations with regards to the Department of Justice (DOJ). Information about the demand curves for each company and specific cost information was conducted by other analysts and is provided below. You have been asked to do the following analyses and report the results: (1) Calculate the current revenue, cost and profit of KBC and RHB assuming that they are currently maximizing profit. (2) Find how much KBC's profit would change if the company goes through with the merger. Summarize all of the profit calculations and assumptions using tables (I do not need to see your Excel file, just the results your boss would want to see.) (3) Advise KBC on the most they should be willing to pay for RHB, or advise against the acquisition. You should consider how much profit changes, the price that it would likely take to acquire RHB, and the likelihood that the DOJ will contest the merger. If it is likely to be contentious then there will be additional (unpredictable) costs for attorney fees and costs of defending the merger to the DOJ. You must detail specific reasons for why the DOJ might challenge the merger based on an HHI calculation (market shares are found below) in addition to other considerations for how consumers and workers will be affected that the DOJ might care about. Note that the demands, costs, and profit below are annual. If KBC and RHB are currently profitable, then they will probably be in business and earning annual profit) for a long time. You will need to consider this when deciding whether you should pursue a merger and how much it will take to get RHB to accept the offer. We have not discussed how to value a long stream of annual profits, so you can do this in any way you want, but however you value future profits you must do it consistently for both companies, including the value to the current owners of RHB of the company they own. One simple way to value a stream of income is the sum of 5 years of profits. Demand and Cost Details (all information is annual): KBC Q = 4060 - 3P RHB Q = 2000-P Combined Q = 6060-4P Demand Curve Demand Curve In the table above we have the demand curves for KBC alone, RHB alone, and an estimate for the demand for the combined firm's product if they were to merge. The quantity, Q, is for a case of 1,200 bottles, and is the standard unit sold to distributors who then resell to individual stores at a markup. When you calculate prices, therefore, keep in mind this quantity and do not think about prices you would typically see in a store for a 6- pack. Capacity Constraints Due to the size of the bottling plants, there is a limit as to how much beer can be made even if the machines were run continuously and drivers were ready to move the product at any given hour. KBC's plant can make no more than 410 cases and RHBs plant can make no more than 200 cases in a year. If they merge, the new company will have access to both plants meaning total capacity is 610 cases. Costs To keep the problem relatively simple, we will assume that the variable cost of making a case of beer depends only on paying workers and for ingredients. There are constraints on labor and ingredients given below. Each firm also has fixed costs related to their production facilities Workers KBC and RHB pay their workers a base salary plus benefits. KBC's workers receive $15/hour. RHB workers are unionized and receive $20/hour. You will not be able to have some union workers and some non-union workers, so whatever salary you decide to pay your workers must be the same across companies if you merge. If the companies merge, they must pay their workers either $15 or $20 an hour: nothing in between. You should take a stand on what the combined company will pay its workers, taking into consideration profit as well as any issues related to the DOJ with the proposed merger. That is, will the merger be more likely or less likely to get challenged if you have unionized workers with collectively bargained salaries? You must decide if you think this is important. Each case of beer takes 10 hours of worker time and there are 4,000 available worker hours at KBC and 3,000 available worker hours at RHB. You can transfer workers from one plant to the other if the companies combine or you can lay off workers who are no longer needed in the case of a merger, so only the total worker capacity matters to the merged company. Ingredients All beer uses water, barley, hops and yeast. We will assume that each case costs $100 to produce in terms of ingredients. KBC can access $50,000 worth of ingredients from local suppliers. RHB has access to $40,000 of ingredients. A merged company would have access to both supplies: $90,000 of ingredients. Hint: Pay attention to whether the numbers you are working with are total costs, or costs per case. Some things, like workers, I have given as a total. Some, like ingredients, I have given per case. You may have to do some math to make everything fit together, so label your values clearly. Fixed Costs KBC has fixed costs of $800 per year related to its production facility. RHB has similar fixed costs of $500/year. Since a combined firm would operate both facilities, they still have to pay both fixed costs. Set Up You now have all of the information you need to solve the profit maximization problems. First, find the profit maximizing price per case and quantity of cases for KBC given their demand, cost and constraint information. Then do the same calculation for RHB, to determine how profitable they are on their own. Then redo the problem with the joint demand curve and combined constraints to see how profitable a combined firm would be if they merge. State your decision about uniononunion workers clearly. Market Concentration In addition to make calculations related to maximizing profit, you are asked to provide information on whether the DOJ is likely to challenge the merger. The DOJ factors in market concentration (HHI) as well as how this will affect customers, workers, and rival businesses. In order to make an HHI calculation the market shares for the entire beer industry in the four states that KBC operates are given below, in addition to whether the particular company is a "craft beer" or "big beer" specialist. Use this information in a way that makes sense to your analysis, but if you separate them into 2 markets, you will have to do math in order to figure out each firm's market share in that market. There is no "right" or "wrong" way here: do what makes sense to you and briefly explain why. Market Share 0.47 Company AN-Beach Cantina Fedora SBC National KBC RHB Brew Time Buckeye Western Diplomat Top Notch Free Bird 0.14 0.11 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Company Type Big Beer Big Beer Big Beer Craft Beer Big Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer Craft Beer









