Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
python code, need the graph in output, show the complete code pls CODE import copy import random import pandas as pd import time import matplotlib.pyplot
python code, need the graph in output, show the complete code pls
CODE
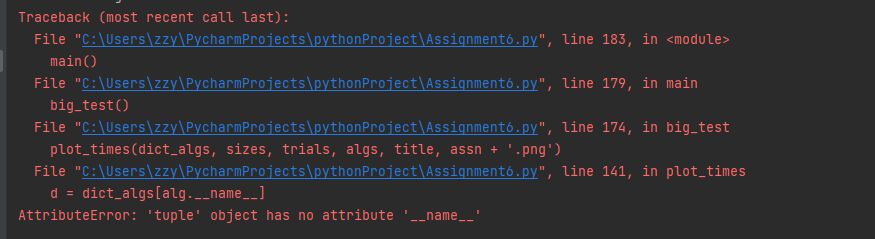
import copy import random import pandas as pd import time import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def display_hash(hash_table): for i in range(len(hash_table)): print(i, hash_table[i]) print() def hash_chaining_build(arr): size = int(len(arr) / 10) hash_table = [[] for _ in range(size)] for key in arr: hash_key = hash_function(key, size) hash_table[hash_key].append(key) # print(hash_table) return hash_table def hash_probing_build(arr): size = len(arr) * 2 hash_table = [None for _ in range(size)] for key in arr: hash_key = hash_function(key, size) i = 0 while hash_table[hash_key]: i += 1 hash_key = hash_function_probing(hash_key, size, i) hash_table[hash_key] = key return hash_table def hash_chaining_search(hash_table, arr): size = len(hash_table) found = [False] * len(arr) for j in range(len(arr)): key = arr[j] hash_key = hash_function(key, size) for item in hash_table[hash_key]: if item == key: found[j] = True break return found def hash_probing_search(hash_table, arr): size = len(hash_table) found = [False] * len(arr) # found = [False for i in range(size)] for j in range(len(arr)): key = arr[j] hash_key = hash_function(key, size) i = 0 while hash_table[hash_key] != key: i += 1 hash_key = hash_function_probing(hash_key, size, i) found[j] = True return found def hash_function(key, size): return key % size def hash_function_probing(hash_key, size, i): a, b, c = 5, 7, 9 hash_key = (hash_key + a * i ** 2 + b * i + c) % size return hash_key def random_list(size): # arr = [i**3 for i in range(size)] # random.shuffle(arr) # return arr return random.sample(range(size * 10), size) def run_algs(algs, sizes, trials): dict_algs = {} for alg in algs: dict_algs[alg[2]] = {} for size in sizes: for alg in algs: dict_algs[alg[2]][size] = 0 for trial in range(1, trials + 1): arr = random_list(size) arr_copy = copy.deepcopy(arr) random.shuffle(arr_copy) for alg in algs: start_time = time.time() build = alg[0] ds = build(arr) search = alg[1] found = search(ds, arr_copy) if size == sizes[0]: print(alg[2]) print(ds) print(found) end_time = time.time() net_time = end_time - start_time dict_algs[alg[2]][size] += 1000 * net_time return dict_algs # def mini_test(): # size = 100 # arr = random_list(size) # ht_chaining = hash_chaining_build(arr) # ht_proving = hash_probing_build(arr) # display_hash(ht_chaining) # display_hash(ht_proving)0 # random.shuffle(arr) # found = hash_chaining_search(ht_chaining, arr) # print("Hash Chaining Search: ") # print(found) # found = hash_probing_search(ht_proving, arr) # print("Hash Probing Search: ") # print(found) def plot_times(dict_algs, sizes, trials, algs, title, file_name): alg_num = 0 plt.xticks([j for j in range(len(sizes))], [str(size) for size in sizes]) for alg in algs: alg_num += 1 d = dict_algs[alg.__name__] x_axis = [j + 0.05 * alg_num for j in range(len(sizes))] y_axis = [d[i] for i in sizes] plt.bar(x_axis, y_axis, width=0.05, alpha=0.75, label=alg.__name__) plt.legend() plt.title(title) plt.xlabel("Size") plt.ylabel("Time for " + str(trials) + " trials (ms)") plt.savefig(file_name) plt.show() def print_times(dict_algs): pd.set_option("display.max_rows", 500) pd.set_option("display.max_columns", 500) pd.set_option("display.width", 1000) df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_algs).T print(df) def big_test(): assn = "Assignment6" sizes = [100, 1000, 10000] algs = [(hash_probing_build, hash_probing_search, "Hash Probing"), (hash_chaining_build, hash_chaining_search, "Hash Chaining")] trials = 1 title = "Empirical Performance of Search Structures" dict_algs = run_algs(algs, sizes, trials) for alg in dict_algs: print(alg) for size in dict_algs[alg]: print(size, dict_algs[alg][size] / trials) print_times(dict_algs) plot_times(dict_algs, sizes, trials, algs, title, assn + '.png') def main(): # mini_test() big_test() if __name__ == "__main__": main() Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


