Question: Q2) [43 Marks] A study is performed by a company, called ShipComp, to understand maritime (ship) accidents. A list of factors that influence the accident
![Q2) [43 Marks] A study is performed by a company, called](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/10/6708b1c527643_0446708b1c4eea63.jpg)
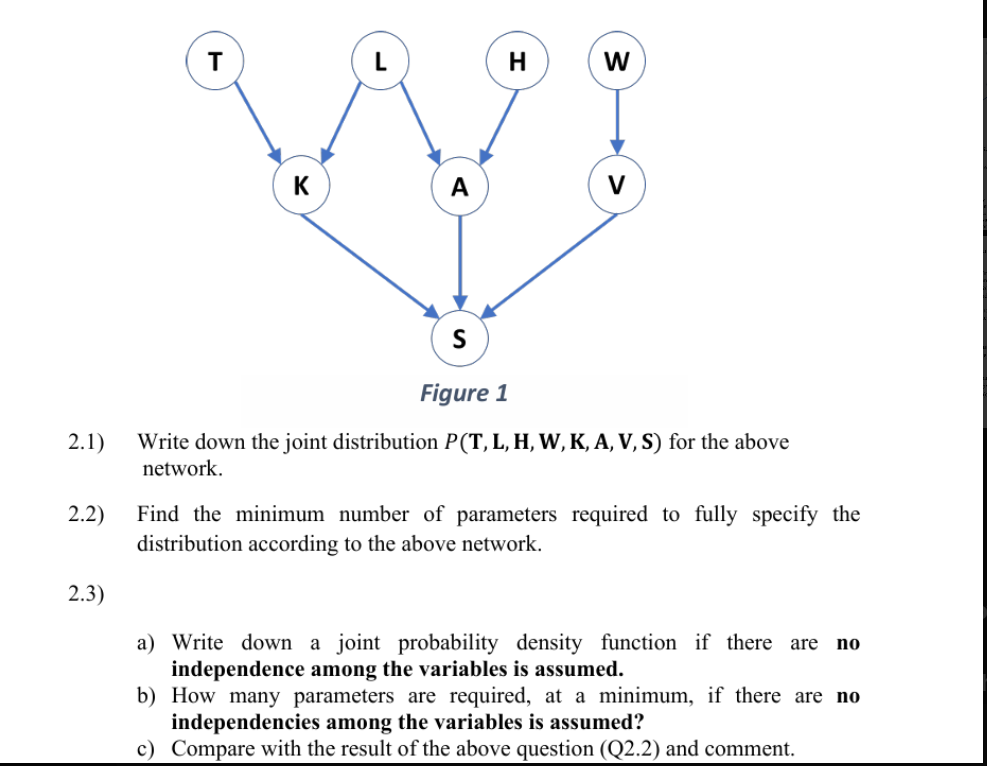


Q2) [43 Marks] A study is performed by a company, called ShipComp, to understand maritime (ship) accidents. A list of factors that influence the accident severity along with their possible values, and a Bayesian network (Figure 1) that represents the relationship between these factors (variables) are given below. S (Severity of accident) {Minor, Catastrophic, Major} T (Tonnage) {less than 3000, between 3000 and 20000, more than 20000)} L (Length) {Large, Small} H (Human factors) {Yes, No} W (Weather) {Cloud, Wind, Fog, Rain} K (Kilowatt Power) {Less than 3000, more than 3000} A (Accident type) { Collision, Grounding, Other} V (Visibility) {High, Average, Low} T H W K A V S Figure 1 2.1) Write down the joint distribution P(T, L, H, W, K, A, V, S) for the above network. 2.2) Find the minimum number of parameters required to fully specify the distribution according to the above network. 2.3) a) Write down a joint probability density function if there are no independence among the variables is assumed. b) How many parameters are required, at a minimum, if there are no independencies among the variables is assumed? c) Compare with the result of the above question (Q2.2) and comment.24) From a previous study, the company, ShipComp, has found out that the Kilowatt Power (K) is conditionally independent of Length (L) given the Tonnage (T). The company ShipComp wants to modify the Bayesian network given in Figure 1 by incorporating this new information. Assume now that Kilowatt Power (K) is conditionally independent of Length (L) given the Tonnage (T), perform the following. a) What change will happen to the Bayesian network (shown in Figure 1) when the above assumption is considered. Draw the new Bayesian network considering the above assumption (you may draw this by hand). b) Compute the change in the minimum number of parameters required for this new Bayesian network, compared to the minimum number of parameters required for the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1. Comment on the results. 2.5) d-separation method can be used to find two sets of independent or conditionally independent variables in a Bayesian network. Use the Bayesian network given in Figure 1 to answer the following: 2.6) 2.7) For each of the statements/questions given below from (a) to (b), perform the following: e List all the possible paths from the first (set of) node/s to the second (set of) node/s considered for the independence check. e State if each of those paths 1s blocking or non-blocking with reasons. e Hence, answer the question about independence. a) Is Human factors (H) conditionally independent of Weather (W) given Kilowatt power (K), Severity of accident (S) and Accident type (A)? by sTLV? For the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1, find all the nodes that are conditionally independent of T (Tonnage) given A (Accident Type) and V (Visibility). Write a R-Program to produce the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1, and perform the d-separation tests for cases given below. Show the plot of the network you obtained and the output (of d-separation test) from your program. a) WLK|S b) H1 V|{K A} 2.8) For the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1, a) b) c) find the Markov blanket of A (Accident type). find all the nodes that are conditionally independent of A (Accident type) given its Markov blanket. use R program to find the Markov blanket of K (Kilowatt Power). Plot the Bayesian network and show the Markov blanket nodes in the network using different colour. 2.9) For the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1, a) b) show the step by step process to perform variable elimination to compute P(S|W = Fog, A = Catastrophic, V = High, K = Less than 3000). Use the following variable ordering for the elimination process: T,L, H. what is the treewidth of the network, given the above elimination ordering
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


