Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Q5. Imagine a developing country government that has 2 policy options with regard to the domestic automobile industry. The first one is that it
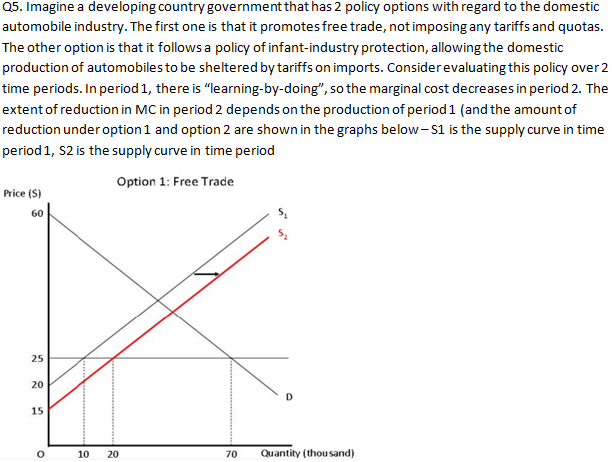
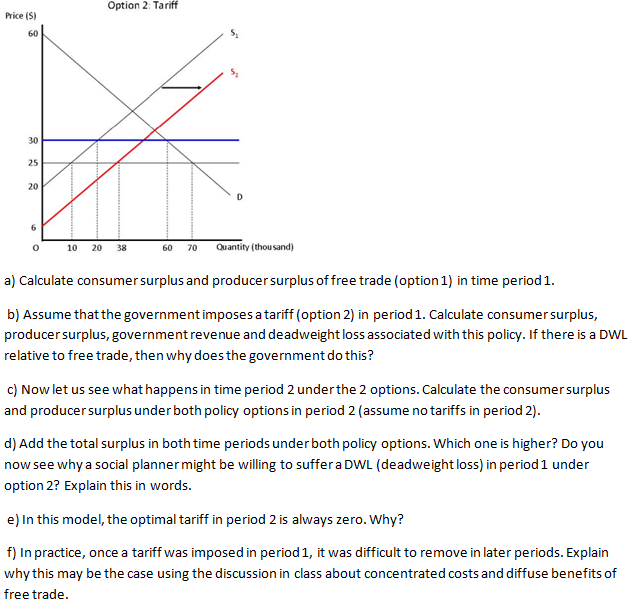
Q5. Imagine a developing country government that has 2 policy options with regard to the domestic automobile industry. The first one is that it promotes free trade, not imposing any tariffs and quotas. The other option is that it follows a policy of infant-industry protection, allowing the domestic production of automobiles to be sheltered by tariffs on imports. Consider evaluating this policy over 2 time periods. In period 1, there is "learning-by-doing", so the marginal cost decreases in period 2. The extent of reduction in MC in period 2 depends on the production of period 1 (and the amount of reduction under option 1 and option 2 are shown in the graphs below-S1 is the supply curve in time period 1, S2 is the supply curve in time period Option 1: Free Trade Price (S) 60 25 20 15 O 10 20 70 Quantity (thousand) Price (S) 60 30 25 20 0 Option 2: Tariff 10 20 38 60 70 Quantity (thousand) a) Calculate consumer surplus and producer surplus of free trade (option 1) in time period 1. b) Assume that the government imposes a tariff (option 2) in period 1. Calculate consumer surplus, producer surplus, government revenue and deadweight loss associated with this policy. If there is a DWL relative to free trade, then why does the government do this? c) Now let us see what happens in time period 2 under the 2 options. Calculate the consumer surplus and producer surplus under both policy options in period 2 (assume no tariffs in period 2). d) Add the total surplus in both time periods under both policy options. Which one is higher? Do you now see why a social planner might be willing to suffer a DWL (deadweight loss) in period 1 under option 2? Explain this in words. e) In this model, the optimal tariff in period 2 is always zero. Why? f) In practice, once a tariff was imposed in period 1, it was difficult to remove in later periods. Explain why this may be the case using the discussion in class about concentrated costs and diffuse benefits of free trade.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a To calculate consumer surplus under free trade option 1 in time period 1 we need to find the area between the demand curve D and the supply curve S1 up to the equilibrium quantity Consumer Surplus 1...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


