

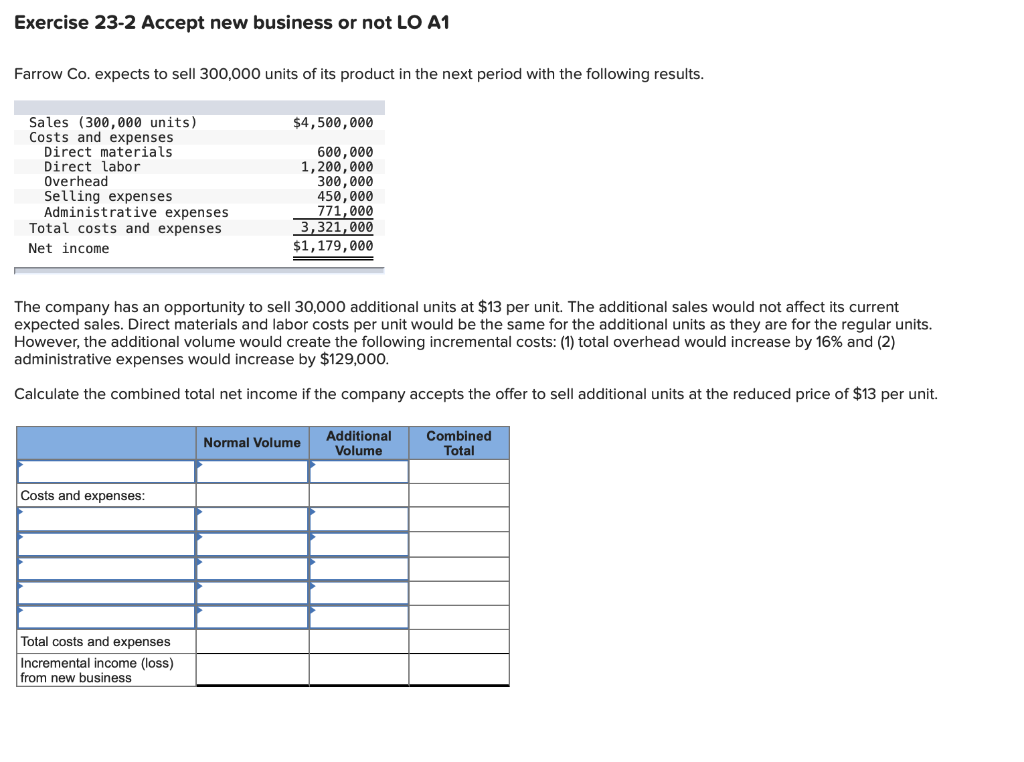
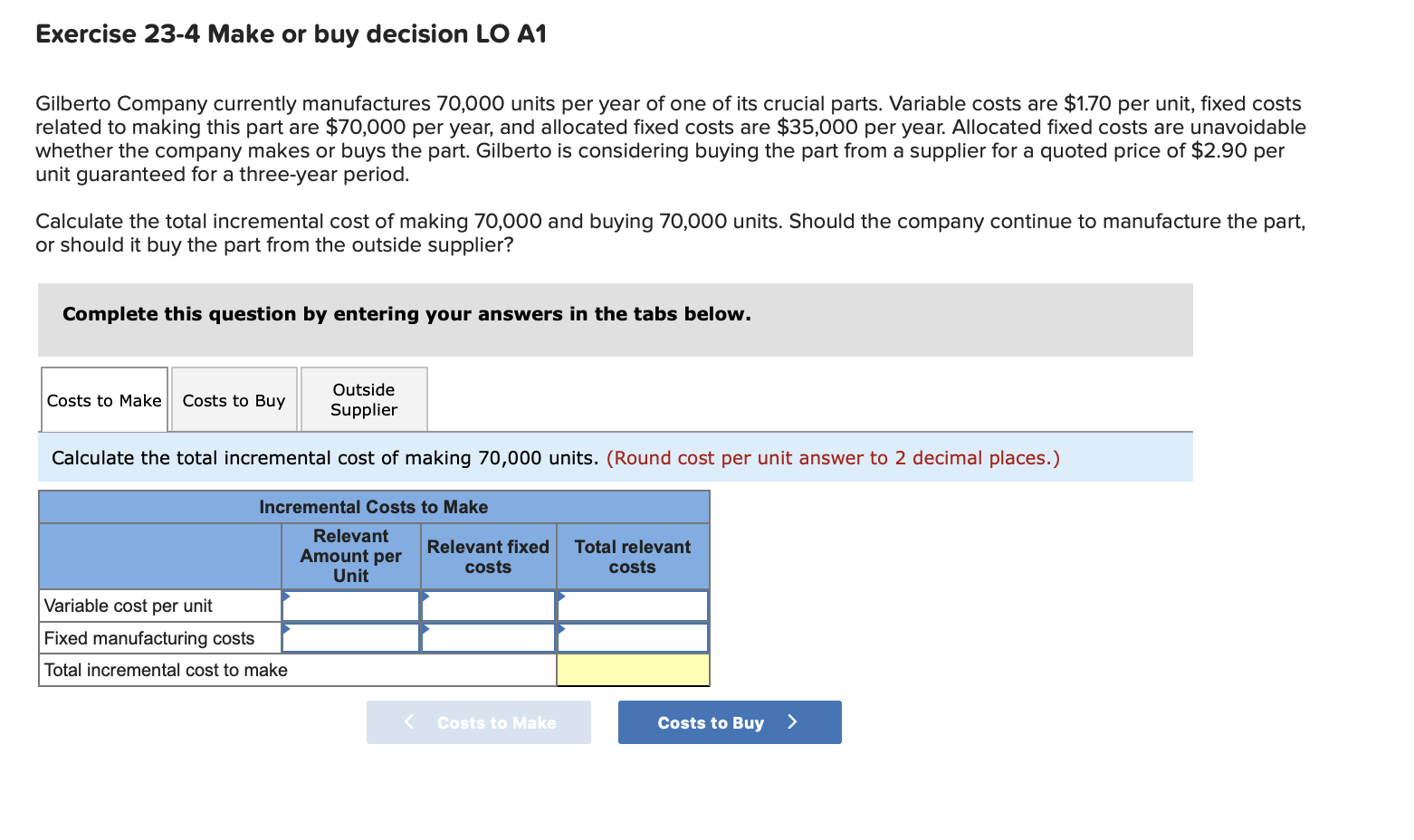
QS 23-16 Product pricing LO P1 Garcia Co. sells snowboards. Each snowboard requires direct materials of $101, direct labor of $31, and variable overhead of $46. The company expects fixed overhead costs of $637,000 and fixed selling and administrative costs of $171,000 for the next year. It expects to produce and sell 10,100 snowboards in the next year. What will be the selling price per unit if Garcia uses a markup of 15% of total cost? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price Per Unit QS 23-17 Product pricing LO P1 Jose Ruiz wants to start a company that makes snowboards. Competitors sell a similar snowboard for $370 each. Jose believes he can produce a snowboard for a total cost of $290 per unit, and he plans a 30% markup on his total cost. 1-a. Compute Jose's planned selling price. Selling price Per Unit 1-b. Can Jose compete with his planned selling price? Yes Exercise 23-2 Accept new business or not LO A1 Farrow Co. expects to sell 300,000 units of its product in the next period with the following results. $4,500,000 Sales (300,000 units) Costs and expenses Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Selling expenses Administrative expenses Total costs and expenses Net income 600,000 1,200,000 300,000 450,000 771,000 3,321,000 $1,179,000 The company has an opportunity to sell 30,000 additional units at $13 per unit. The additional sales would not affect its current expected sales. Direct materials and labor costs per unit would be the same for the additional units as they are for the regular units. However, the additional volume would create the following incremental costs: (1) total overhead would increase by 16% and (2) administrative expenses would increase by $129,000. Calculate the combined total net income if the company accepts the offer to sell additional units at the reduced price of $13 per unit. Normal Volume Additional Volume Combined Total Costs and expenses: Total costs and expenses Incremental income (loss) from new business Exercise 23-4 Make or buy decision LO A1 Gilberto Company currently manufactures 70,000 units per year of one of its crucial parts. Variable costs are $1.70 per unit, fixed costs related to making this part are $70,000 per year, and allocated fixed costs are $35,000 per year. Allocated fixed costs are unavoidable whether the company makes or buys the part. Gilberto is considering buying the part from a supplier for a quoted price of $2.90 per unit guaranteed for a three-year period. Calculate the total incremental cost of making 70,000 and buying 70,000 units. Should the company continue to manufacture the part, or should it buy the part from the outside supplier? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Costs to Make Costs to Buy Outside Supplier Calculate the total incremental cost of making 70,000 units. (Round cost per unit answer to 2 decimal places.) Total relevant costs Incremental Costs to Make Relevant Relevant fixed Amount per costs Unit Variable cost per unit Fixed manufacturing costs Total incremental cost to make QS 23-16 Product pricing LO P1 Garcia Co. sells snowboards. Each snowboard requires direct materials of $101, direct labor of $31, and variable overhead of $46. The company expects fixed overhead costs of $637,000 and fixed selling and administrative costs of $171,000 for the next year. It expects to produce and sell 10,100 snowboards in the next year. What will be the selling price per unit if Garcia uses a markup of 15% of total cost? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price Per Unit QS 23-17 Product pricing LO P1 Jose Ruiz wants to start a company that makes snowboards. Competitors sell a similar snowboard for $370 each. Jose believes he can produce a snowboard for a total cost of $290 per unit, and he plans a 30% markup on his total cost. 1-a. Compute Jose's planned selling price. Selling price Per Unit 1-b. Can Jose compete with his planned selling price? Yes Exercise 23-2 Accept new business or not LO A1 Farrow Co. expects to sell 300,000 units of its product in the next period with the following results. $4,500,000 Sales (300,000 units) Costs and expenses Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Selling expenses Administrative expenses Total costs and expenses Net income 600,000 1,200,000 300,000 450,000 771,000 3,321,000 $1,179,000 The company has an opportunity to sell 30,000 additional units at $13 per unit. The additional sales would not affect its current expected sales. Direct materials and labor costs per unit would be the same for the additional units as they are for the regular units. However, the additional volume would create the following incremental costs: (1) total overhead would increase by 16% and (2) administrative expenses would increase by $129,000. Calculate the combined total net income if the company accepts the offer to sell additional units at the reduced price of $13 per unit. Normal Volume Additional Volume Combined Total Costs and expenses: Total costs and expenses Incremental income (loss) from new business Exercise 23-4 Make or buy decision LO A1 Gilberto Company currently manufactures 70,000 units per year of one of its crucial parts. Variable costs are $1.70 per unit, fixed costs related to making this part are $70,000 per year, and allocated fixed costs are $35,000 per year. Allocated fixed costs are unavoidable whether the company makes or buys the part. Gilberto is considering buying the part from a supplier for a quoted price of $2.90 per unit guaranteed for a three-year period. Calculate the total incremental cost of making 70,000 and buying 70,000 units. Should the company continue to manufacture the part, or should it buy the part from the outside supplier? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Costs to Make Costs to Buy Outside Supplier Calculate the total incremental cost of making 70,000 units. (Round cost per unit answer to 2 decimal places.) Total relevant costs Incremental Costs to Make Relevant Relevant fixed Amount per costs Unit Variable cost per unit Fixed manufacturing costs Total incremental cost to make










