Question: Ques write a program in the language c which meets all the requirements below. 1. Function definitions, declarations and header files Guide C is a
Ques write a program in the language c which meets all the requirements below.

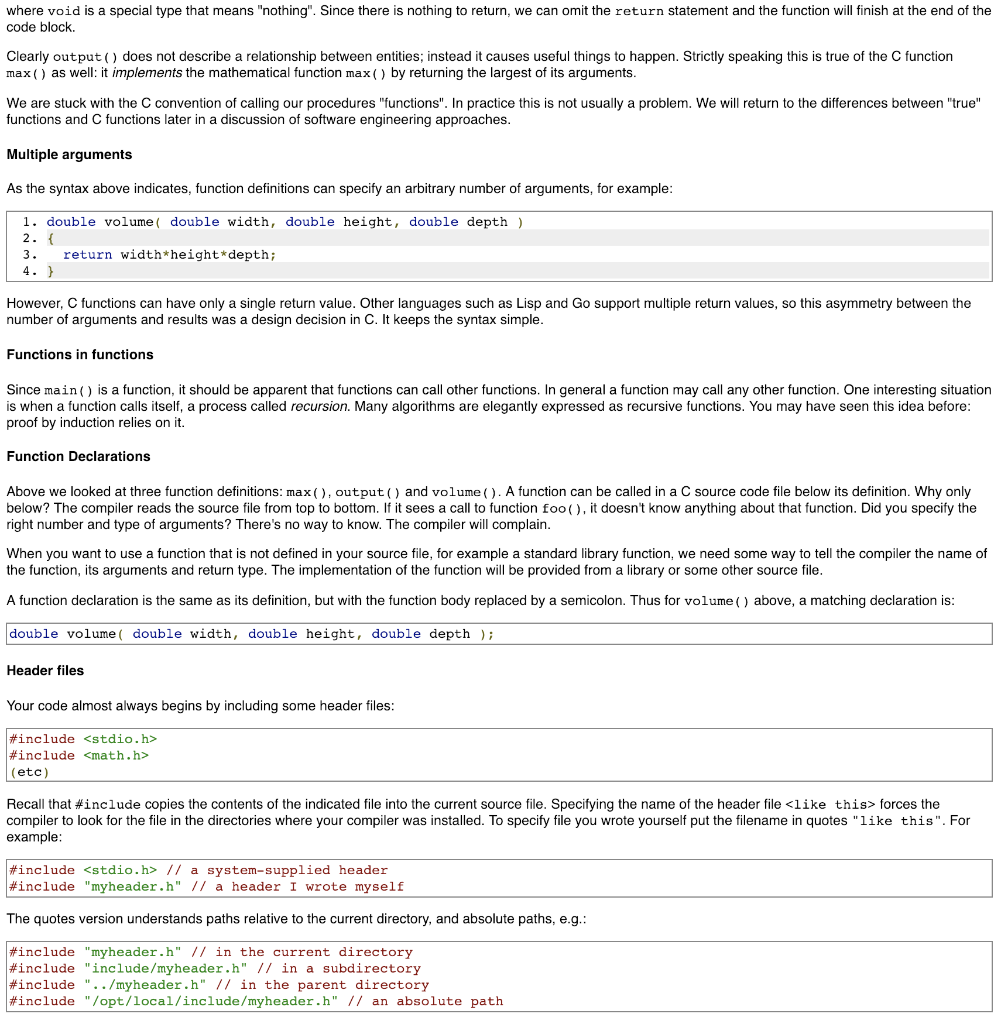
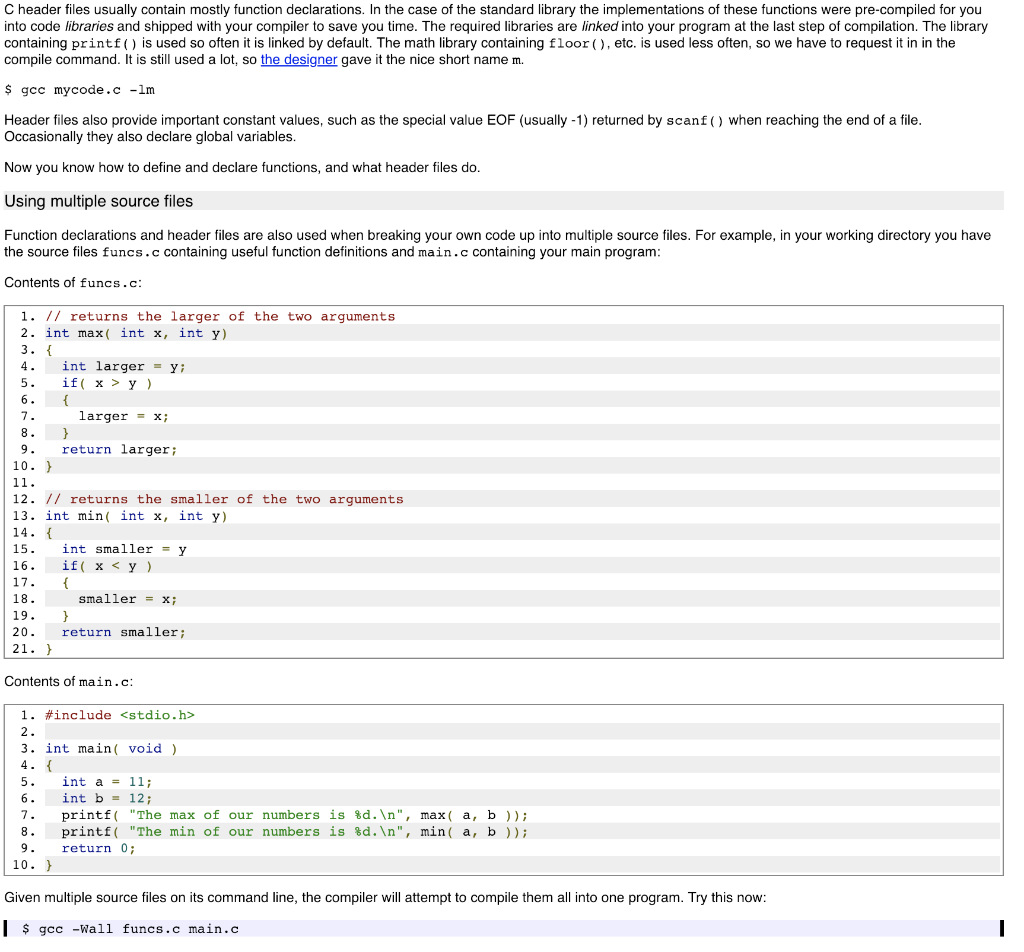
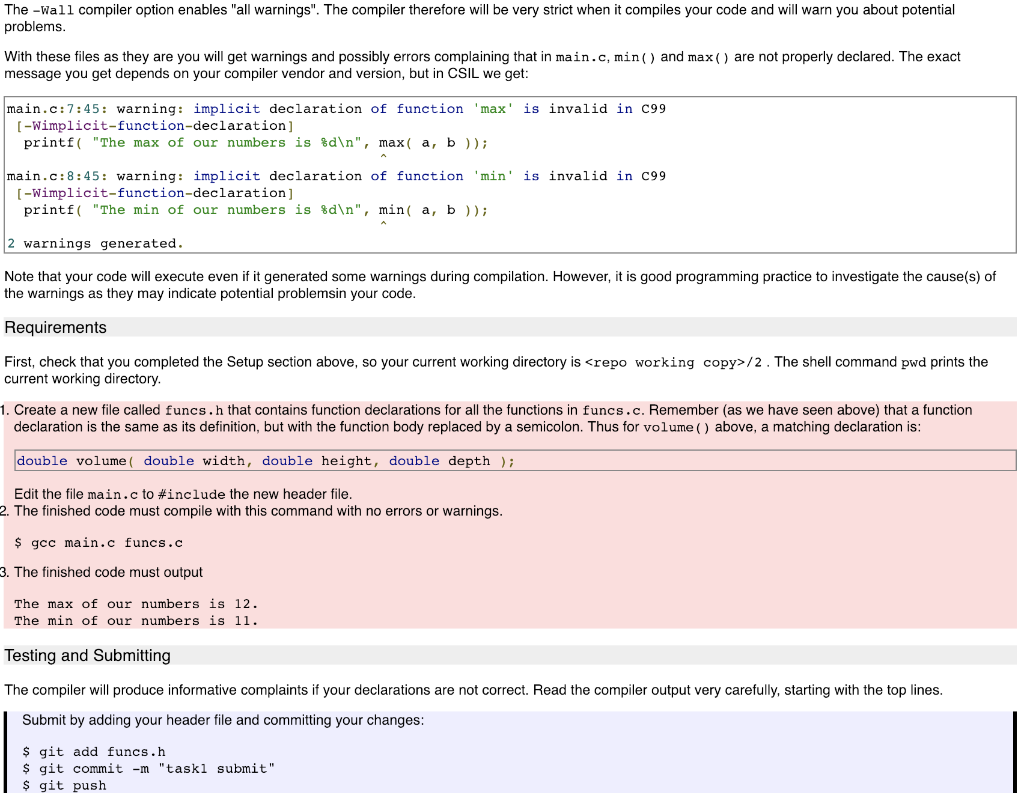
1. Function definitions, declarations and header files Guide C is a structured, procedural programming language, that is, it supports the definition of isolated, self-contained blocks of code that can be re-used as components of larger programs. In C and Python these are called functions, but other languages call them procedures, subroutines, or methods. Given a well-designed function, you can often use it for what it does, and ignore the internal details of how it works. This idea of functional encapsulation makes it feasible for humans to write complex programs by breaking them down into small, more manageable pieces. You have already used several functions provided by the standard library, such as printf and floor, without seeing how they were implemented. One such function is max ( ), which could be implemented and used as follows 1. // returns the larger of the two arguments 2. int max( int x, int y) 4. int larger 5, if( x > y ) Larger X 9. return larger; 10.h 12. int main( void) 13. 14. int a-11; 15. int b = 12; 16. printf( "The max of our numbers is %d ", max ( a, b ); 17. return 0 18. h Reading the first 9 lines of code top-to-bottom, left-to-right, we see Line 1: A comment describing what the following function does. Commenting our code is a good programming style to adopt Lines 2-10 are the function definition, as follows: . The result, or return value of running this function is of type int . The name of the function is max . The function takes two integer arguments called x and y The body of the function, i.e. the code that will execute when the function is called, starts at ( In the body of the function, the keyword return evaluates the expression to it's right which becomes the function's return value, then exits the function Creating functions with only one return statement (only one exit point) is a good programming style to adopt. The body of the function ends at the closing ) . . Having been defined in lines 2 to 10, function max() is called on line 16. The values of integers a and b are assigned to x and y inside max (), the function does its work, and the return value is passed as the second argument to printf() The syntax for C functions is type functionName type arg_namel [, type arg_name2, ...) // code-block function body enclosed by curly braces Note that main() itself is a normal function. The system calls it to start the program The name "function" is a little unfortunate, since these are not the same as mathematical functions. Mathematical functions express relationships, while program functions perform sequences of operations on data. To see the difference, consider the function max() above and the following function output() 1. void output ( double val ) 3. printf( "the value is %.2f ", val ); where void is a special type that means "nothing". Since there is nothing to return, we can omit the return statement and the function will finish at the end of the code block. Clearly output) does not describe a relationship between entities; instead it causes useful things to happen. Strictly speaking this is true of the C function max () as wel: it implements the mathematical function max() by returning the largest of its arguments We are stuck with the C convention of calling our procedures "functions". In practice this is not usually a problem. We will return to the differences between "true" functions and C functions later in a discussion of software engineering approaches Multiple arguments As the syntax above indicates, function definitions can specify an arbitrary number of arguments, for example 1. double volumedouble width, double height, double depth ) 3. return width*height*depth; However, C functions can have only a single return value. Other languages such as Lisp and Go support multiple return values, so this asymmetry between the number of arguments and results was a design decision in C. It keeps the syntax simple Functions in functions Since main) is a function, it should be apparent that functions can call other functions. In general a function may call any other function. One interesting situation is when a function calls itself, a process called recursion. Many algorithms are elegantly expressed as recursive functions. You may have seen this idea before proof by induction relies on it. Function Declarations Above we looked at three function definitions: max (), output( and volume (). A function can be called in a C source code file below its definition. Why only below? The compiler reads the source file from top to bottom. If it sees a call to function foo(), it doesn't know anything about that function. Did you specify the right number and type of arguments? There's no way to know. The compiler will complain When you want to use a function that is not defined in your source file, for example a standard library function, we need some way to tell the compiler the name of the function, its arguments and return type. The implementation of the function will be provided from a library or some other source file A function declaration is the same as its definition, but with the function body replaced by a semicolon. Thus for volume() above, a matching declaration is double volume( double width, double height, double depth); Header files Your code almost always begins by including some header files #include #include (etc)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


