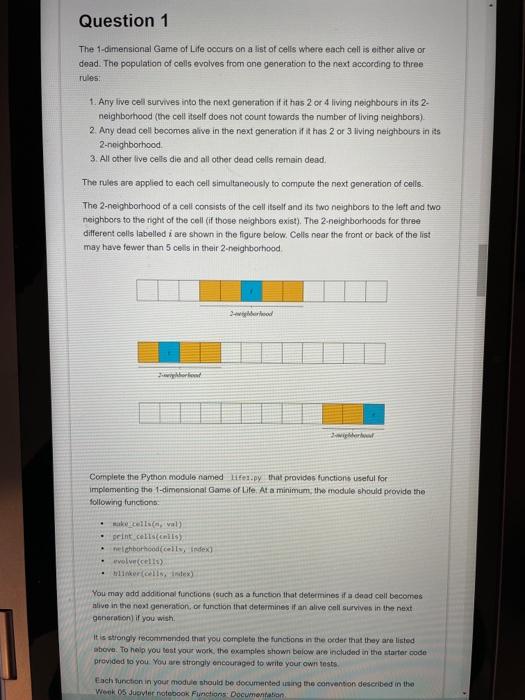
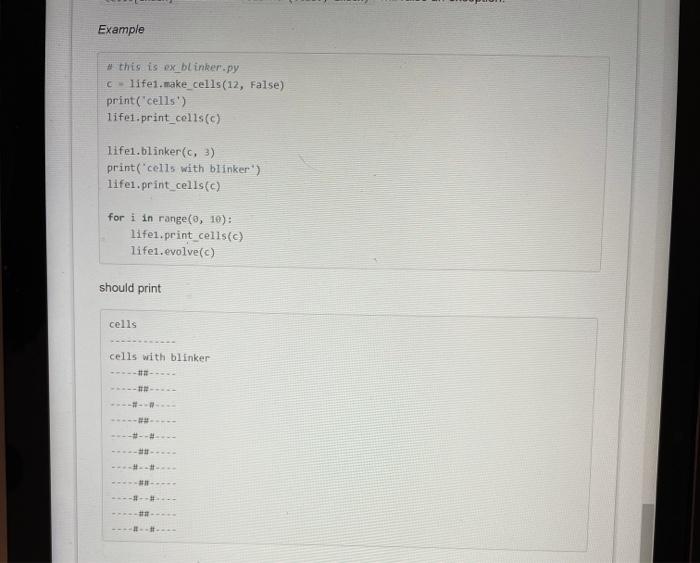
Question 1 The 1-dimensional Game of Life occurs on a list of cells where each coll is either alive or dead. The population of cells evolves from one generation to the next according to three rules: 1. Any live cell survives into the next generation if it has 2 or 4 living neighbours in its 2- neighborhood (the coll itself does not count towards the number of living neighbors) 2. Any dead cell becomes alive in the next generation if it has 2 or 3 living neighbours in its 2-neighborhood 3. All other live cells die and all other dead cells remain dead. The rules are applied to each cell simultaneously to compute the next generation of cells. The 2-neighborhood of a coll consists of the cell itself and its two neighbors to the left and two neighbors to the right of the cell (if those neighbors exist). The 2-neighborhoods for three different colls labelled i are shown in the figure below. Cells near the front or back of the list may have fewer than 5 cells in their 2-neighborhood world Complete the Python module named lifes.py that provides functions useful for implementing the 1-dimensional Game of Life. At a minimum, the module should provide the following functions sukcells, val) print cells alls) nel borhood cells Index evolve cells) koreninex) You may add additional functions (such as a function that determines if a dead cell becomes alive in the next generation, or function that determines if an alive cell survives in the next generation if you wish. It is strongly recommended that you complete the functions in the order that they are listed above. To help you lost your work, the examples shown below are included in the starter code provided to you. You we strongly encouraged to write your own tests Each function in your module should be documented using the convention described in the Week 05 Javier notebook Functions Documentation Each function in your module should be documented using the convention described in the Week 05 Jupyter notebook Functions: Documentation Each function is described below make_cells (note that this function is already implemented for you) make cells.val) Returns a list of length where all of the elements are equal to the boolean value val Raises a valueError if is less than zero Example life cake_cellsis. False) should return the list false false false false Valsel print_cells print_cells(cells) Prints a list cells where all of the elements of cells are equal to either true or False Use for true and for sale include a newline after printing the cells Example this is a printats. Itemske cells False) (0) - true