Question 1 This question is a long free-response question. Show your work for each part of the question. ? A cylindrical object can roll down
Question 1
This question is a long free-response question. Show your work for each part of the question.
?
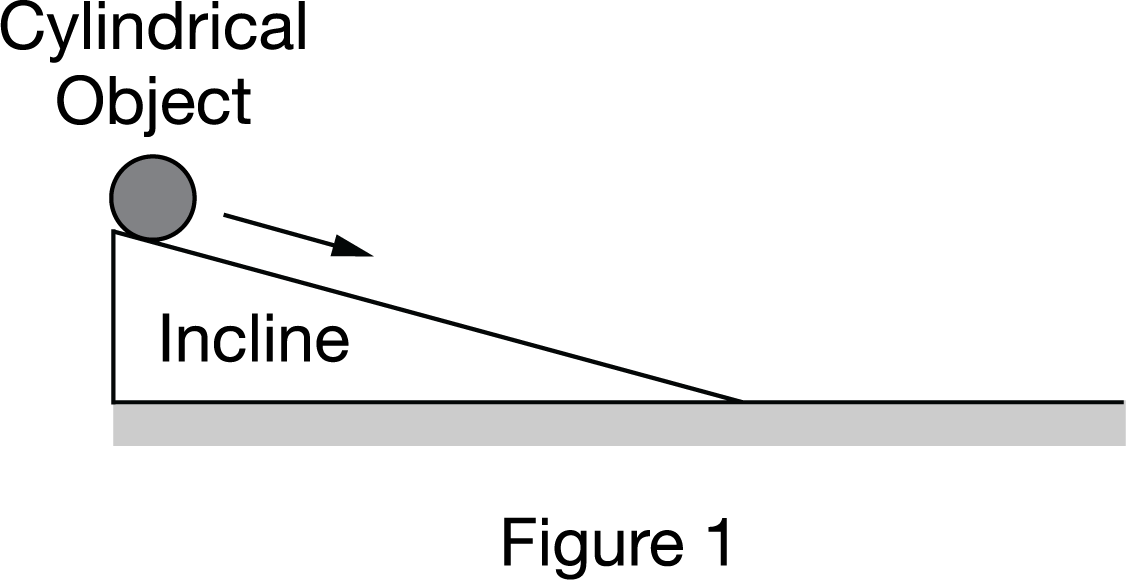

A cylindrical object can roll down an incline, as shown in Figure 1. The incline is slightly less than one meter in length. A group of students wants to determine the acceleration of the object while it is rolling down the incline. The students have access to the following equipment.
? A stopwatch, which can measure time intervals up to 999?s with a precision of 0.01?s
? A clock, which can measure time intervals up to 12?hours with a precision of 1?minute (60?s)
? A meterstick, which can measure lengths up to 1?m with a precision of 1?mm
? A pair of calipers, which can measure lengths up to 10?cm with a precision of 0.05?mm
(a) Assume the object moves with a constant acceleration as it rolls down the incline. Write an equation that includes acceleration and quantities that can be measured or obtained from measurements by using the available equipment in the list.
Question 2(b) Design an experimental procedure the students could use to measure the quantities required to determine the acceleration of the object.
In the table below, list the quantities and associated symbols that would be measured in your experiment and the equipment used to measure them. Also list the equipment that would be used to measure each quantity. You do not need to fill in every row. If you need additional rows, you may add them to the space just below the table.
| Quantity to be Measured | Symbol for Quantity | Equipment for Measurement |
| ? | ? | ? |
| ? | ? | ? |
| ? | ? | ? |
| ? | ? | ? |
| ? | ? | ? |
Describe the overall procedure to be used, referring to the table. Provide enough detail so that another student could replicate the experiment, including any steps necessary to reduce experimental uncertainty. As needed, use the symbols defined in the table and/or include a simple diagram of the setup.
Question 3(c)
i. What quantities could be graphed to yield a straight line that could be used to determine the acceleration of the object? Only indicate quantities that either were measured in part (b) or could be determined from quantities measured in part (b).
?Vertical axis Horizontal axis
ii. How could the graph be used to analyze the data and determine the acceleration?
Upload filesDelete File Mode
Question 4 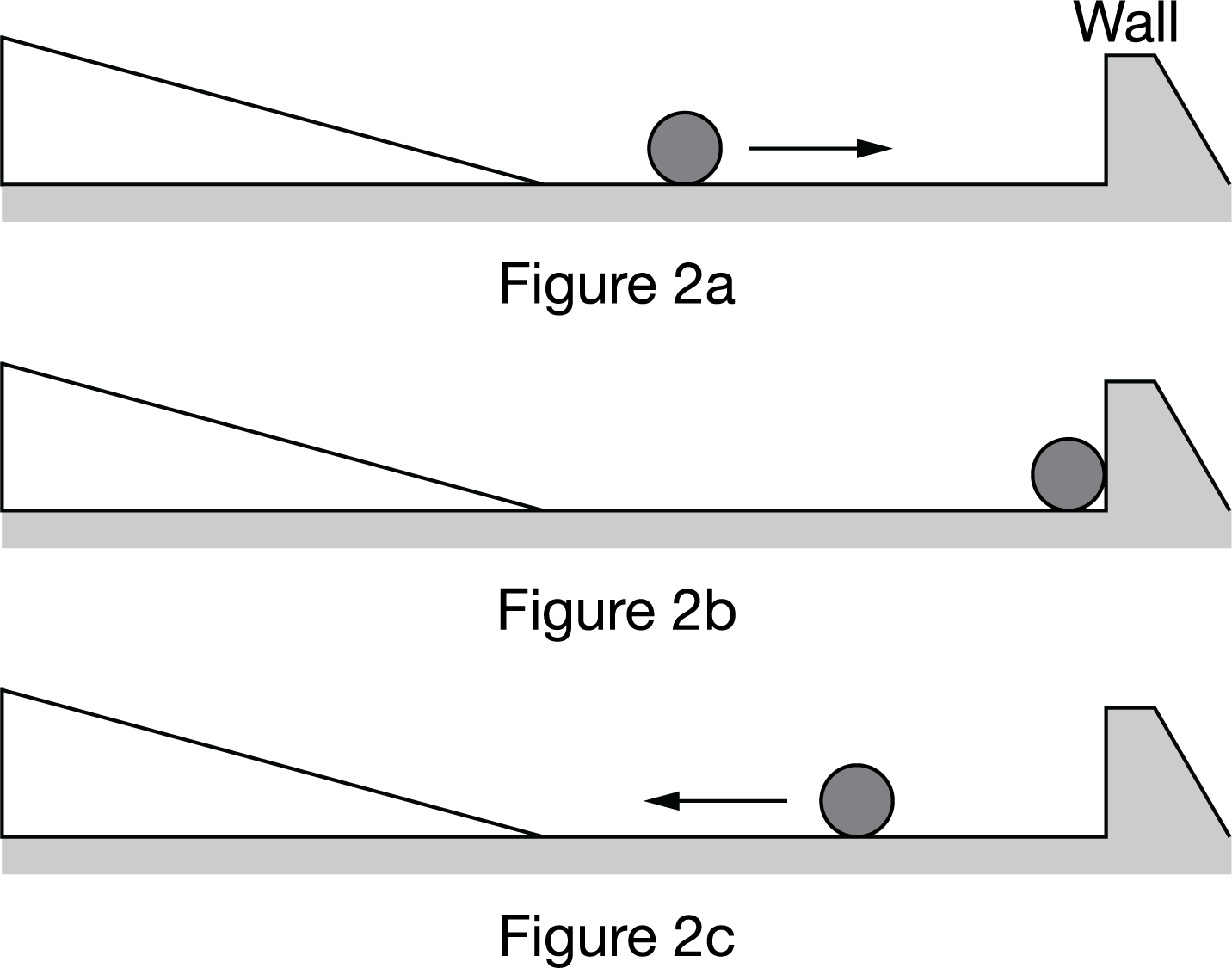
(d) After rolling down the incline, the cylindrical object rolls across a horizontal surface, as shown in Figure 2a . The object then hits a vertical wall (Figure 2b ) and bounces off the wall with the same speed it had before hitting the wall (Figure 2c ). Note that during the bounce the object is in contact with the wall for a time interval that is very small, but not zero.
i. On the dot below, which represents the object during the time it is in contact with the wall, draw an arrow showing the direction of the object?s acceleration during the bounce.
![]()
ii. During the time the object is in contact with the wall, is the magnitude of the acceleration greater than, less than, or the same as it was while it was rolling down the ramp?

Cylindrical Object Incline Figure 1 Figure 2a Figure 2b Figure 2c Wall 15 m/s T 100 m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
This can be answered by considering the Newtons law Fma ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


