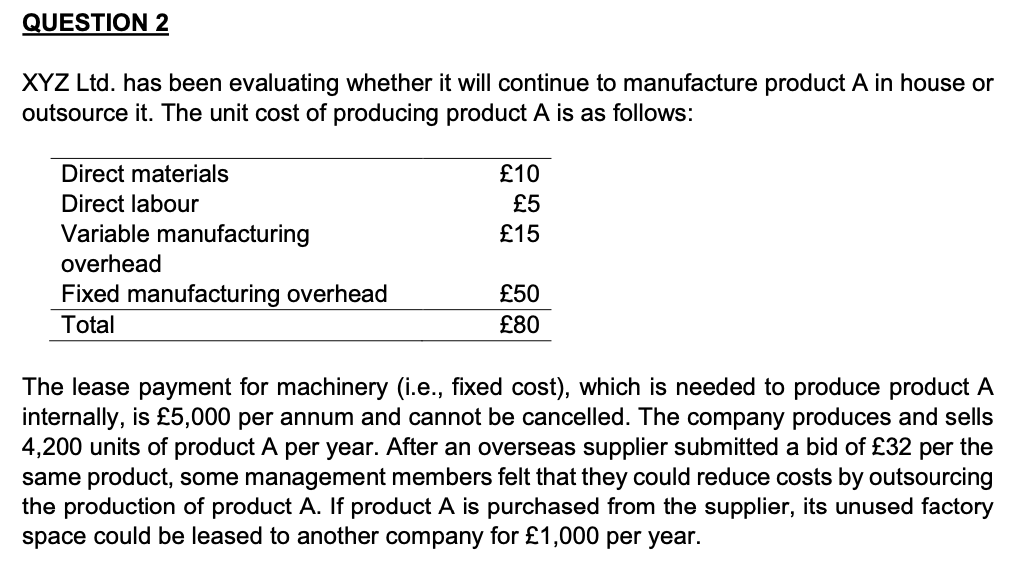


QUESTION 2 XYZ Ltd. has been evaluating whether it will continue to manufacture product A in house or outsource it. The unit cost of producing product A is as follows: 10 5 15 Direct materials Direct labour Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Total 50 80 The lease payment for machinery (i.e., fixed cost), which is needed to produce product A internally, is 5,000 per annum and cannot be cancelled. The company produces and sells 4,200 units of product A per year. After an overseas supplier submitted a bid of 32 per the same product, some management members felt that they could reduce costs by outsourcing the production of product A. If product A is purchased from the supplier, its unused factory space could be leased to another company for 1,000 per year. REQUIRED: Please note: a maximum word count applies to some parts of this question. (a) Define an opportunity cost and discuss whether it is relevant to decision making in general. (3 marks; max 105 words) Explain how the treatment of opportunity costs is different for financial reporting and decision-making purposes. (4 marks; max 140 words) (b) Explain how a sunk cost is different from an opportunity cost, and discuss how the difference affects decision making. Use examples in XYZ Ltd. to support your answer. (8 marks; max 280 words) Explain two attributes of information that are relevant to decision making. (6 marks; max 210 words) (c) Using the information provided above: (i) Determine the maximum amount per unit the company should pay an overseas supplier. (ii) Indicate if the company should make or buy product A based on the total monetary difference between in-house production and outsourcing. (7 marks) (iii) In (c) (ii), assume that the company could eliminate production supervisors with salaries totalling 5,000 if product A is outsourced. Indicate if the company should make or buy product A based on the revised monetary difference of the two options. (4 marks) (iv) In (c) (ii), assume that the company could produce 1,000 units of product B using the machine hours to be released from product A if it is outsourced. Product B can be sold at 100 per unit, and the total variable costs needed to produce it is the same as product A. Indicate if the company should make or buy product A based on the revised monetary difference of the two options. (5 marks) (d) Regarding the results shown in (c), discuss whether your conclusion should be changed if the company does not have any experience of doing business with the overseas supplier in the past. (3 marks; max 105 words) Using examples, explain two qualitative factors that companies should consider when making insourcing or outsourcing decisions based on the cost-volume-profit analysis. (6 marks; max 210 words) (Total marks for question 2: 50 marks) QUESTION 2 XYZ Ltd. has been evaluating whether it will continue to manufacture product A in house or outsource it. The unit cost of producing product A is as follows: 10 5 15 Direct materials Direct labour Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Total 50 80 The lease payment for machinery (i.e., fixed cost), which is needed to produce product A internally, is 5,000 per annum and cannot be cancelled. The company produces and sells 4,200 units of product A per year. After an overseas supplier submitted a bid of 32 per the same product, some management members felt that they could reduce costs by outsourcing the production of product A. If product A is purchased from the supplier, its unused factory space could be leased to another company for 1,000 per year. REQUIRED: Please note: a maximum word count applies to some parts of this question. (a) Define an opportunity cost and discuss whether it is relevant to decision making in general. (3 marks; max 105 words) Explain how the treatment of opportunity costs is different for financial reporting and decision-making purposes. (4 marks; max 140 words) (b) Explain how a sunk cost is different from an opportunity cost, and discuss how the difference affects decision making. Use examples in XYZ Ltd. to support your answer. (8 marks; max 280 words) Explain two attributes of information that are relevant to decision making. (6 marks; max 210 words) (c) Using the information provided above: (i) Determine the maximum amount per unit the company should pay an overseas supplier. (ii) Indicate if the company should make or buy product A based on the total monetary difference between in-house production and outsourcing. (7 marks) (iii) In (c) (ii), assume that the company could eliminate production supervisors with salaries totalling 5,000 if product A is outsourced. Indicate if the company should make or buy product A based on the revised monetary difference of the two options. (4 marks) (iv) In (c) (ii), assume that the company could produce 1,000 units of product B using the machine hours to be released from product A if it is outsourced. Product B can be sold at 100 per unit, and the total variable costs needed to produce it is the same as product A. Indicate if the company should make or buy product A based on the revised monetary difference of the two options. (5 marks) (d) Regarding the results shown in (c), discuss whether your conclusion should be changed if the company does not have any experience of doing business with the overseas supplier in the past. (3 marks; max 105 words) Using examples, explain two qualitative factors that companies should consider when making insourcing or outsourcing decisions based on the cost-volume-profit analysis. (6 marks; max 210 words) (Total marks for question 2: 50 marks)









