Question:
2.4: An oil prospector will drill a succession of holes in a given area to find a productive well. The probability that he is successful on a given trial is 0.3.
2.4.1 Use both the Geometric and Negative Binomial probability distribution functions to calculate the probability that the third hole drilled is the first to yield a productive well? (3)
2.4.2 If the prospector can afford to drill at most ten wells, what is the probability that he will fail to find a productive well? Use the Binomial and Geometric distributions to calculate the probability and appropriately interpret your answer.
2.5 We observe a sequence of independent identical trials with two possible outcomes on
each trial, ?? and ??, and with ??(??) = ??. The number of the trial on which we observe the fifth success, ?? has a negative binomial distribution with parameters ?? = 7 and ??. Suppose that we observe the fifth success on trial number 12.
2.5.1 Find the value of p that maximizes ??(?? = 12).
2.5.2 Generalize the result from part (2.5.1) to find the value of ?? that maximizes
??(?? = ??0) when ?? has a negative binomial distribution with parameters ?? (known) and ??.
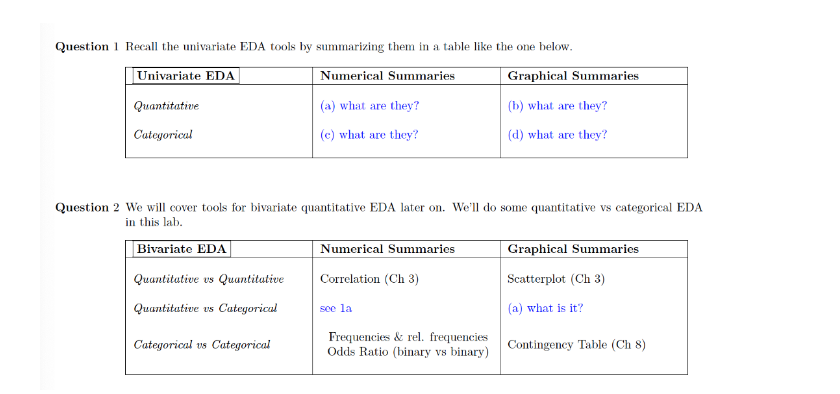
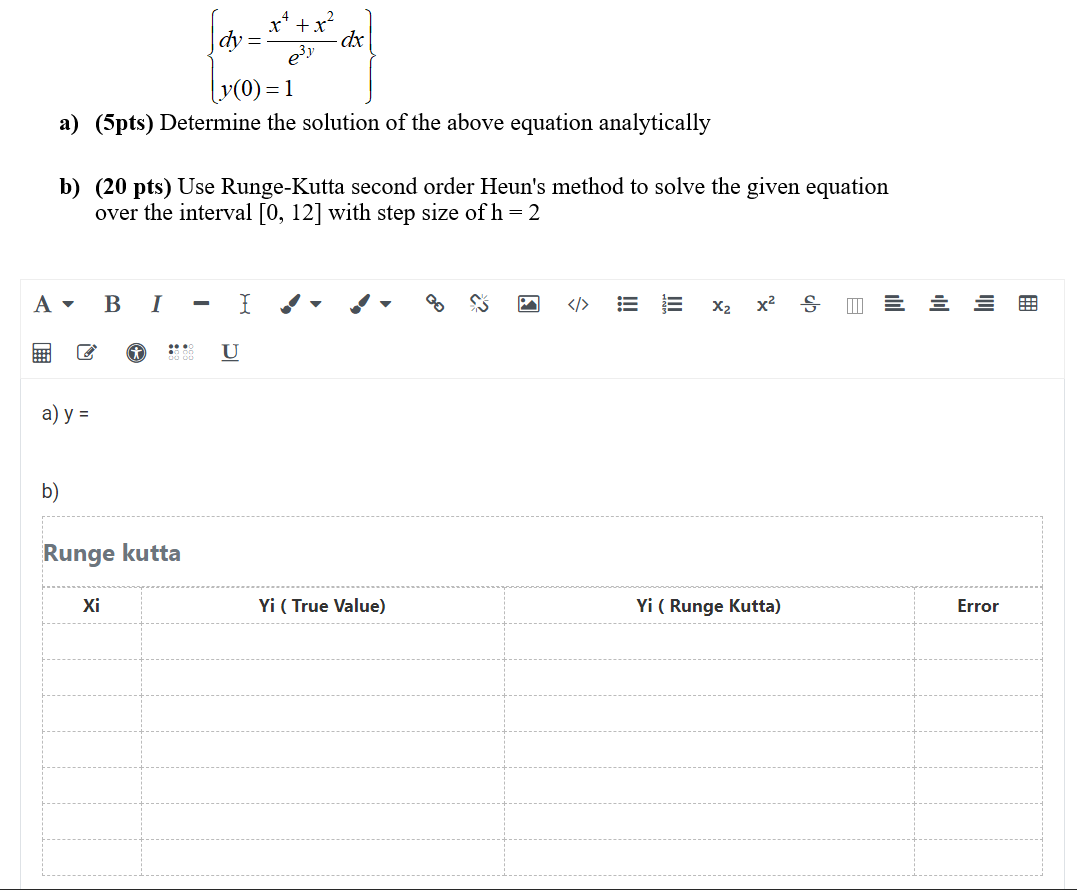
Question 1 Recall the univariate EDA tools by summarizing them in a table like the one below. Univariate EDA Numerical Summaries Graphical Summaries Quantitative (a) what are they? (b) what are they? Categorical (c) what are they? (d) what are they? Question 2 We will cover tools for bivariate quantitative EDA later on. We'll do some quantitative vs categorical EDA in this lab. Bivariate EDA Numerical Summaries Graphical Summaries Quantitative us Quantitative Correlation (Ch 3) Scatterplot (Ch 3) Quantitative us Categorical soe la (a) what is it? Categorical us Categorical Frequencies & rel. frequencies Odds Ratio (binary vs binary) Contingency Table (Ch 8)Consider the following conditional density function extracted from a joint bivariate normal density function. A student thinks that there is a mistake, that the two variables were uncorrelated. It the student is correct, and everything else is correct, what are the correct Hyla-3.5 and f(y | x) ~ NUbe an = 25+0.42 TE (3.5 - 3) = 2.60, Jax an = (1 -0.4')0.4" = 0.36660) Select one: A bivariate normal density with variance 0.4 and mean Q b. A univariate normal density with mean 2.5 and standard deviation 0.4 " A bivariate normal density with mean of X equal 3.5 and mean of Y equal 0.4 d. A univariate normal density with mean 0 and standard deviation 1Explain the differences among the completely randomized design, randomized complete block designs, and factorial design. Choose the correct answer below. A. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines a single factor and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to two fixed factors, factor A and factor B. In a factorial design, the researcher has a factor whose level cannot be fixed. O B. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines many factors and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to two fixed factors, factor A and factor B. In a factorial design, the researcher has a factor whose level cannot be fixed. O C. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines a single factor and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to a factor whose level cannot be fixed. In a factorial design, the researcher has two fixed factors, factor A and factor B. O D. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines a random factor and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to a factor whose level is fixed. In a factorial design, the researcher has two fixed factors, factor A and factor B.dy dx y(0) = 1 a) (5pts) Determine the solution of the above equation analytically b) (20 pts) Use Runge-Kutta second order Heun's method to solve the given equation over the interval [0, 12] with step size of h = 2 3 I X2 x2 S U a) y = b) Runge kutta Xi Yi ( True Value) Yi ( Runge Kutta) Error