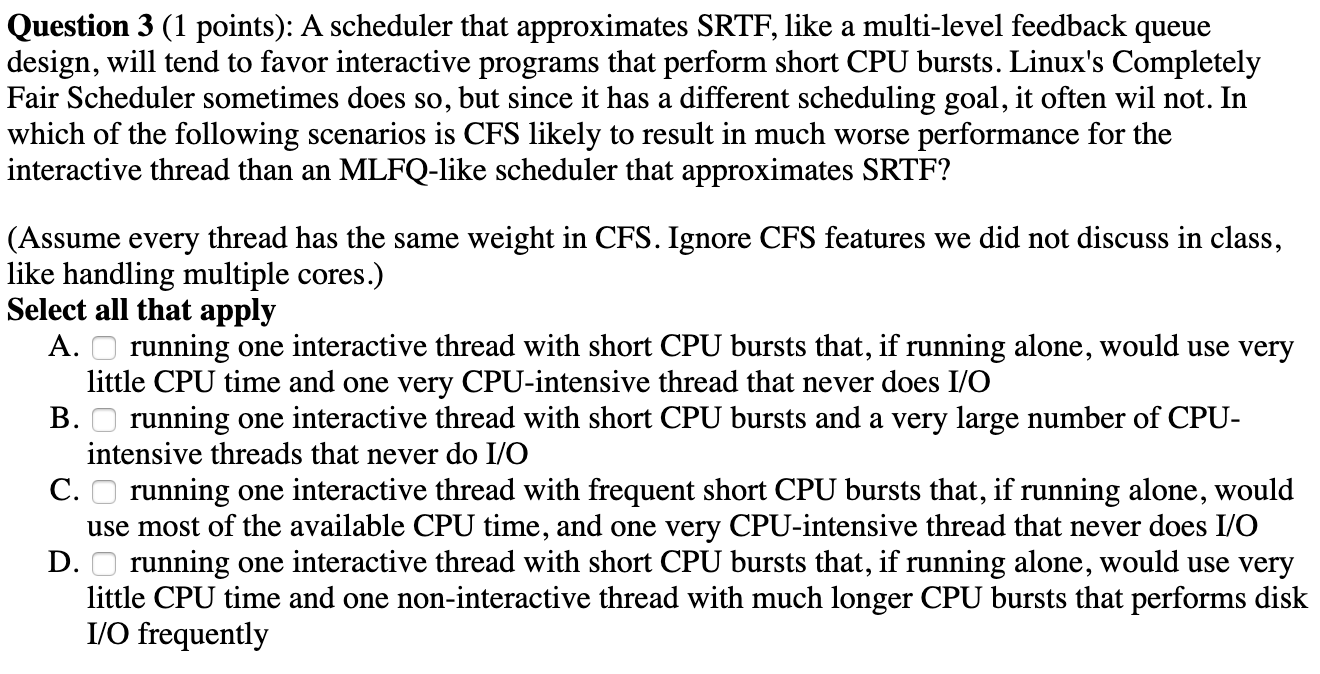
Question 3 (1 points): A scheduler that approximates SRTF, like a multi-level feedback queue design, will tend to favor interactive programs that perform short CPU bursts. Linux's Completely Fair Scheduler sometimes does so, but since it has a different scheduling goal, it often wil not. In which of the following scenarios is CFS likely to result in much worse performance for the interactive thread than an MLFQ-like scheduler that approximates SRTF? (Assume every thread has the same weight in CFS. Ignore CFS features we did not discuss in class, like handling multiple cores.) Select all that apply A. running one interactive thread with short CPU bursts that, if running alone, would use very little CPU time and one very CPU-intensive thread that never does I/O B. running one interactive thread with short CPU bursts and a very large number of CPU- intensive threads that never do I/O C. running one interactive thread with frequent short CPU bursts that, if running alone, would use most of the available CPU time, and one very CPU-intensive thread that never does I/O D. running one interactive thread with short CPU bursts that, if running alone, would use very little CPU time and one non-interactive thread with much longer CPU bursts that performs disk I/O frequently Question 3 (1 points): A scheduler that approximates SRTF, like a multi-level feedback queue design, will tend to favor interactive programs that perform short CPU bursts. Linux's Completely Fair Scheduler sometimes does so, but since it has a different scheduling goal, it often wil not. In which of the following scenarios is CFS likely to result in much worse performance for the interactive thread than an MLFQ-like scheduler that approximates SRTF? (Assume every thread has the same weight in CFS. Ignore CFS features we did not discuss in class, like handling multiple cores.) Select all that apply A. running one interactive thread with short CPU bursts that, if running alone, would use very little CPU time and one very CPU-intensive thread that never does I/O B. running one interactive thread with short CPU bursts and a very large number of CPU- intensive threads that never do I/O C. running one interactive thread with frequent short CPU bursts that, if running alone, would use most of the available CPU time, and one very CPU-intensive thread that never does I/O D. running one interactive thread with short CPU bursts that, if running alone, would use very little CPU time and one non-interactive thread with much longer CPU bursts that performs disk I/O frequently







