Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 3 Charlene Chandler, the general manager of Lee Manufacturing Inc. has become increasingly concerned, over the past six months, about the profitability of
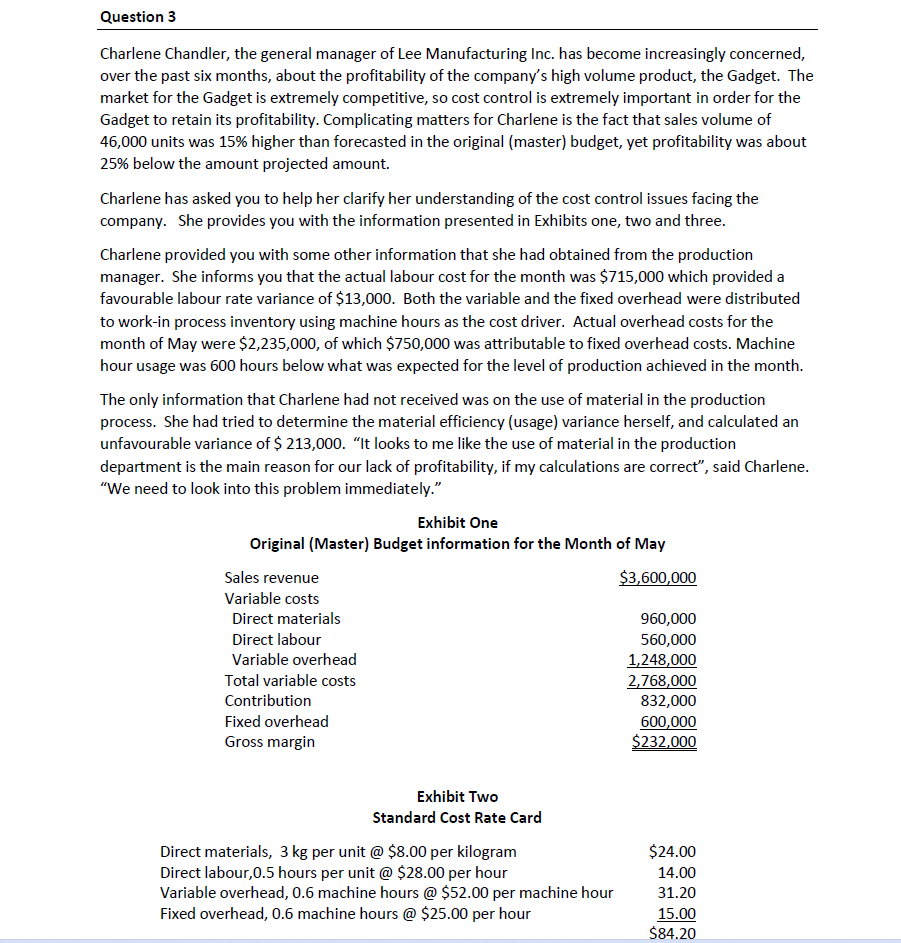

Question 3 Charlene Chandler, the general manager of Lee Manufacturing Inc. has become increasingly concerned, over the past six months, about the profitability of the company's high volume product, the Gadget. The market for the Gadget is extremely competitive, so cost control is extremely important in order for the Gadget to retain its profitability. Complicating matters for Charlene is the fact that sales volume of 46,000 units was 15% higher than forecasted in the original (master) budget, yet profitability was about 25% below the amount projected amount. Charlene has asked you to help her clarify her understanding of the cost control issues facing the company. She provides you with the information presented in Exhibits one, two and three. Charlene provided you with some other information that she had obtained from the production manager. She informs you that the actual labour cost for the month was $715,000 which provided a favourable labour rate variance of $13,000. Both the variable and the fixed overhead were distributed to work-in process inventory using machine hours as the cost driver. Actual overhead costs for the month of May were $2,235,000, of which $750,000 was attributable to fixed overhead costs. Machine hour usage was 600 hours below what was expected for the level of production achieved in the month. The only information that Charlene had not received was on the use of material in the production process. She had tried to determine the material efficiency (usage) variance herself, and calculated an unfavourable variance of $213,000. "It looks to me like the use of material in the production department is the main reason for our lack of profitability, if my calculations are correct", said Charlene. "We need to look into this problem immediately." Exhibit One Original (Master) Budget information for the Month of May Sales revenue Variable costs Direct materials Direct labour Variable overhead Total variable costs Contribution Fixed overhead Gross margin Exhibit Two $3,600,000 960,000 560,000 1,248,000 2,768,000 832,000 600,000 $232,000 Standard Cost Rate Card Direct materials, 3 kg per unit @ $8.00 per kilogram $24.00 Direct labour,0.5 hours per unit @ $28.00 per hour 14.00 Variable overhead, 0.6 machine hours @ $52.00 per machine hour 31.20 Fixed overhead, 0.6 machine hours @ $25.00 per hour 15.00 $84.20 Exhibit Three Information for May Required: Raw materials inventory, May 1 Raw materials inventory, May 31 Material purchased in May Actual cost of the material purchases Units produced in May as a % of original budget $0.00 $24,000 150,000 kg. $1,260,000 115% 1. What volume of production was expected to be produced and sold in the month of May, based on the original master budget? 2. What was the denominator level of activity that was used to determine the standard cost per machine hour for the fixed overhead? 3. Calculate the following variances: a. Labour rate variance b. Labour efficiency variance 4. Calculate the following variances: a. Variable overhead rate (spending) variance b. Variable overhead efficiency variance 5. Calculate the following variances: a. Fixed overhead rate (spending) variance b. Production volume variance 6. Calculate the material price variance 7. Charlene Chandler calculated the material efficiency (usage) variance. Do you agree with her calculation? Explain why. If you do not agree with her calculation, re-calculate the variance and explain why Charlene's calculation was not correct.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


