Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 4 [20 marks A fluid is drained by gravity from the bottom of a tank to another tank below. The depth of the liquid
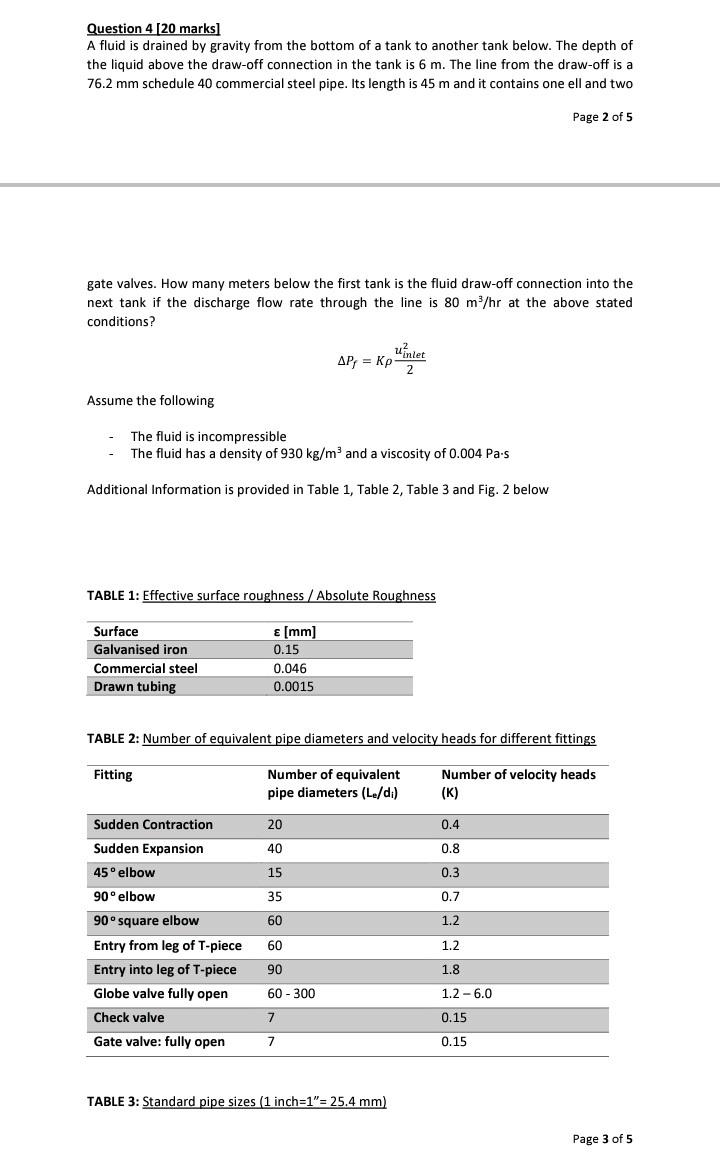
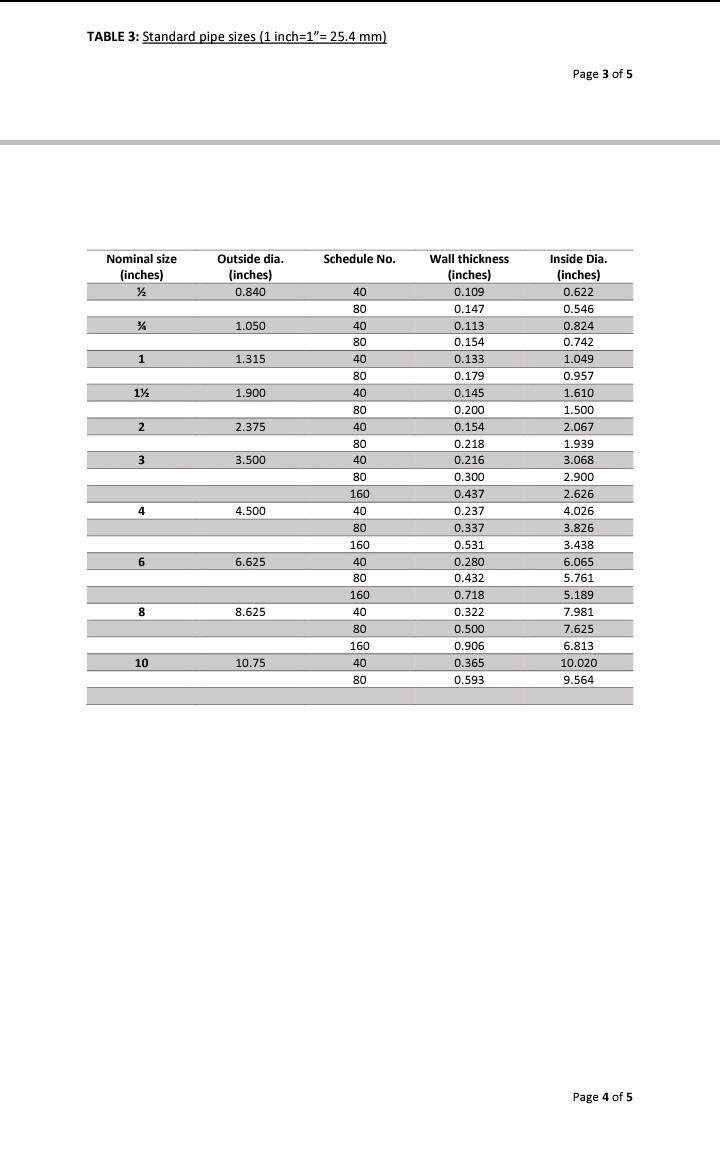
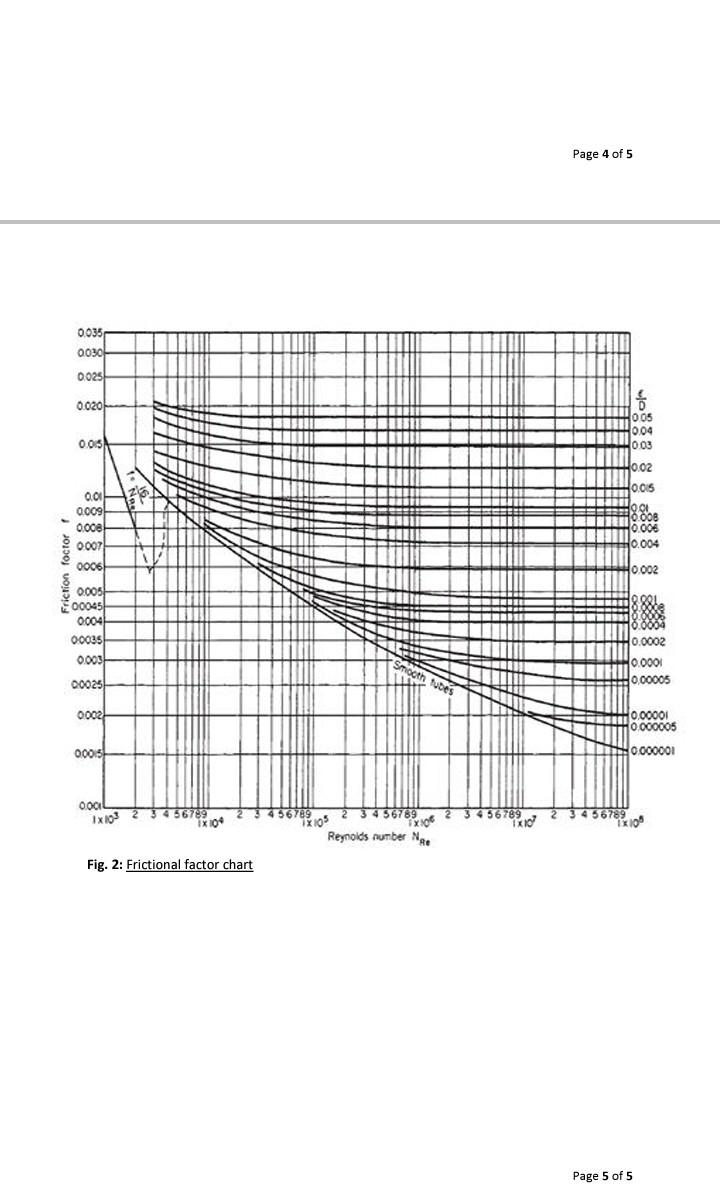
Question 4 [20 marks A fluid is drained by gravity from the bottom of a tank to another tank below. The depth of the liquid above the draw-off connection in the tank is 6 m. The line from the draw-off is a 76.2 mm schedule 40 commercial steel pipe. Its length is 45 m and it contains one ell and two Page 2 of 5 gate valves. How many meters below the first tank is the fluid draw-off connection into the next tank if the discharge flow rate through the line is 80 m/hr at the above stated conditions? u? inlet AP, = Kp 2 Assume the following The fluid is incompressible The fluid has a density of 930 kg/m and a viscosity of 0.004 Pa.s Additional Information is provided in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Fig. 2 below TABLE 1: Effective surface roughness / Absolute Roughness Surface Galvanised iron Commercial steel Drawn tubing E [mm] 0.15 0.046 0.0015 TABLE 2: Number of equivalent pipe diameters and velocity heads for different fittings Fitting Number of equivalent pipe diameters (L/di) Number of velocity heads (K) 20 0.4 40 0.8 0.3 15 35 0.7 60 1.2 Sudden Contraction Sudden Expansion 45 elbow 90 elbow 90 square elbow Entry from leg of T-piece Entry into leg of T-piece - Globe valve fully open Check valve Gate valve: fully open 60 1.2 1.8 90 60 - 300 1.2-6.0 7 0.15 7 0.15 TABLE 3: Standard pipe sizes (1 inch=1"= 25.4 mm) Page 3 of 5 TABLE 3: Standard pipe sizes (1 inch=1"= 25.4 mm) Page 3 of 5 Schedule No. Nominal size (inches) Outside dia. (inches) 0.840 40 80 1.050 1 1 1.315 40 80 40 80 40 80 1x 1.900 2 2 2.375 40 3 3 3.500 80 40 80 160 Wall thickness (inches) 0.109 0.147 0.113 0.154 0.133 0.179 0.145 0.200 0.154 0.218 0.216 0.300 0.437 0.237 0.337 0.531 0.280 0.432 0.718 0.322 0.500 0.906 0.365 0.593 Inside Dia. (inches) 0.622 0.546 0.824 0.742 1.049 0.957 1.610 1.500 2.067 1.939 3.068 2.900 2.626 4.026 3.826 3.438 6.065 5.761 5.189 7.981 7.625 6.813 10.020 9.564 4 4.500 6 6.625 40 80 160 40 80 160 40 8 8 8.625 80 160 40 80 10 10.75 Page 4 of 5 Page 4 of 5 0.035 0030 0025 0.020 005 10.04 0.03 OOSN A 0.01 38 0.009 10.02 40.015 OOL 40.00 0.004 H0.002 0.000 0007 0006 Friction foctor 0005 00045 0004 00035 0.003H Smooth tubes 0.0002 0.0001 Po 00005 00025 0002 H0.00001 Ho 000005 0.000001 oooist 0004 1 x103 2 34 56789 1x104 56789 56789 IKIO 3456789 2 3 4 56789 TX105 TXIO Reynolds number Nae Txion Fig. 2: Frictional factor chart Page 5 of 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


