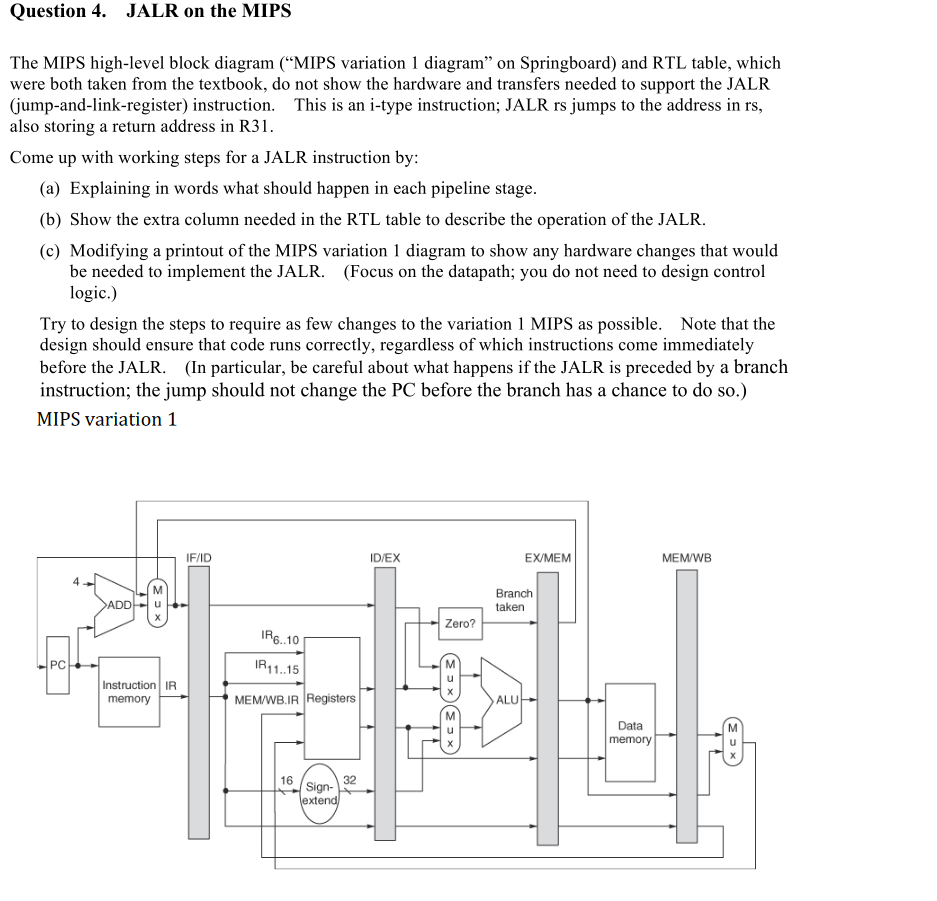
Question 4. JALR on the MIPS The MIPS high-level block diagram ("MIPS variation 1 diagram" on Springboard) and RTL table, which were both taken from the textbook, do not show the hardware and transfers needed to support the JALR (jump-and-link-register) instruction. This is an i-type instruction; JALR rs jumps to the address in rs, also storing a return address in R31 Come up with working steps for a JALR instruction by (a) Explaining in words what should happen in each pipeline stage (b) Show the extra column needed in the RTL table to describe the operation of the JALR. (c) Modifying a printout of the MIPS variation 1 diagram to show any hardware changes that would be needed to implement the JALR. (Focus on the datapath; you do not need to design control logic.) Try to design the steps to require as few changes to the variation 1 MIPS as possible. Note that the design should ensure that code runs correctly, regardless of which instructions come immediately before the JALR. (In particular, be careful about what happens if the JALR is preceded by a branch instruction; the jump should not change the PC before the branch has a chance to do so.) MIPS variation 1 IF/ID IDIEX EXMEM ME/WE Branch Zero? R6..10 PC Instruction IR MEM/WB.IR Registers ALU Data 16 sign Question 4. JALR on the MIPS The MIPS high-level block diagram ("MIPS variation 1 diagram" on Springboard) and RTL table, which were both taken from the textbook, do not show the hardware and transfers needed to support the JALR (jump-and-link-register) instruction. This is an i-type instruction; JALR rs jumps to the address in rs, also storing a return address in R31 Come up with working steps for a JALR instruction by (a) Explaining in words what should happen in each pipeline stage (b) Show the extra column needed in the RTL table to describe the operation of the JALR. (c) Modifying a printout of the MIPS variation 1 diagram to show any hardware changes that would be needed to implement the JALR. (Focus on the datapath; you do not need to design control logic.) Try to design the steps to require as few changes to the variation 1 MIPS as possible. Note that the design should ensure that code runs correctly, regardless of which instructions come immediately before the JALR. (In particular, be careful about what happens if the JALR is preceded by a branch instruction; the jump should not change the PC before the branch has a chance to do so.) MIPS variation 1 IF/ID IDIEX EXMEM ME/WE Branch Zero? R6..10 PC Instruction IR MEM/WB.IR Registers ALU Data 16 sign







