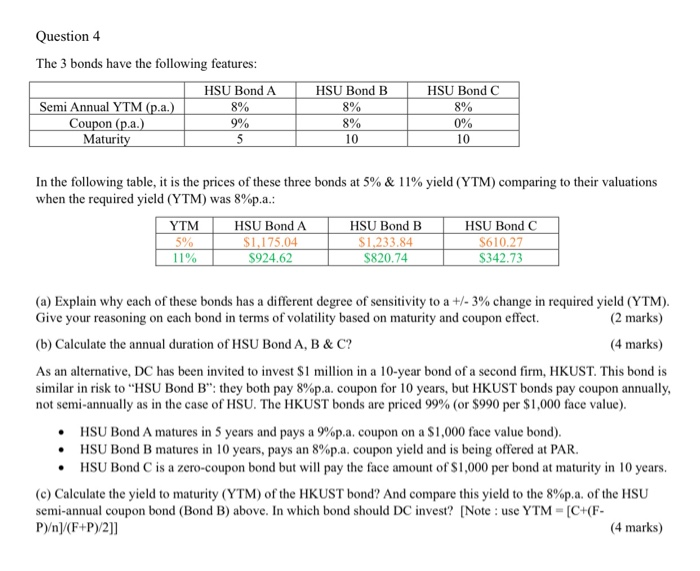
Question 4 The 3 bonds have the following features: HSU Bond A Semi Annual YTM (p.a.) 8% Coupon (p.a.) 9% Maturity HSU Bond B 8% 8% HSU Bond C 8% 0% 10 10 In the following table, it is the prices of these three bonds at 5% & 11% yield (YTM) comparing to their valuations when the required yield (YTM) was 8%p.a.: YTM 5% 11% HSU Bond A USURA $1,175.04 S924.62 HSU Bond B $1,233.84 S820.74 H SU Bond C S610.27 $342.73 (a) Explain why each of these bonds has a different degree of sensitivity to a +/- 3% change in required yield (YTM). Give your reasoning on each bond in terms of volatility based on maturity and coupon effect. (2 marks) (b) Calculate the annual duration of HSU Bond A, B & C? (4 marks) As an alternative, DC has been invited to invest $1 million in a 10-year bond of a second firm, HKUST. This bond is similar in risk to "HSU Bond B": they both pay 8%p.a. coupon for 10 years, but HKUST bonds pay coupon annually, not semi-annually as in the case of HSU. The HKUST bonds are priced 99% (or $990 per $1,000 face value). HSU Bond A matures in 5 years and pays a 9%p.a. coupon on a $1,000 face value bond). HSU Bond B matures in 10 years, pays an 8%p.a. coupon yield and is being offered at PAR. HSU Bond C is a zero-coupon bond but will pay the face amount of $1,000 per bond at maturity in 10 years. (c) Calculate the yield to maturity (YTM) of the HKUST bond? And compare this yield to the 8%p.a. of the HSU semi-annual coupon bond (Bond B) above. In which bond should DC invest? [Note : use YTM - (C+(F- P)]/(F+P)/2]] (4 marks) Question 4 The 3 bonds have the following features: HSU Bond A Semi Annual YTM (p.a.) 8% Coupon (p.a.) 9% Maturity HSU Bond B 8% 8% HSU Bond C 8% 0% 10 10 In the following table, it is the prices of these three bonds at 5% & 11% yield (YTM) comparing to their valuations when the required yield (YTM) was 8%p.a.: YTM 5% 11% HSU Bond A USURA $1,175.04 S924.62 HSU Bond B $1,233.84 S820.74 H SU Bond C S610.27 $342.73 (a) Explain why each of these bonds has a different degree of sensitivity to a +/- 3% change in required yield (YTM). Give your reasoning on each bond in terms of volatility based on maturity and coupon effect. (2 marks) (b) Calculate the annual duration of HSU Bond A, B & C? (4 marks) As an alternative, DC has been invited to invest $1 million in a 10-year bond of a second firm, HKUST. This bond is similar in risk to "HSU Bond B": they both pay 8%p.a. coupon for 10 years, but HKUST bonds pay coupon annually, not semi-annually as in the case of HSU. The HKUST bonds are priced 99% (or $990 per $1,000 face value). HSU Bond A matures in 5 years and pays a 9%p.a. coupon on a $1,000 face value bond). HSU Bond B matures in 10 years, pays an 8%p.a. coupon yield and is being offered at PAR. HSU Bond C is a zero-coupon bond but will pay the face amount of $1,000 per bond at maturity in 10 years. (c) Calculate the yield to maturity (YTM) of the HKUST bond? And compare this yield to the 8%p.a. of the HSU semi-annual coupon bond (Bond B) above. In which bond should DC invest? [Note : use YTM - (C+(F- P)]/(F+P)/2]] (4 marks)