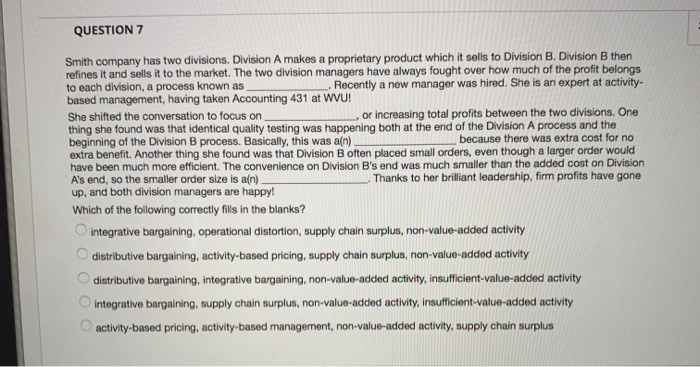
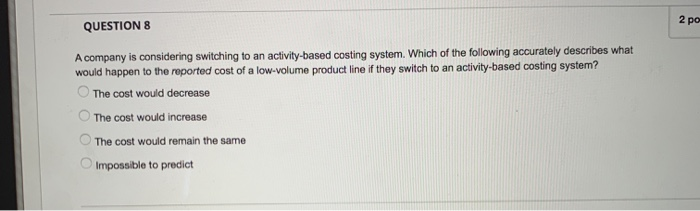
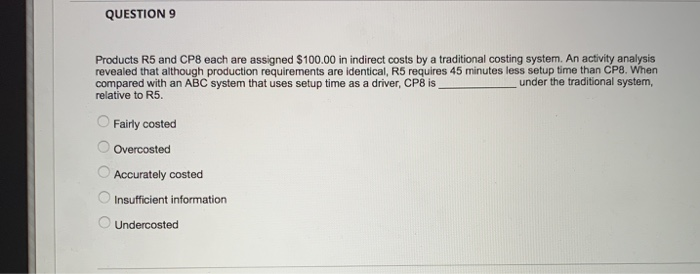
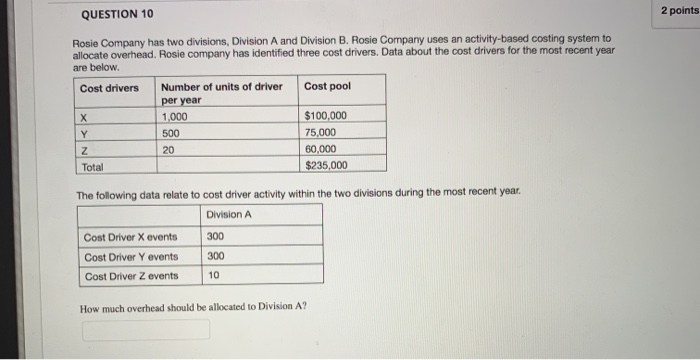
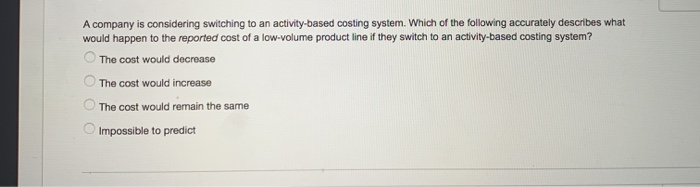
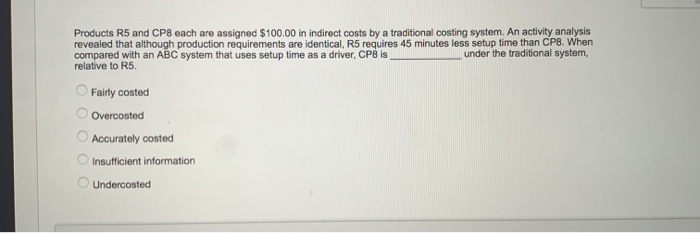
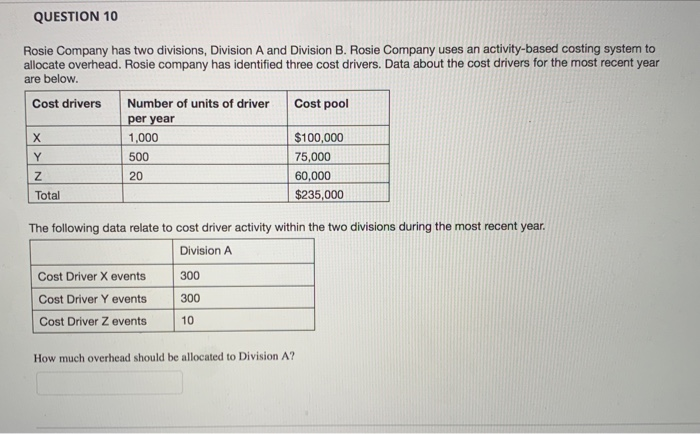
QUESTION 7 Smith company has two divisions. Division A makes a proprietary product which it sells to Division B. Division B then refines it and sells it to the market. The two division managers have always fought over how much of the profit belongs to each division, a process known as based management, having taken Accounting 431 at WVU! She shifted the conversation to focus on thing she found was that identical quality testing was happening both at the end of the Division A process and the beginning of the Division B process. Basically, this was a(n) extra benefit. Another thing she found was that Division B often placed small orders, even though a larger order would have been much more efficient. The convenience on Division B's end was much smaller than the added cost on Division A's end, so the smaller order size is a(n) up, and both division managers are happy! Recently a new manager was hired. She is an expert at activity- or increasing total profits between the two divisions. One because there was extra cost for no Thanks to her brilliant leadership, firm profits have gone Which of the following correctly fills in the blanks? integrative bargaining, operational distortion, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity distributive bargaining, activity-based pricing, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity distributive bargaining, integrative bargaining, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity integrative bargaining, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity activity-based pricing, activity-based management, non-value-added activity, supply chain surplus OOOO 2 po QUESTION 8 A company is considering switching to an activity-based costing system. Which of the following accurately describes what would happen to the reported cost of a low-volume product line if they switch to an activity-based costing system? The cost would decrease The cost would increase The cost would remain the same Impossible to predict OOOO QUESTION 9 Products R5 and CP8 each are assigned $100.00 in indirect costs by a traditional costing system. An activity analysis revealed that although production requirements are identical,, R5 requires 45 minutes less setup time than CP8. When compared with an ABC system that uses setup time as a driver, CP8 is relative to R5 under the traditional system, Fairly costed Overcosted Accurately costed Insufficient information Undercosted 2 points QUESTION 10 Rosie Company has two divisions, Division A and Division B. Rosie Company uses an activity-based costing system to allocate overhead. Rosie company has identified three cost drivers. Data about the cost drivers for the most recent year are below. Number of units of driver Cost pool Cost drivers per year 1,000 $100,000 X 75,000 500 Y 60,000 20 Z $235,000 Total The following data relate to cost driver activity within the two divisions during the most recent year Division A 300 Cost Driver X events Cost Driver Y events 300 10 Cost Driver Z events How much overhead should be allocated to Division A? QUESTION 7 Smith company has two divisions. Division A makes a proprietary product which it sells to Division B. Division B then refines it and sells it to the market. The two division managers have always fought over how much of the profit belongs to each division, a process known as based management, having taken Accounting 431 at WVU! Recently a new manager was hired. She is an expert at activity- She shifted the conversation to focus on thing she found was that identical quality testing was happening both at the end of the Division A process and the beginning of the Division B process. Basically, this was a(n) extra benefit. Another thing she found was that Division B often placed small orders, even though a larger order would have been much more efficient. The convenience on Division B's end was much smaller than the added cost on Division A's end, so the smaller order size is a(n) up, and both division managers are happy! or increasing total profits between the two divisions. One because there was extra cost for no Thanks to her brilliant leadership, firm profits have gone Which of the following correctly fills in the blanks? integrative bargaining, operational distortion, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity O distributive bargaining, activity-based pricing, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity distributive bargaining, integrative bargaining, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity integrative bargaining, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity activity-based pricing, activity-based management, non-value-added activity, supply chain surplus A company is considering switching to an activity-based costing system. Which of the following accurately describes what would happen to the reported cost of a low-volume product line if they switch to an activity-based costing system? The cost would decrease The cost would increase The cost would remain the same Impossible to predict Products R5 and CP8 each are assigned $100.00 in indirect costs by a traditional costing system. An activity analysis revealed that although production requirements are identical, R5 requires 45 minutes less setup time than CP8. When compared with an ABC system that uses setup time as a driver, CP8 is relative to R5 under the traditional system, Fairly costed Overcosted Accurately costed Insufficient information Undercosted OOOOO QUESTION 10 Rosie Company has two divisions, Division A and Division B. Rosie Company uses an activity-based costing system to allocate overhead. Rosie company has identified three cost drivers. Data about the cost drivers for the most recent year are below. Cost drivers Number of units of driver Cost pool per year 1,000 $100,000 X 500 75,000 20 60,000 $235,000 Z Total The following data relate to cost driver activity within the two divisions during the most recent year Division A Cost Driver X events 300 300 Cost Driver Y events 10 Cost Driver Z events How much overhead should be allocated to Division A? QUESTION 7 Smith company has two divisions. Division A makes a proprietary product which it sells to Division B. Division B then refines it and sells it to the market. The two division managers have always fought over how much of the profit belongs to each division, a process known as based management, having taken Accounting 431 at WVU! She shifted the conversation to focus on thing she found was that identical quality testing was happening both at the end of the Division A process and the beginning of the Division B process. Basically, this was a(n) extra benefit. Another thing she found was that Division B often placed small orders, even though a larger order would have been much more efficient. The convenience on Division B's end was much smaller than the added cost on Division A's end, so the smaller order size is a(n) up, and both division managers are happy! Recently a new manager was hired. She is an expert at activity- or increasing total profits between the two divisions. One because there was extra cost for no Thanks to her brilliant leadership, firm profits have gone Which of the following correctly fills in the blanks? integrative bargaining, operational distortion, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity distributive bargaining, activity-based pricing, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity distributive bargaining, integrative bargaining, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity integrative bargaining, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity activity-based pricing, activity-based management, non-value-added activity, supply chain surplus OOOO 2 po QUESTION 8 A company is considering switching to an activity-based costing system. Which of the following accurately describes what would happen to the reported cost of a low-volume product line if they switch to an activity-based costing system? The cost would decrease The cost would increase The cost would remain the same Impossible to predict OOOO QUESTION 9 Products R5 and CP8 each are assigned $100.00 in indirect costs by a traditional costing system. An activity analysis revealed that although production requirements are identical,, R5 requires 45 minutes less setup time than CP8. When compared with an ABC system that uses setup time as a driver, CP8 is relative to R5 under the traditional system, Fairly costed Overcosted Accurately costed Insufficient information Undercosted 2 points QUESTION 10 Rosie Company has two divisions, Division A and Division B. Rosie Company uses an activity-based costing system to allocate overhead. Rosie company has identified three cost drivers. Data about the cost drivers for the most recent year are below. Number of units of driver Cost pool Cost drivers per year 1,000 $100,000 X 75,000 500 Y 60,000 20 Z $235,000 Total The following data relate to cost driver activity within the two divisions during the most recent year Division A 300 Cost Driver X events Cost Driver Y events 300 10 Cost Driver Z events How much overhead should be allocated to Division A? QUESTION 7 Smith company has two divisions. Division A makes a proprietary product which it sells to Division B. Division B then refines it and sells it to the market. The two division managers have always fought over how much of the profit belongs to each division, a process known as based management, having taken Accounting 431 at WVU! Recently a new manager was hired. She is an expert at activity- She shifted the conversation to focus on thing she found was that identical quality testing was happening both at the end of the Division A process and the beginning of the Division B process. Basically, this was a(n) extra benefit. Another thing she found was that Division B often placed small orders, even though a larger order would have been much more efficient. The convenience on Division B's end was much smaller than the added cost on Division A's end, so the smaller order size is a(n) up, and both division managers are happy! or increasing total profits between the two divisions. One because there was extra cost for no Thanks to her brilliant leadership, firm profits have gone Which of the following correctly fills in the blanks? integrative bargaining, operational distortion, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity O distributive bargaining, activity-based pricing, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity distributive bargaining, integrative bargaining, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity integrative bargaining, supply chain surplus, non-value-added activity, insufficient-value-added activity activity-based pricing, activity-based management, non-value-added activity, supply chain surplus A company is considering switching to an activity-based costing system. Which of the following accurately describes what would happen to the reported cost of a low-volume product line if they switch to an activity-based costing system? The cost would decrease The cost would increase The cost would remain the same Impossible to predict Products R5 and CP8 each are assigned $100.00 in indirect costs by a traditional costing system. An activity analysis revealed that although production requirements are identical, R5 requires 45 minutes less setup time than CP8. When compared with an ABC system that uses setup time as a driver, CP8 is relative to R5 under the traditional system, Fairly costed Overcosted Accurately costed Insufficient information Undercosted OOOOO QUESTION 10 Rosie Company has two divisions, Division A and Division B. Rosie Company uses an activity-based costing system to allocate overhead. Rosie company has identified three cost drivers. Data about the cost drivers for the most recent year are below. Cost drivers Number of units of driver Cost pool per year 1,000 $100,000 X 500 75,000 20 60,000 $235,000 Z Total The following data relate to cost driver activity within the two divisions during the most recent year Division A Cost Driver X events 300 300 Cost Driver Y events 10 Cost Driver Z events How much overhead should be allocated to Division A