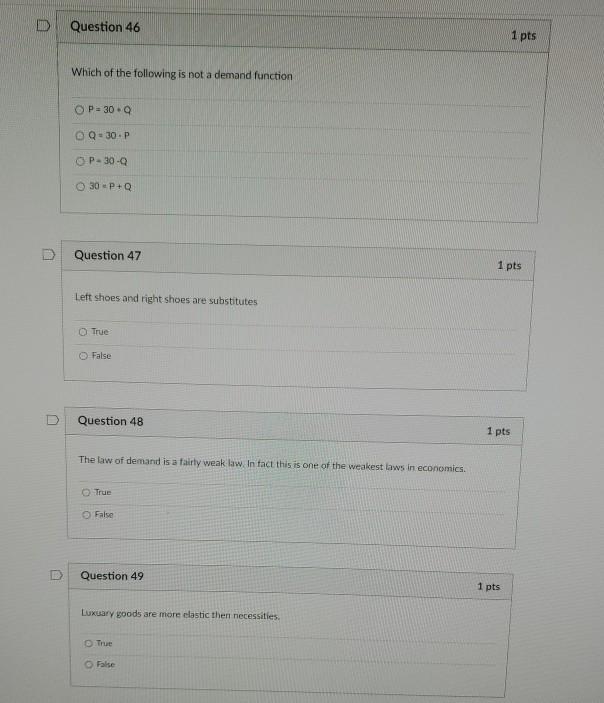
Question
Question: Algorithm : Reduction (Polynomial-time reduction, Packings and coverings) : More reduction (Satisfiabiliy, Hamilton Cycle) (Other references: CLRS ch 34 (& 34.5.3), KT 8.1, 8.2,
Question:
Algorithm : Reduction (Polynomial-time reduction, Packings and coverings)
: More reduction (Satisfiabiliy, Hamilton Cycle)
(Other references: CLRS ch 34 (& 34.5.3), KT 8.1, 8.2, 8.5)
Relationships on social networks have a very obvious representation as a graph. Many social networks use a symmetric friend relation. We can say that if there is an edge between accounts u and v that u and v are friends.
There is an interesting principle from social network theory called triadic closure. This is the observation that if two people a and b in a social network have a friend c in common, then there is an increased likelihood that a and b will become friends. What we would like to do is to identify clusters of friends, where a group of users are all friends with each other.
For a given social network graph G, consider the following problems:
(a) Does there exist a cluster of friends that involves a third of the accounts represented in the graph? That is, if G has n accounts, determine whether there is such a cluster of size exactly floor(n/3) n .
(b) Does there exist a cluster of friends that involves at least five of the accounts represented in the graph? That is, if G has n accounts, determine whether there 1 is such a cluster of size at least 5.
One of these problems is known to be solvable in polynomial time and the other is not. Determine which is which.
For the problem that is known to be solvable in polynomial time, give a brief justification.
For the problem that is not known to be solvable in polynomial time, give a reduction to one of the problems listed at the top (Packings and Coverings Satisfiability, Hamiltonian cycle)
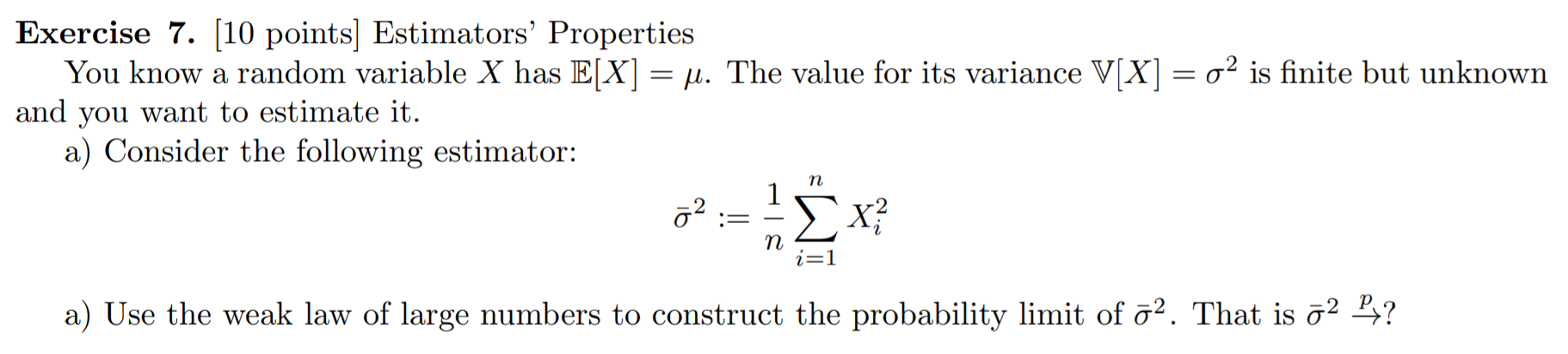
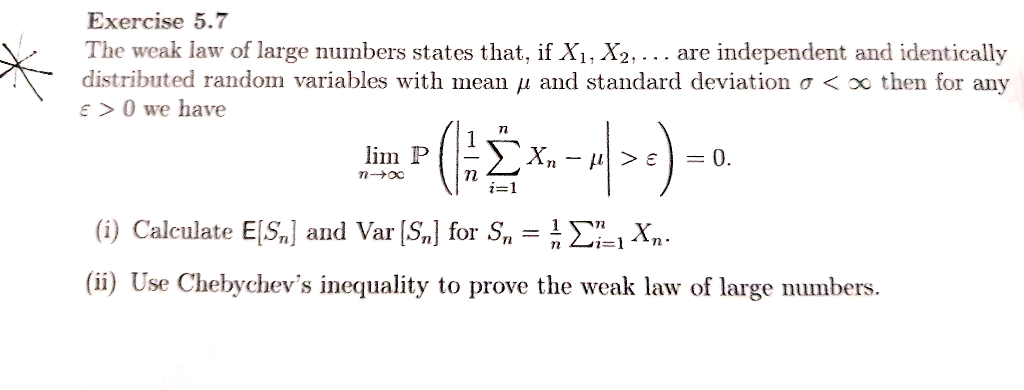

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


