Question: There are four different approaches to setting an approximate price level for a product. List the four approaches and then pick the one likely selected for Neuro Sonic when it launched. Briefly explain why. (Chapter 13)
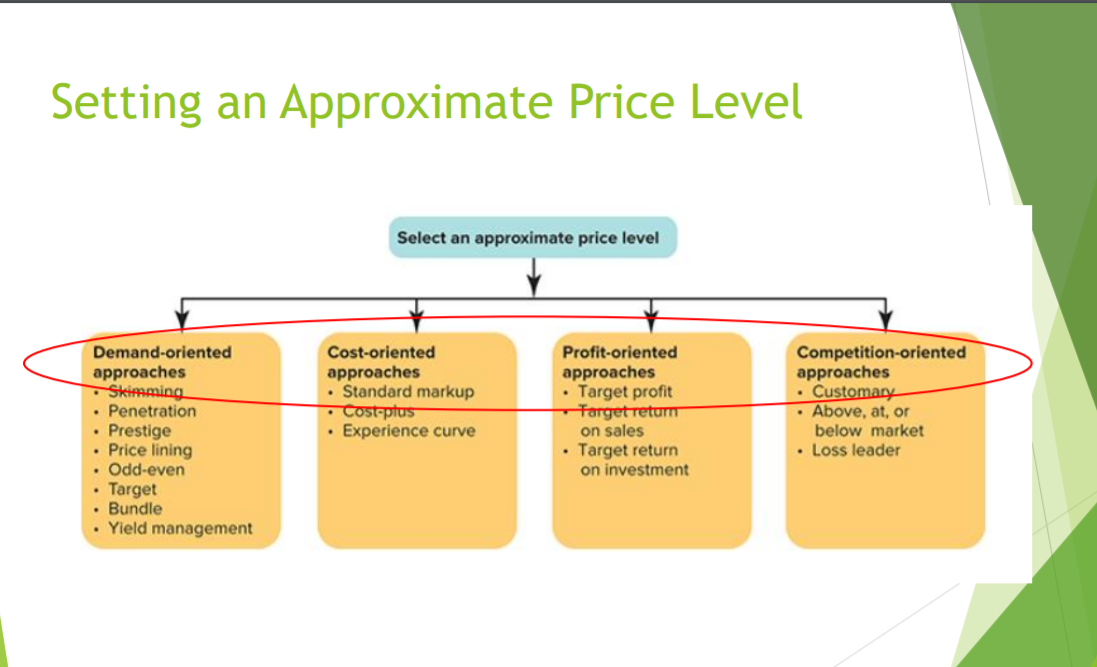
4 Different approaches to setting an approximate price level for a product:
Demand-oriented approaches:
- Skimming
- Penetration
- Prestige
- Price lining
- Odd-even
- Target
- Bundle
- Yield management
Cost-oriented approaches:
- Standard markup
- Cost-plus
- Experience curve
Profit-oriented approaches:
- Target profit
- Target return on sales
- Target return on investment
Competition-oriented approaches:
- Customary
- Above, at , or below market
- Loss leader
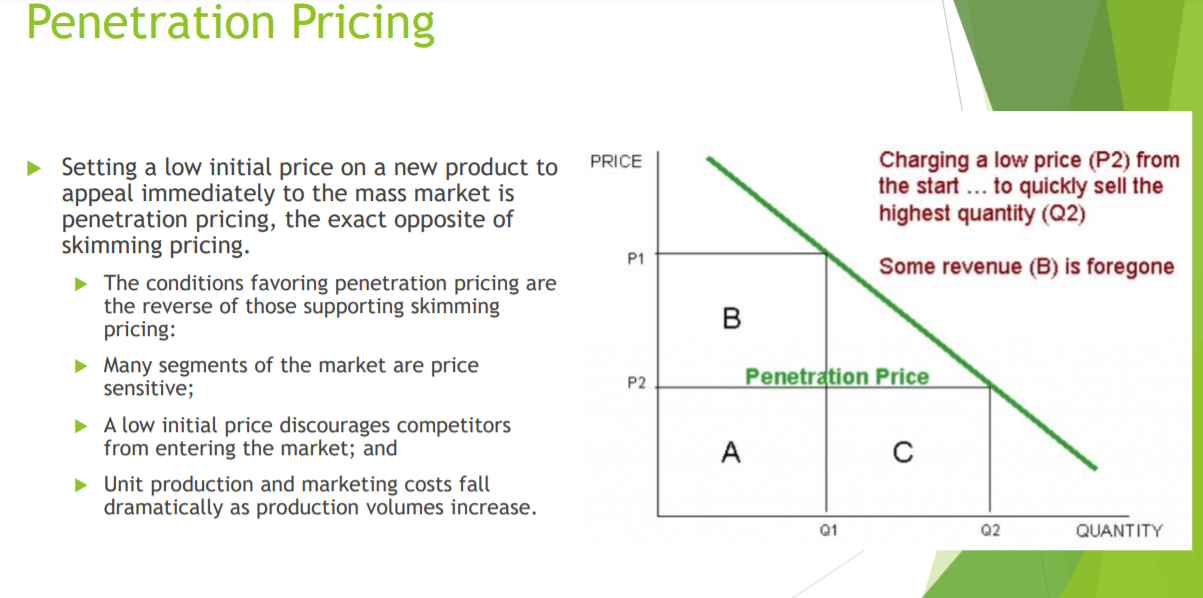
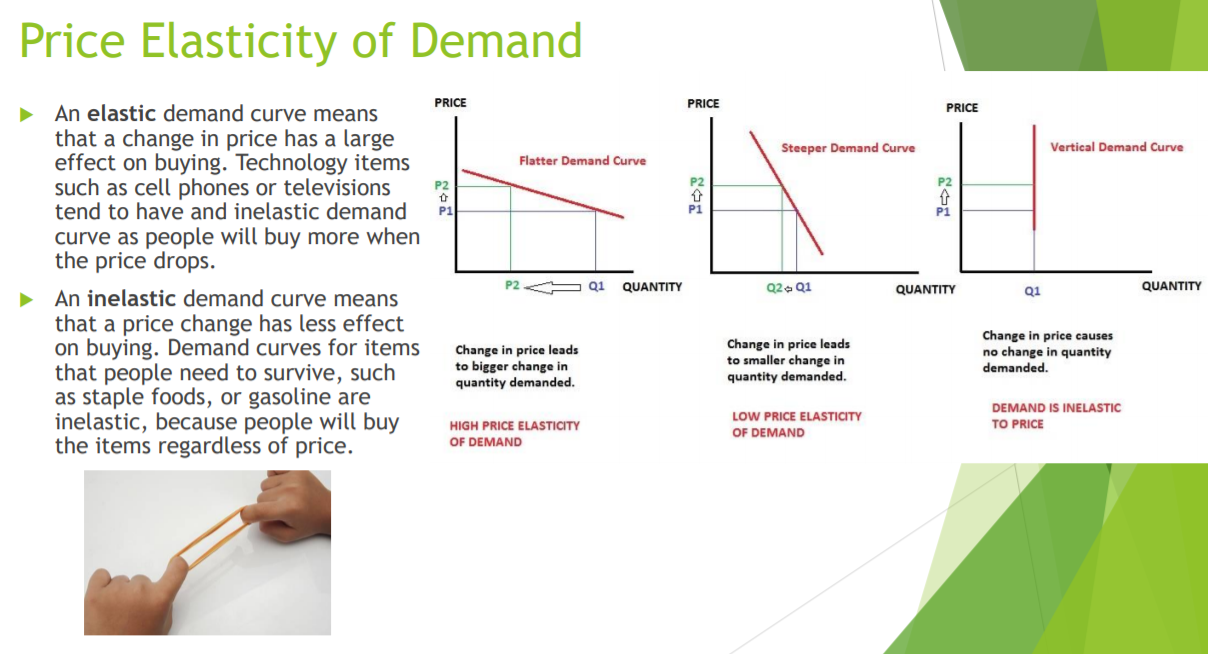
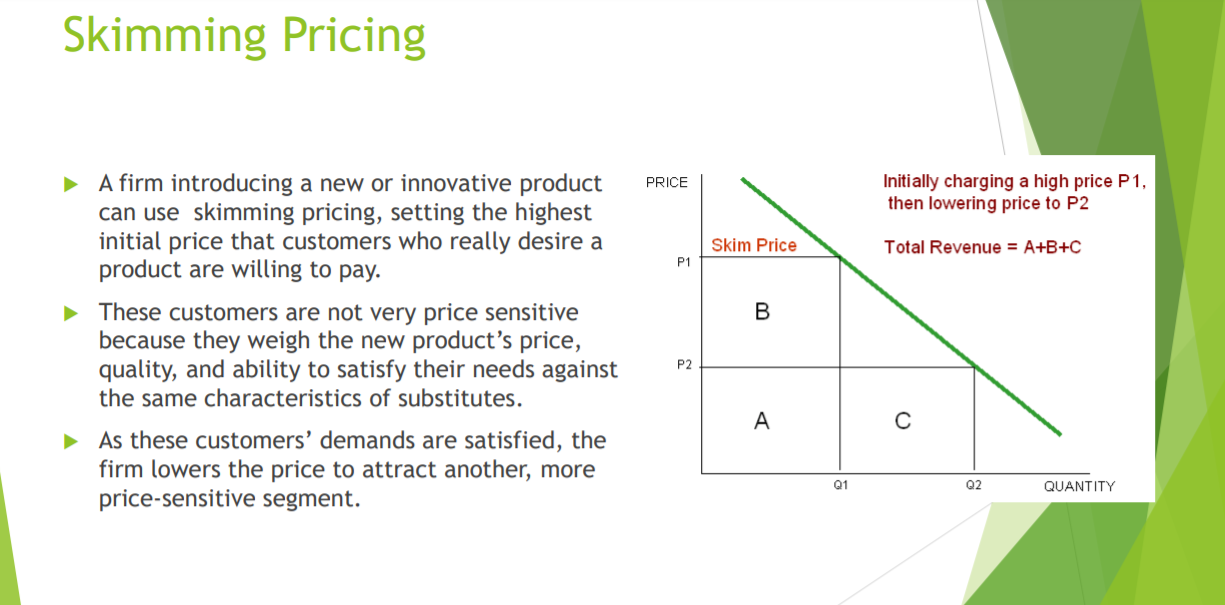
Cost-Oriented Approaches Rather than emphasize demand, cost, or profit factors, a price setter can stress what competitors (or "the market") are doing. Customary Pricing (Swatch) Above-, At-, or Below-Market Pricing (Rolex / Hudsons Bay / Walmart) Loss-Leader Pricing (Toilet Paper)Penetration Pricing Charging a low price (P2) from the start lo qulcidy sell the highest quantity (02) r Setting a low initial price on a new product to \"\"05 appeal immediately to the mass market is penetration pricing, the exact opposite of skimming pricing. P' Some revenue (B) Is foregone r The conditions favoring penetration pricing are the reverse of those supporting skimming pricing: B > Many segments of the market are price sensitive; P2 Peuah " h A low initial price discourages competitors from entering the market; and P Unit production and marketing costs fall dramatically as production volumes increase. 01 QUANTITY Price Elasticity of Demand PRICE PRICE An elastic demand curve means PRICE that a change in price has a large Steeper Demand Curve Vertical Demand Curve effect on buying. Technology items Flatter Demand Curve such as cell phones or televisions P2 tend to have and inelastic demand P1 curve as people will buy more when the price drops. P2 Q1 QUANTITY Q2 + Q1 An inelastic demand curve means QUANTITY Q1 QUANTITY that a price change has less effect Change in price leads Change in price causes on buying. Demand curves for items Change in price leads no change in quantity to bigger change in to smaller change in that people need to survive, such demanded. quantity demanded. quantity demanded. as staple foods, or gasoline are DEMAND IS INELASTIC inelastic, because people will buy LOW PRICE ELASTICITY HIGH PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND TO PRICE the items regardless of price. OF DEMANDSetting an Approximate Price Level Select an approximate price level Demand-oriented Cost-oriented Profit-oriented Competition-oriented approaches approaches approaches approaches Skimming . Standard markup . Target profit . Customary . Penetration Cost-plus Target return . Above, at, or . Prestige . Experience curve on sales below market . Price lining . Target return . Loss leader Odd-even on investment . Target Bundle Yield managementSkimming Pricing Initially charging a high price P1. then lowering price la P2 P A firm introducing a new or innovative product PRICE can use skimming pricing, setting the highest initial price that customers who really desire a product are willing to pay. P' Skim Price Total Revenue = A+B+C > These customers are not very price sensitive because they weigh the new product's price, quality, and ability to satisfy their needs against P' the same characteristics of substitutes. b As these customers' demands are satisfied, the firm lowers the price to attract another, more . . . o1 pr'ICE-SEOSIUVE segment. QUANTITY