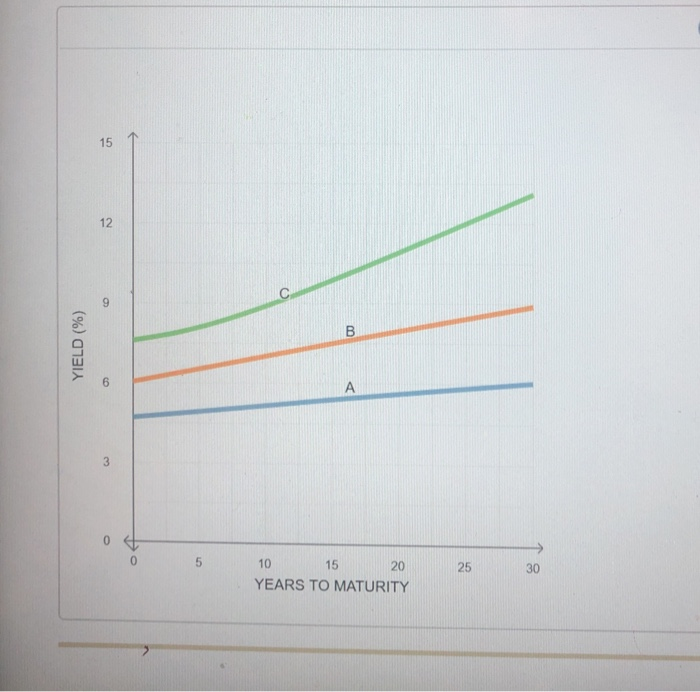
Rating agencies-such as Standard & Poor's (S&P), Moody's Investor Service, and Fitch Ratings-assign credit ratings to bonds based on both quantitative and qualitative factors. These ratings are considered indicators of the issuers default risk, which impacts the bond's Interest rate and the issuer's cost of debt capital Based on these ratings, bonds are classified into investment-grade bonds and junk bonds. Which of the following bonds is likely to be classified as an investment-grade bond? A bond with 30% return on capital, total debt to total capital of 15%, and 6% yield A bond with 10% return on capital, total debt to total capital of 85%, and 13% yield You heard that rating agencies have upgraded a bond's rating. The yield on the bond is likely toand the bond's price will Assume you make the following investments: A $10,000 investment in a 10-year T-bond that has a yield of 14.00% . A $20,000 investment in a 10-year corporate bond with an A% rating and a yield of 18.20% Assume you make the following investments * A $10,000 investment in 10-year T-bond that has a yield of 14.00% * A $20,000 investment in a 10-year corporate bond with an A% rating and a yield of 18.20% Based on this information, and the knowledge that the difference in liquidity risk premiums between the two bonds is the corporate bond's default risk premium? 40%, what is your estimate of @ 5.32% @ 4. 18% @ 5.70% @ 3.80% Bonds often pay a coupon twice a year. For the valuation of bonds that make semiannual payments, the number of periods doubles, whereas the amount of cash flow decreases by half. Using the values of cash flows and number of periods, the valuation model is adjusted accordingly Assume that a S3,000,000 par value, semiannual coupon US-Treasury note with five years to maturity (YTM) has a coupon rate of 3%, The yield to maturity of the bond is 8.00%. Using this information and ignoring the other costs involved, the value of the Treasury note is Based on your calculations and understanding of semiannual coupon bonds, complete the following statements The T-note described is currently selling at a be expected to formula is assumed to have a value of Assuming that interest rates remain constant over the life of the note, its price should as the T-note approaches maturity , when valuing a semiannual coupon bond, the time period (N) in the present value periods The higher the risk of a security, the higher its expected return will be. A bond's risk level is reflected in its yield, but understanding the different risks involved when investing in bonds is important. The following graph shows the relationship between interest rates and maturity for three security classes: U.S. Treasury securities. AA-rated corporate bonds, and BBB-rated corporate bonds 15 12 6 20 25 15 YEARS TO MATURITY 10 Use the dropdown menus to identify the group of securities that correspond to each yield curve. Curve A Curve B Curve C Simone Garibaldi is retiring soon, so she is concerned about her investments providing her steady income every year. She is aware that if interest rates interest rates might lead to annual income from her investments. What kind of risk is Simone most concerned about protecting against? the potential earnings power of the cash flow from her investments will increase. In particular, she is concerned that a decline in Interest rate risk Reinvestment rate risk Rating agencies-such as Standard & Poor's (S&P), Moody's Investor Service, and Fitch Ratings-assign credit ratings to bonds based on both quantitative and qualitative factors. These ratings are considered indicators of the issuers default risk, which impacts the bond's Interest rate and the issuer's cost of debt capital Based on these ratings, bonds are classified into investment-grade bonds and junk bonds. Which of the following bonds is likely to be classified as an investment-grade bond? A bond with 30% return on capital, total debt to total capital of 15%, and 6% yield A bond with 10% return on capital, total debt to total capital of 85%, and 13% yield You heard that rating agencies have upgraded a bond's rating. The yield on the bond is likely toand the bond's price will Assume you make the following investments: A $10,000 investment in a 10-year T-bond that has a yield of 14.00% . A $20,000 investment in a 10-year corporate bond with an A% rating and a yield of 18.20% Assume you make the following investments * A $10,000 investment in 10-year T-bond that has a yield of 14.00% * A $20,000 investment in a 10-year corporate bond with an A% rating and a yield of 18.20% Based on this information, and the knowledge that the difference in liquidity risk premiums between the two bonds is the corporate bond's default risk premium? 40%, what is your estimate of @ 5.32% @ 4. 18% @ 5.70% @ 3.80% Bonds often pay a coupon twice a year. For the valuation of bonds that make semiannual payments, the number of periods doubles, whereas the amount of cash flow decreases by half. Using the values of cash flows and number of periods, the valuation model is adjusted accordingly Assume that a S3,000,000 par value, semiannual coupon US-Treasury note with five years to maturity (YTM) has a coupon rate of 3%, The yield to maturity of the bond is 8.00%. Using this information and ignoring the other costs involved, the value of the Treasury note is Based on your calculations and understanding of semiannual coupon bonds, complete the following statements The T-note described is currently selling at a be expected to formula is assumed to have a value of Assuming that interest rates remain constant over the life of the note, its price should as the T-note approaches maturity , when valuing a semiannual coupon bond, the time period (N) in the present value periods The higher the risk of a security, the higher its expected return will be. A bond's risk level is reflected in its yield, but understanding the different risks involved when investing in bonds is important. The following graph shows the relationship between interest rates and maturity for three security classes: U.S. Treasury securities. AA-rated corporate bonds, and BBB-rated corporate bonds 15 12 6 20 25 15 YEARS TO MATURITY 10 Use the dropdown menus to identify the group of securities that correspond to each yield curve. Curve A Curve B Curve C Simone Garibaldi is retiring soon, so she is concerned about her investments providing her steady income every year. She is aware that if interest rates interest rates might lead to annual income from her investments. What kind of risk is Simone most concerned about protecting against? the potential earnings power of the cash flow from her investments will increase. In particular, she is concerned that a decline in Interest rate risk Reinvestment rate risk