Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
read through and answer question 1 and 2 first. then 3 and 4 ENVS3731/3771 Assignment calibration and testing work model Parameterisation of a rower-uptake stress

read through and answer question 1 and 2 first. then 3 and 4
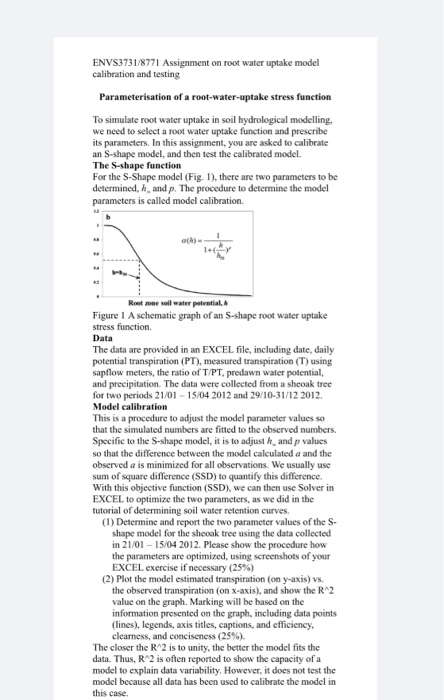
ENVS3731/3771 Assignment calibration and testing work model Parameterisation of a rower-uptake stress funcio Te simulater water kein wol hydrological modeling we need to select a root water uptake function and prescribe its parameters. In this as you are associate an S-shape model, and then to the calibrated model The S-shape function For the S-Shape model (Fig. 1. there are two t o be determined. And p. The procedure to decih sodel parameters is called model calibration Figure 1 A schematic graph of an Shapero wake wake es function The data are provided in an EXCEL file, including de polenta transpiration (PT), card trans (T) apelow meters, the ratio of T PT. predn a poli and precipitation. The data were collected from a shook tee for a periods 21/01-15:04 2012 and 29:10-31/12 2012 Modalitaan This is a procedure to add the model name was that the simulated numbers are fitted to the observad o s Specific to the shaped it s so that the difference between the model calculated and the observed as mintimired for all obat sum ofare difference (SSD) quantify thes e With this objective function (SSDL we can then use Solaris EXCEL to open the two parameters, as we d he tutorial of determining soil wali mention (1) Determine and report the two parameter values of the shape model for the shoek tree using the data collected in 21/01 - 15:04 2012. Plcome show the procedure how the parametre optimising some of you 2) Ples the destined to transion and how the R2 value on the graph Making will be honed the information presented on the graph including da t lines, legends as titles, caption, and efficiency clcarness, and concise (25% The closer the R isto unity, the hair the model is the data. Thus, R2 is otten reported to show the capacity of a model to explain data wahili However, it does not the model because all data luas been used to calitate the model in this case Model testing Now you are to test the model using the data collected in 29/10-31/12 2012. This part of the mothe d for model cation The Nash suncliffe coefficient of efficiency is often used to report the model performance. The calculate formula of Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient of efficiency where is the Nash-Suncliffe coefficient of efficiency the measured value is the simulated values the average value of measurements and is the number of (3) Calculate and report daily transpiration based on the calibrated S-shape function (you have done this in for 29/10-31/12 2012. and let the rest day of the year, y asistimated daily transpiration and b e daily transpiration Marking will be based on the information presented on the graph (25%) (4) Calculate and report NSE. Please show the procedure of your calculation (25%) ENVS3731/8771 Assignment on root water uptake model calibration and testing Parameterisation of a root-water-uptake stress function To simulate root water uptake in soil hydrological modelling, we need to select a root water uptake function and prescribe its parameters. In this assignment, you are asked to calibrate an S-shape model, and then test the calibrated model. The S-shape function For the S-Shape model (Fig. 1), there are two parameters to be determined, h, and p. The procedure to determine the model parameters is called model calibration. Roone soil water potential Figure 1 A schematic graph of an S-shape root water uptake stress function. Data The data are provided in an EXCEL file, including date, daily potential transpiration (PT), measured transpiration (T) using sapflow meters, the ratio of T/PT, predawn water potential, and precipitation. The data were collected from a sheoak tree for two periods 21/01 - 15/04 2012 and 29/10-31/12 2012 Model calibration This is a procedure to adjust the model parameter values so that the simulated numbers are fitted to the observed numbers Specific to the S-shape model, it is to adjust h and p values so that the difference between the model calculated a and the observed a is minimized for all observations. We usually use Sum of square difference (SSD) to quantify this difference. With this objective function (SSD), we can then use Solver in EXCEL to optimize the two parameters, as we did in the tutorial of determining soil water retention curves. (1) Determine and report the two parameter values of the S- shape model for the shooak tree using the data collected in 21/01 - 15/04 2012. Please show the procedure how the parameters are optimized, using screenshots of your EXCEL exercise if necessary (25%) (2) Plot the model estimated transpiration (on y-axis) vs. the observed transpiration (on x-axis), and show the R^2 value on the graph. Marking will be based on the information presented on the graph, including data points (lines), legends, axis titles, captions, and efficiency. clcarness, and conciseness (25%). The closer the R 2 is to unity, the better the model fits the data. Thus, R^2 is often reported to show the capacity of a model to explain data variability. However, it does not test the model because all data has been used to calibrate the model in this case. ENVS3731/3771 Assignment calibration and testing work model Parameterisation of a rower-uptake stress funcio Te simulater water kein wol hydrological modeling we need to select a root water uptake function and prescribe its parameters. In this as you are associate an S-shape model, and then to the calibrated model The S-shape function For the S-Shape model (Fig. 1. there are two t o be determined. And p. The procedure to decih sodel parameters is called model calibration Figure 1 A schematic graph of an Shapero wake wake es function The data are provided in an EXCEL file, including de polenta transpiration (PT), card trans (T) apelow meters, the ratio of T PT. predn a poli and precipitation. The data were collected from a shook tee for a periods 21/01-15:04 2012 and 29:10-31/12 2012 Modalitaan This is a procedure to add the model name was that the simulated numbers are fitted to the observad o s Specific to the shaped it s so that the difference between the model calculated and the observed as mintimired for all obat sum ofare difference (SSD) quantify thes e With this objective function (SSDL we can then use Solaris EXCEL to open the two parameters, as we d he tutorial of determining soil wali mention (1) Determine and report the two parameter values of the shape model for the shoek tree using the data collected in 21/01 - 15:04 2012. Plcome show the procedure how the parametre optimising some of you 2) Ples the destined to transion and how the R2 value on the graph Making will be honed the information presented on the graph including da t lines, legends as titles, caption, and efficiency clcarness, and concise (25% The closer the R isto unity, the hair the model is the data. Thus, R2 is otten reported to show the capacity of a model to explain data wahili However, it does not the model because all data luas been used to calitate the model in this case Model testing Now you are to test the model using the data collected in 29/10-31/12 2012. This part of the mothe d for model cation The Nash suncliffe coefficient of efficiency is often used to report the model performance. The calculate formula of Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient of efficiency where is the Nash-Suncliffe coefficient of efficiency the measured value is the simulated values the average value of measurements and is the number of (3) Calculate and report daily transpiration based on the calibrated S-shape function (you have done this in for 29/10-31/12 2012. and let the rest day of the year, y asistimated daily transpiration and b e daily transpiration Marking will be based on the information presented on the graph (25%) (4) Calculate and report NSE. Please show the procedure of your calculation (25%) ENVS3731/8771 Assignment on root water uptake model calibration and testing Parameterisation of a root-water-uptake stress function To simulate root water uptake in soil hydrological modelling, we need to select a root water uptake function and prescribe its parameters. In this assignment, you are asked to calibrate an S-shape model, and then test the calibrated model. The S-shape function For the S-Shape model (Fig. 1), there are two parameters to be determined, h, and p. The procedure to determine the model parameters is called model calibration. Roone soil water potential Figure 1 A schematic graph of an S-shape root water uptake stress function. Data The data are provided in an EXCEL file, including date, daily potential transpiration (PT), measured transpiration (T) using sapflow meters, the ratio of T/PT, predawn water potential, and precipitation. The data were collected from a sheoak tree for two periods 21/01 - 15/04 2012 and 29/10-31/12 2012 Model calibration This is a procedure to adjust the model parameter values so that the simulated numbers are fitted to the observed numbers Specific to the S-shape model, it is to adjust h and p values so that the difference between the model calculated a and the observed a is minimized for all observations. We usually use Sum of square difference (SSD) to quantify this difference. With this objective function (SSD), we can then use Solver in EXCEL to optimize the two parameters, as we did in the tutorial of determining soil water retention curves. (1) Determine and report the two parameter values of the S- shape model for the shooak tree using the data collected in 21/01 - 15/04 2012. Please show the procedure how the parameters are optimized, using screenshots of your EXCEL exercise if necessary (25%) (2) Plot the model estimated transpiration (on y-axis) vs. the observed transpiration (on x-axis), and show the R^2 value on the graph. Marking will be based on the information presented on the graph, including data points (lines), legends, axis titles, captions, and efficiency. clcarness, and conciseness (25%). The closer the R 2 is to unity, the better the model fits the data. Thus, R^2 is often reported to show the capacity of a model to explain data variability. However, it does not test the model because all data has been used to calibrate the model in this case Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started