Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Refer to the following model of the economy for Q1-Q4 Consider the following Mundell-Fleming short-run model of a small open economy under floating exchange

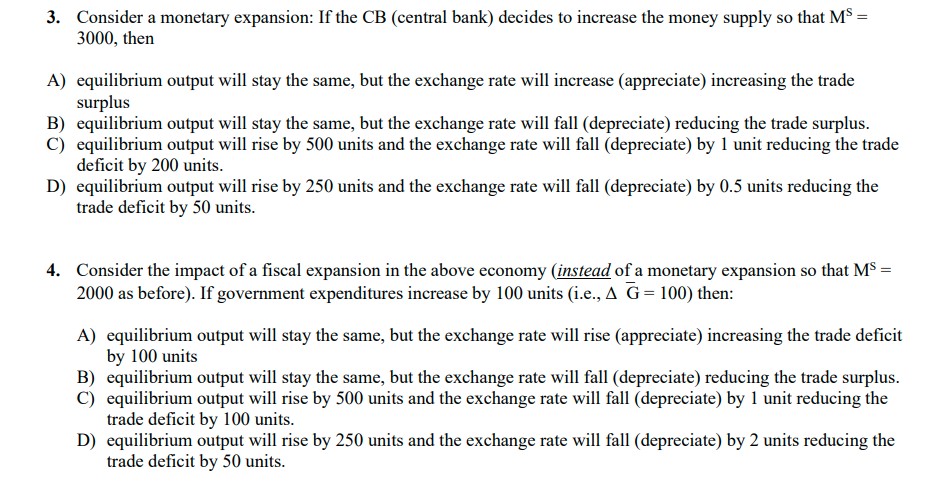
Refer to the following model of the economy for Q1-Q4 Consider the following Mundell-Fleming short-run model of a small open economy under floating exchange rates given in equations (1)-(9). Assume there is perfect capital mobility so that the domestic interest rate equals the world interest rate, i.e., r = r*. The nominal exchange rate is denoted by e. (1) C = (2) I = (4) G = 200 (5) T = 100 230+ 0.8 (Y - T); 234- 30 r (6) NX = 120 - 50 ( P/P*)e (7) PE = C + I + G + NX (7) Y = PE Goods market equilibrium Md (8) = 2Y - 40 r P Md = MS P Money market equilibrium Suppose that the central bank sets the nominal money supply MS=2000 and that P =2. Also suppose that the foreign price P*= 1 while the world interest rate r* = 6. 1. The equilibrium output level in this economy Y eq is given by A) Yeq = 370 B) Yeq = 620 C) Yeq=1120 D) Yeq = 1620 2. The equilibrium exchange rate e q is given by: A) e eq 4 and we have a trade deficit B) e eq = 3.5 and we have a trade deficit C) e eq=2 and we have a trade surplus D) e q = 4.5 and we have a trade deficit 3. Consider a monetary expansion: If the CB (central bank) decides to increase the money supply so that Ms = 3000, then A) equilibrium output will stay the same, but the exchange rate will increase (appreciate) increasing the trade surplus B) equilibrium output will stay the same, but the exchange rate will fall (depreciate) reducing the trade surplus. C) equilibrium output will rise by 500 units and the exchange rate will fall (depreciate) by 1 unit reducing the trade deficit by 200 units. D) equilibrium output will rise by 250 units and the exchange rate will fall (depreciate) by 0.5 units reducing the trade deficit by 50 units. 4. Consider the impact of a fiscal expansion in the above economy (instead of a monetary expansion so that Ms = 2000 as before). If government expenditures increase by 100 units (i.e., A G = 100) then: A) equilibrium output will stay the same, but the exchange rate will rise (appreciate) increasing the trade deficit by 100 units B) equilibrium output will stay the same, but the exchange rate will fall (depreciate) reducing the trade surplus. C) equilibrium output will rise by 500 units and the exchange rate will fall (depreciate) by 1 unit reducing the trade deficit by 100 units. D) equilibrium output will rise by 250 units and the exchange rate will fall (depreciate) by 2 units reducing the trade deficit by 50 units.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.39 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The equilibrium output level in this economy is given by Y PE Using the equation 7 we can solve for ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


