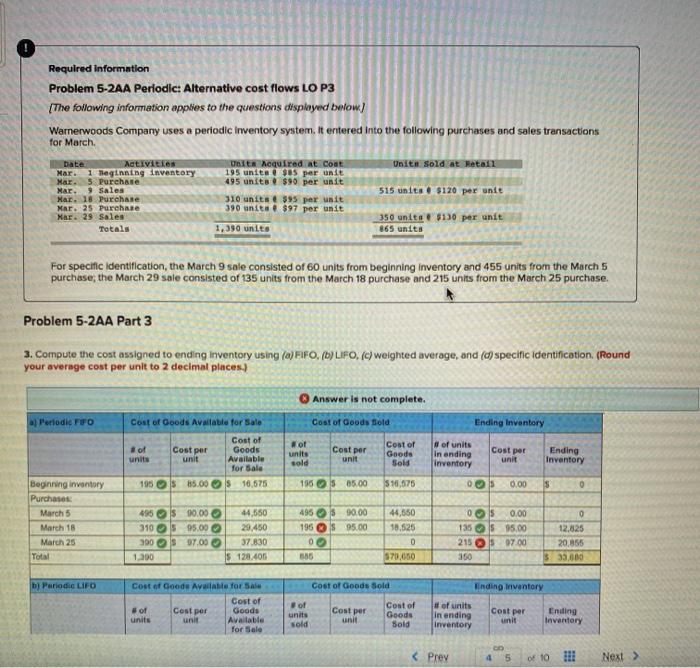
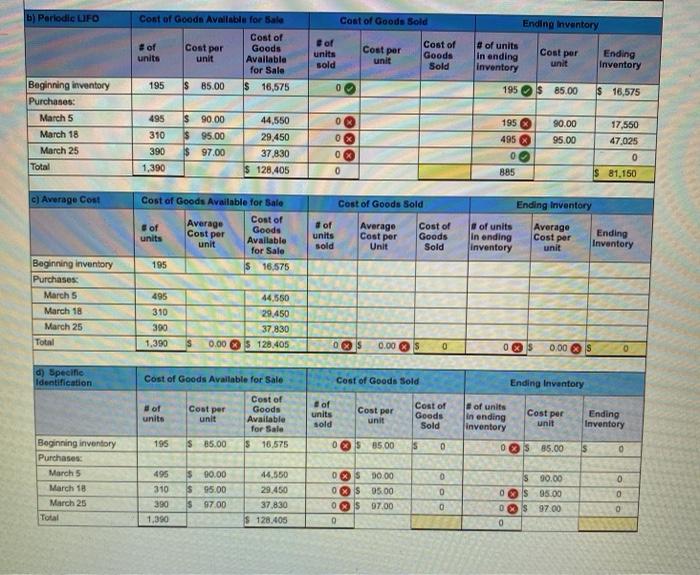
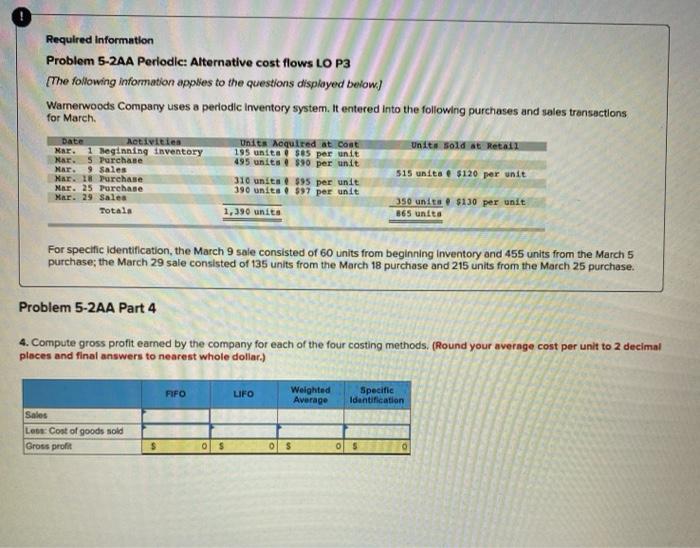
Required Information Problem 5-2AA Periodic: Alternative cost flows LO P3 [The following information applies to the questions displayed buntow) Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Unit Sold at Retail Date Activities Mar. 1 Teginning Inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals UBIER Acquired At Cost 195 units $us per unit 495 unita $90 per unit 310 units 395 per unit 390 units 597 per unit 515 units $120 per unit 350 units $130 per unit 865 units 1.390 units For specific Identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 60 units from beginning inventory and 455 units from the March 5 purchase, the March 29 sale consisted of 135 units from the March 18 purchase and 215 units from the March 25 purchase, Problem 5-2AA Part 3 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending Inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (e) weighted average, and (a) specific identification (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) aj Periode FFO Coat of Goods Available for Sale Cost of of Cost per Goods units unit Available for Sale 195S 85.00 $ 16,675 Answer is not complete. Cost of Goods told Ending Inventory Hot Cost of of units units Goods Cost per Ending In anding sold unit Sold unit inventory Inventory 155S 65.00 $ 10,575 OOS 0.00 s 0 Cost per Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 495 $10.00 3105 95.00 390 97.00 1.200 44,550 29.450 37.830 S 128.406 495 $90.00 195 S 95.00 0 585 44,650 10.525 0 570.050 os 0.00 135S 95.00 215 S0700 350 0 12,825 20,855 $ 33,000 b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Ending inventory Cost of Goode Aviate for SA Cost of of Cost per Goods units unit Available for Sale of units sold Cost per unit Cost of Goods Sold Cost per # of units in ending Inventory Ending Inventory b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cont of Good Available for sale Cost of # of Cost per Goods units unit Available for Sale 195 $ 85.00 $ 16,575 of units sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold # of units In ending Inventory Cost per unit unit Ending Inventory 195$ 85.00 $ 16,575 Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 495 310 390 $ 90.00 $ 95.00 $97.00 195 x 495 90.00 95.00 17,560 47 025 44,550 29.450 37.830 $ 128,405 0 0 0 0 0 1,390 0 $ 81,150 885 C) Average Cout Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of of Goods units unit Available for Sale 195 $16.575 Average Cost per of units sold Average Cost per Unit Cost of Goods Sold of units in ending inventory Average Cost per Ending Inventory unit Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 495 310 390 1.390 44.550 29,450 37830 0.00 S 128.405 03 S 0.00 S 0 0 $ 0.00 S d) Specific Identification Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost per of units of units sold Cost per Cost of Goods Available for Sale s 16.575 unit Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit of units in ending Inventory unit Ending Inventory 195 $ 85.00 0 XS 85.00 s 0 0 S 85.00 s 0 Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 0 0 495 310 390 1,390 $ 0.00 $ 95.00 $97.00 lo 0 44,550 29.450 37.830 $ 128.405 ORS 00.00 0 $ 95.00 0 S 97.00 0 S 90.00 0S 95.00 0 $97.00 0 0 0 Required information Problem 5-2AA Periodie: Alternative cost flows LO P3 (The following information applies to the questions displayed below) Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic Inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Nar. S Purchase Nar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totala Units equired at Cont 195 unita $85 per unit 495 units $30 per unit 310 unita $95 per unit 390 units . $97 per unit 1,390 units Unit Sold at Retai 515 units $120 per unit 350 units $130 per unit 365 unita For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 60 units from beginning inventory and 455 units from the March 5 purchase; the March 29 sale consisted of 135 units from the March 18 purchase and 215 units from the March 25 purchase. Problem 5-2AA Part 4 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar) FIFO LIFO Weighted Average Specific Identification Sales Le Cost of goods sold Gross profit $ ols ols os 0