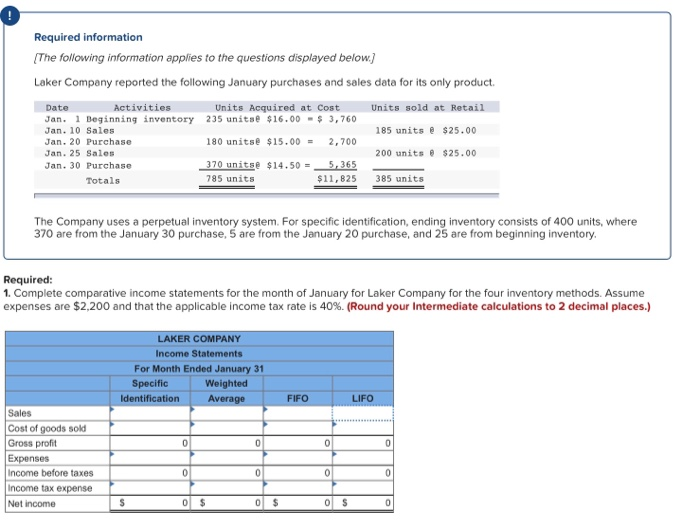
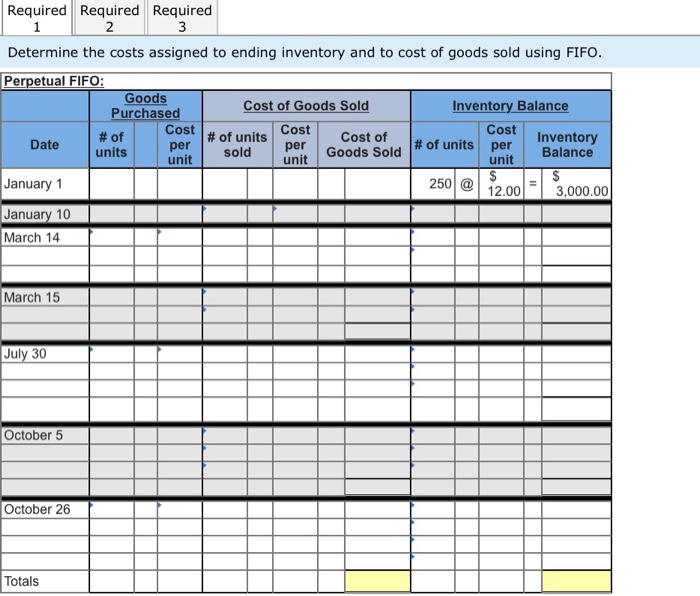
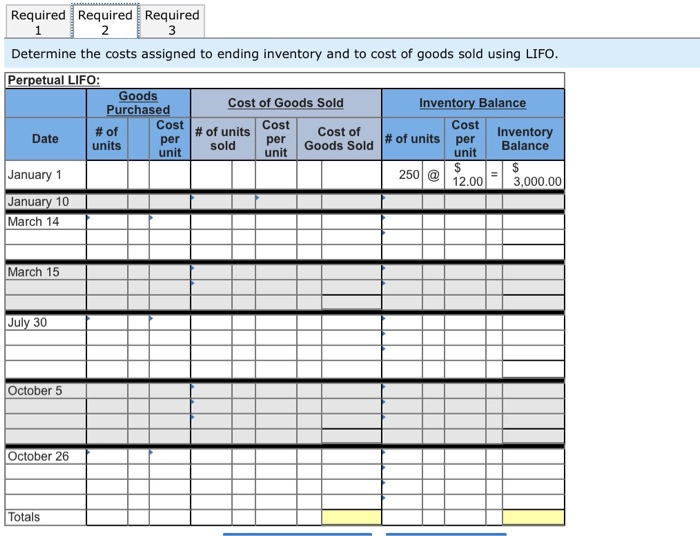
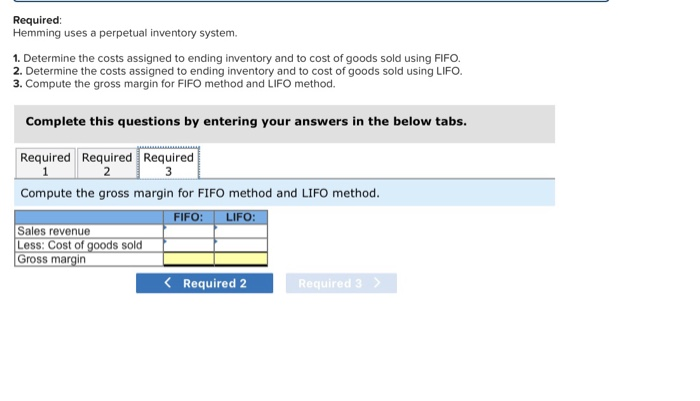
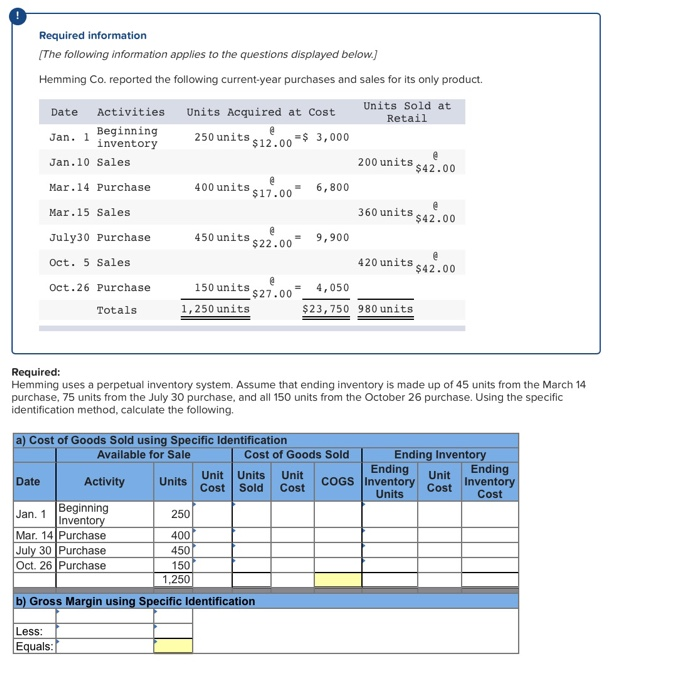
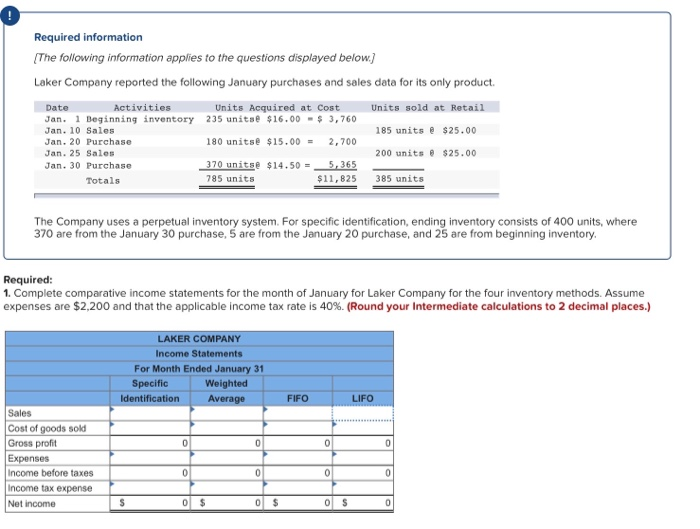
Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product Units sold at Retail 185 units @ $25.00 Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 235 unitse $16.00 - $ 3,760 Jan. 10 Sales Jan. 20 Purchase 180 units@ $15.00 = 2,700 Jan. 25 Sales Jan. 30 Purchase 370 units@ $14.50 = 5,365 Totals 795 units $11,825 200 units @ $25.00 385 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 400 units, where 370 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 25 are from beginning inventory Required: 1. Complete comparative income statements for the month of January for Laker Company for the four inventory methods. Assume expenses are $2,200 and that the applicable income tax rate is 40%. (Round your Intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) LAKER COMPANY Income Statements For Month Ended January 31 Specific Weighted Identification Average FIFO 0 0 0 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Expenses Income before taxes Income tax expense Net income 00 Required information (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Hemming Co. reported the following current-year purchases and sales for its only product. Date Activities Beginning Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 250 units 512.00-$ 3,000 Jan. inventory Jan.10 Sales 200 units 542.00 Mar.14 Purchase 400 units .00- 6,800 Mar.15 Sales 360 units 542.00 July30 Purchase 450 units $22.00= 9,900 @ Oct. 5 Sales 420 unite 420 units 542.00 @ 150 units s27.00 150 unit = Oct.26 Purchase Totals 4,050 $23,750 980 units 1,250 units Required: Hemming uses a perpetual inventory system. 1. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. 2. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO 3. Compute the gross margin for FIFO method and LIFO method. Required Required Required 1 2 Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. Perpetual FIFO: Goods Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance Purchased Cost # of units Cost # of Date Inventory per units # of units Goods Sold per unit unit Balance January 1 250 @ 12.00 = 1 3,000.00 January 10 March 14 Cost Cost of per sold unit March 15 July 30 October 5 October 26 Totals Required Required Required 23 Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. Perpetual LIFO: Goods | Cost of Goods Sold Purchased Cost # of # of units Cost Cost of Date per units unit Goods Sold unit Inventory Balance Cost # of units per Inventory Balance unit per sold January 1 250 @ 12.00 - 3,000.00 January 10 March 14 March 15 July 30 October 5 October 26 Totals Required: Hemming uses a perpetual inventory system. 1. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. 2. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. 3. Compute the gross margin for FIFO method and LIFO method. Complete this questions by entering your answers in the below tabs. Required Required Required 2 3 Compute the gross margin for FIFO method and LIFO method. FIFO: LIFO: Sales revenue Less: Cost of goods sold Gross margin Required 2 Required 3 Required information (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Hemming Co. reported the following current-year purchases and sales for its only product. Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail Date Activities Jan. Beginning inventory Jan.10 Sales 250 units 12.00 - $ 3,000 200 units $42.00 Mar.14 Purchase 400 units 512 units. = 6,800 Mar.15 Sales 360 units $42.00 July30 Purchase 450 units = 9,900 @ Oct. 5 Sales 420 unite 420 units s42.00 150 units s27.00 = 4,050 Oct.26 Purchase Totals 1,250 units $23,750 980 units Required: Hemming uses a perpetual inventory system. Assume that ending inventory is made up of 45 units from the March 14 purchase, 75 units from the July 30 purchase, and all 150 units from the October 26 purchase. Using the specific identification method, calculate the following. Ending Unit Units a) Cost of Goods Sold using Specific Identification Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Unit Units Ending Activity Unit Date COGS Inventory Inventory Cost Sold Cost Units Cost Cost Jan. 1 Beginning 250 Inventory Mar. 14 Purchase 400 July 30 Purchase 4501 Oct. 26 Purchase 150 1,250 b) Gross Margin using Specific Identification Less: Equals: Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product Units sold at Retail 185 units @ $25.00 Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 235 unitse $16.00 - $ 3,760 Jan. 10 Sales Jan. 20 Purchase 180 units@ $15.00 = 2,700 Jan. 25 Sales Jan. 30 Purchase 370 units@ $14.50 =_5,365 Totals 795 units $11,825 200 units @ $25.00 385 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 400 units, where 370 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 25 are from beginning inventory Required: 1. Complete comparative income statements for the month of January for Laker Company for the four inventory methods. Assume expenses are $2,200 and that the applicable income tax rate is 40%. (Round your Intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) LAKER COMPANY Income Statements For Month Ended January 31 Specific Weighted Identification Average FIFO 0 0 0 I Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Expenses Income before taxes Income tax expense Net income 00