Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
RUN CODE TEST CASES ASSIGNMENT DOCS GRADE MORE 7 points Status: Not Submitted In this exercise, we will be looking at our example code for
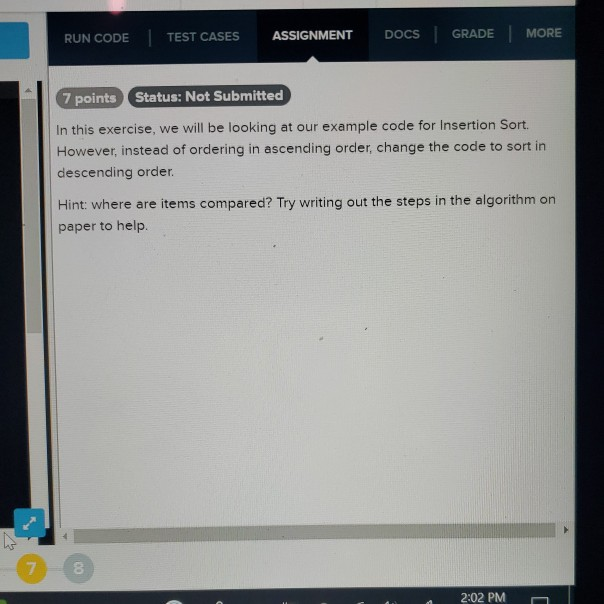
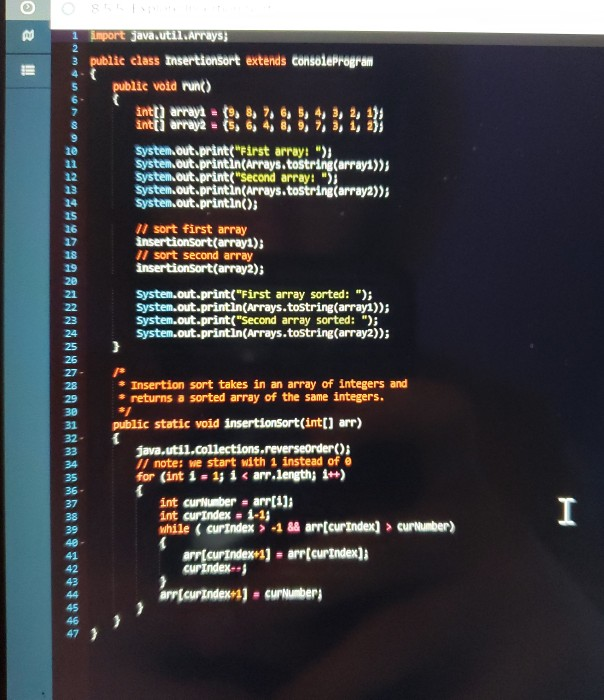
RUN CODE TEST CASES ASSIGNMENT DOCS GRADE MORE 7 points Status: Not Submitted In this exercise, we will be looking at our example code for Insertion Sort. However, instead of ordering in ascending order, change the code to sort in descending order. Hint: where are items compared? Try writing out the steps in the algorithm on paper to help 7 8 2:02 PM 0 2 !! import java.util.Arrays; 3 public class Insertionsort extends consoleprogram public void run() antt arrays (, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 233 intti array2 = (5, 6, 4, 8, 9, 7, 3, 1, 2); System.out.print("First array: "); System.out.println(Arrays.tostring(array:>> System.out.print("second array: "); system.out.printinarrays.tostring(array2)); System.out.println(); 11 sort first array insertionsort(array); 11 sort second array insertionsort(array2); System.out.print("First array sorted: "); System.out.println(Arrays.tostring(array1)); System.out.print("Second array sorted: "); System.out.println(Arrays.tostring(array2)); Insertion sort takes in an array of integers and returns a sorted array of the same integers. public static void insertionsort(int[] arr) 31 java.util.collections.reverseorder(); // note: we start with 1 instead of for (int i = 1; i -1 && arr curindex] > cur number) arp curindex+1) = arr(curIndex); curIndex - arr curIndex+1) - curNumbers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


