Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A. Labelled diagram of the leaf TS and LS, showing the important structures. LS Section (3 marks, I mark per TS Section drawing, I
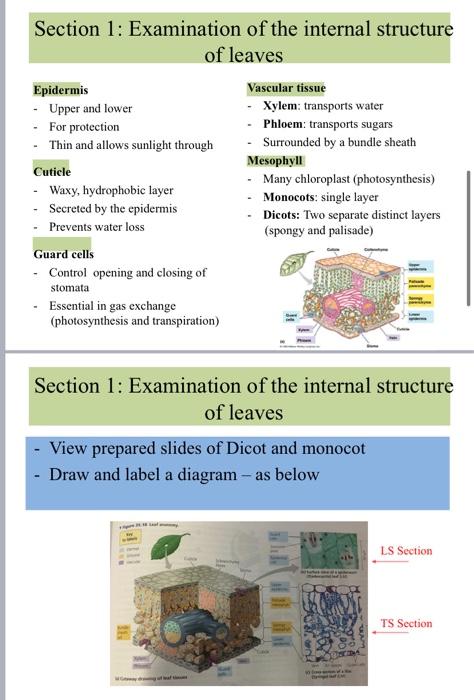
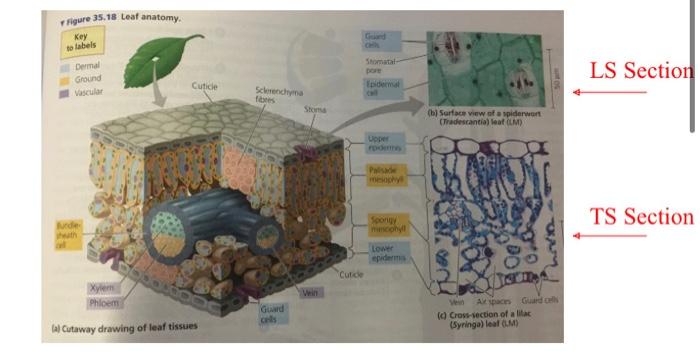
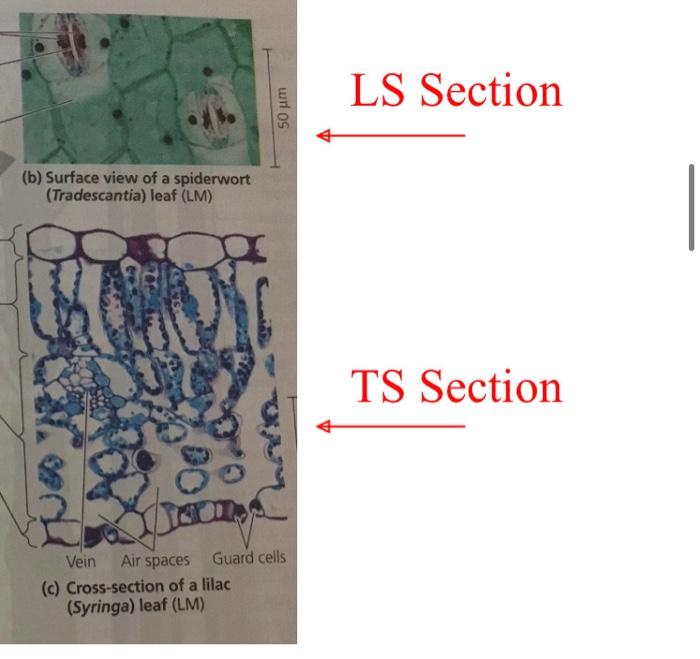
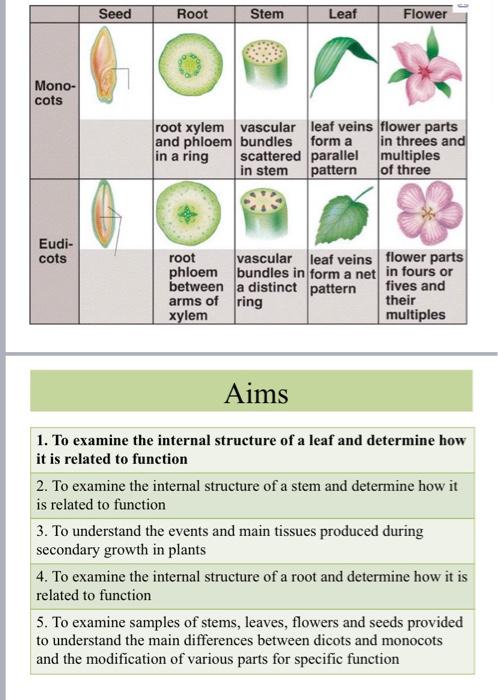
A. Labelled diagram of the leaf TS and LS, showing the important structures. LS Section (3 marks, I mark per TS Section drawing, I mark for labels) B. Explain the functions of the various tissues you observed in the leaf section, in point form. Explain whether you think your leaf is a dicot or a monocot. (4 marks) Section 1: Examination of the internal structure of leaves Epidermis -Upper and lower - For protection Thin and allows sunlight through Cuticle - Waxy, hydrophobic layer - Secreted by the epidermis - Prevents water loss Guard cells - Control opening and closing of stomata Essential in gas exchange (photosynthesis and transpiration) Vascular tissue Xylem: transports water Phloem: transports sugars Surrounded by a bundle sheath Mesophyll Many chloroplast (photosynthesis) Monocots: single layer Dicots: Two separate distinct layers (spongy and palisade) . Section 1: Examination of the internal structure of leaves View prepared slides of Dicot and monocot - Draw and label a diagram - as below arbet LS Section TS Section Figure 35.18 Leaf anatomy. Key to labels Dermal Ground Vascular Jurde heath Cuticle Xylem Phloem lal Cutaway drawing of leaf tissues Sclemenchyma fibres Guard Stoma Vein Guard Cuticle Stomatal- pore Epidermal Upper Palisade Spongy mimophyll Lower epidermis (b) Surface view of a spiderwort (Tradescantia) leaf (LM) Ve Ak space Guard cells (c) Cross-section of a lilac (Syringa) leaf (M) LS Section TS Section (b) Surface view of a spiderwort (Tradescantia) leaf (LM) di 50 m Vein Air spaces Guard cells (c) Cross-section of a lilac (Syringa) leaf (LM) LS Section TS Section Mono- cots Eudi- cots Seed Root root xylem and phloem in a ring root phloem between arms of xylem Stem Leaf vascular bundles scattered parallel in stem pattern leaf veins flower parts form a in threes and multiples of three Flower vascular leaf veins bundles in form a net a distinct pattern ring flower parts in fours or fives and their multiples Aims 1. To examine the internal structure of a leaf and determine how it is related to function 2. To examine the internal structure of a stem and determine how it is related to function 3. To understand the events and main tissues produced during secondary growth in plants 4. To examine the internal structure of a root and determine how it is related to function 5. To examine samples of stems, leaves, flowers and seeds provided to understand the main differences between dicots and monocots and the modification of various parts for specific function
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The picture shows two distinct segments of a leaf one marked LS Segment demonstrating a longitudinal ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


