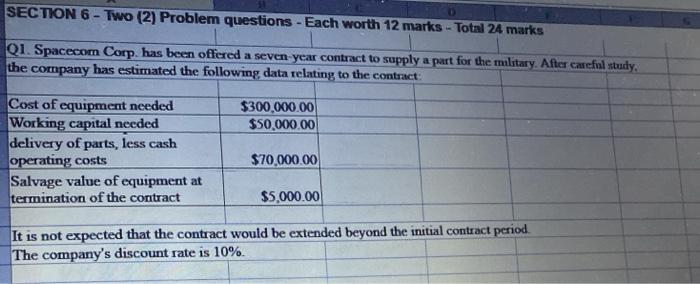
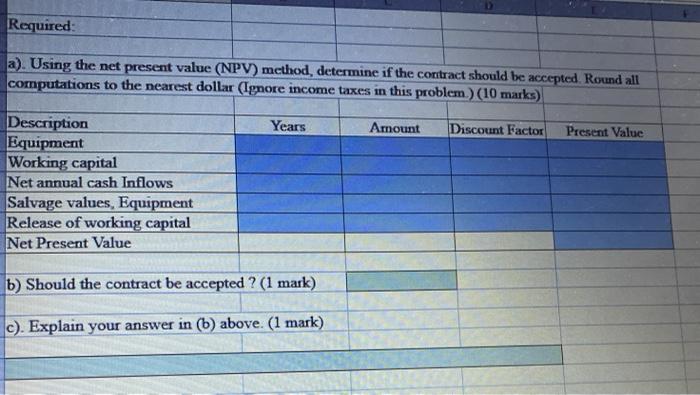
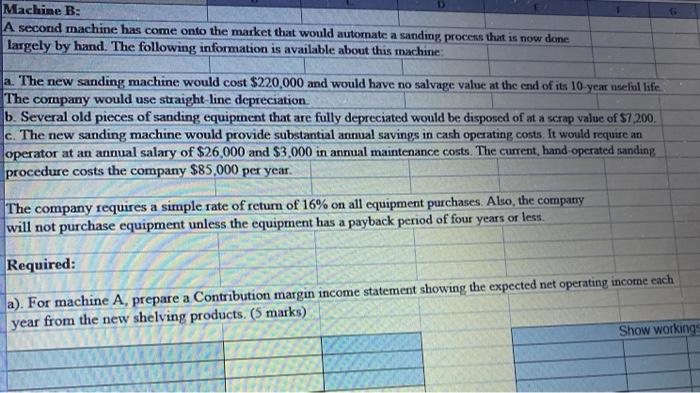
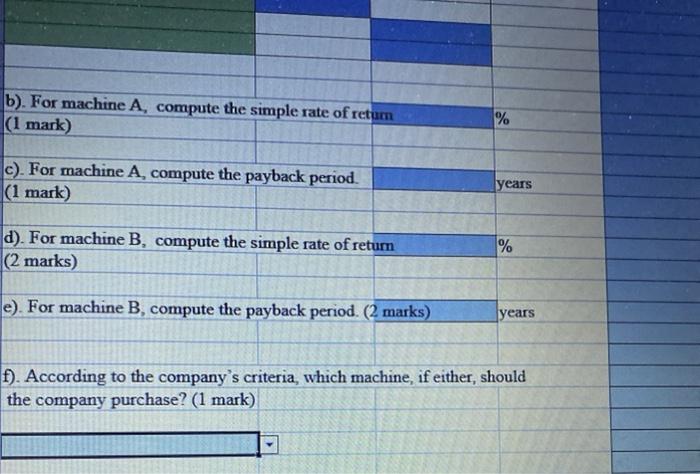
SECTION 6 - Two (2) Problem questions - Each worth 12 marks - Total 24 marks Q1. Spacecom Corp. has been offered a seven-year contract to supply a part for the military. After careful study, the company has estimated the following data relating to the contract: $300,000.00 $50,000.00 Cost of equipment needed Working capital needed delivery of parts, less cash operating costs Salvage value of equipment at termination of the contract $70,000.00 $5,000.00 It is not expected that the contract would be extended beyond the initial contract period. The company's discount rate is 10%. Required: a). Using the net present value (NPV) method, determine if the contract should be accepted Round all computations to the nearest dollar (Ignore income taxes in this problem.) (10 marks) Years Amount Discount Factor Present Value Description Equipment Working capital Net annual cash Inflows Salvage values, Equipment Release of working capital Net Present Value b) Should the contract be accepted ? (1 mark) c). Explain your answer in (b) above. (1 mark) Q2. Executive Funiture is considering purchasing two different items of equipment, as described below: Machine A A machine has just come onto the market that compresses sawdust into various shelving products. Currently, the sawdust disposed of as a waste product. The following information is available about the machine: a. The machine would cost $780,000 and would have a 25% salvage value at the end of its 10-year useful life. The comp uses straight-line depreciation and considers salvage value in computing depreciation deductions b. The shelving products produced by the machine would generate revenues of $350,000 per year. Variable manufacturin costs would be 20% of sales. c. Fixed annual expenses associated with the new shelving products would be advertising, $42,000 salaries. $86,000. utilities. $9,000; and insurance, $13,000. Machine B: A second machine has come onto the market that would automate a sanding process that is now done largely by hand. The following information is available about this machine: a. The new sanding machine would cost $220,000 and would have no salvage value at the end of its 10-year useful li The company would use straight-line depreciation b. Several old pieces of sanding equipment that are fully depreciated would be disposed of at a scrap value of S7,200 c. The new sanding machine would provide substantial annual savings in cash operating costs. It would require an of $26 000 and $3,000 in annual maintenance costs. The current, hand-operated sanding Machine B: A second machine has come onto the market that would automate a sanding process that is now done Largely by hand. The following information is available about this machine a. The new sanding machine would cost $220,000 and would have no salvage value at the end of its 10-year ndeful life The company would use straight line depreciation b. Several old pieces of sanding equipment that are fully depreciated would be disposed of at a scrap value of $1.200 c. The new sanding machine would provide substantial annual savings in cash operating costs. It would require an operator at an annual salary of $26,000 and $3.000 in annual maintenance costs. The current, hand operated sanding procedure costs the company $85,000 per year. The company requires a simple rate of return of 16% on all equipment purchases. Also, the company will not purchase equipment unless the equipment has a payback period of four years or less. Required: a). For machine A, prepare a Contribution margin income statement showing the expected net operating income each year from the new shelving products. (5 marks) Show workings b). For machine A, compute the simple rate of return (1 mark) % c). For machine A, compute the payback period. (1 mark) years d). For machine B, compute the simple rate of retum (2 marks) % e). For machine B, compute the payback period. (2 marks) years f). According to the company's criteria, which machine, if either, should the company purchase? (1 mark)