Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. REMEMBER THAT PROGRAM SEGMENTS ARE TO BE WRITTEN IN JAVA. Assume that the classes listed in the Java Quick Reference have
SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. REMEMBER THAT PROGRAM SEGMENTS ARE TO BE WRITTEN IN JAVA.
- Assume that the classes listed in the Java Quick Reference have been imported where appropriate.
- Unless otherwise noted in the question, assume that parameters in method calls are notnulland that methods are called only when their preconditions are satisfied.
- In writing solutions for each question, you may use any of the accessible methods that are listed in classes defined in that question. Writing significant amounts of code that can be replaced by a call to one of these methods will not receive full credit.
This question involves the implementation of theAddtionPatternclass, which generates a number pattern. TheAdditionPatternobject is constructed with two positive integer parameters, as described below.
- The first positive integer parameter indicates the starting number in the pattern.
- The second positive integer parameter indicates the value that is to be added to obtain each subsequent number in the pattern.
TheAdditionPatternclass also supports the following methods.
- currentNumber,which returns the current number in the pattern
- next,which moves to the next number in the pattern
- prev,which moves to the previous number in the pattern or takes no action if there is no previous number
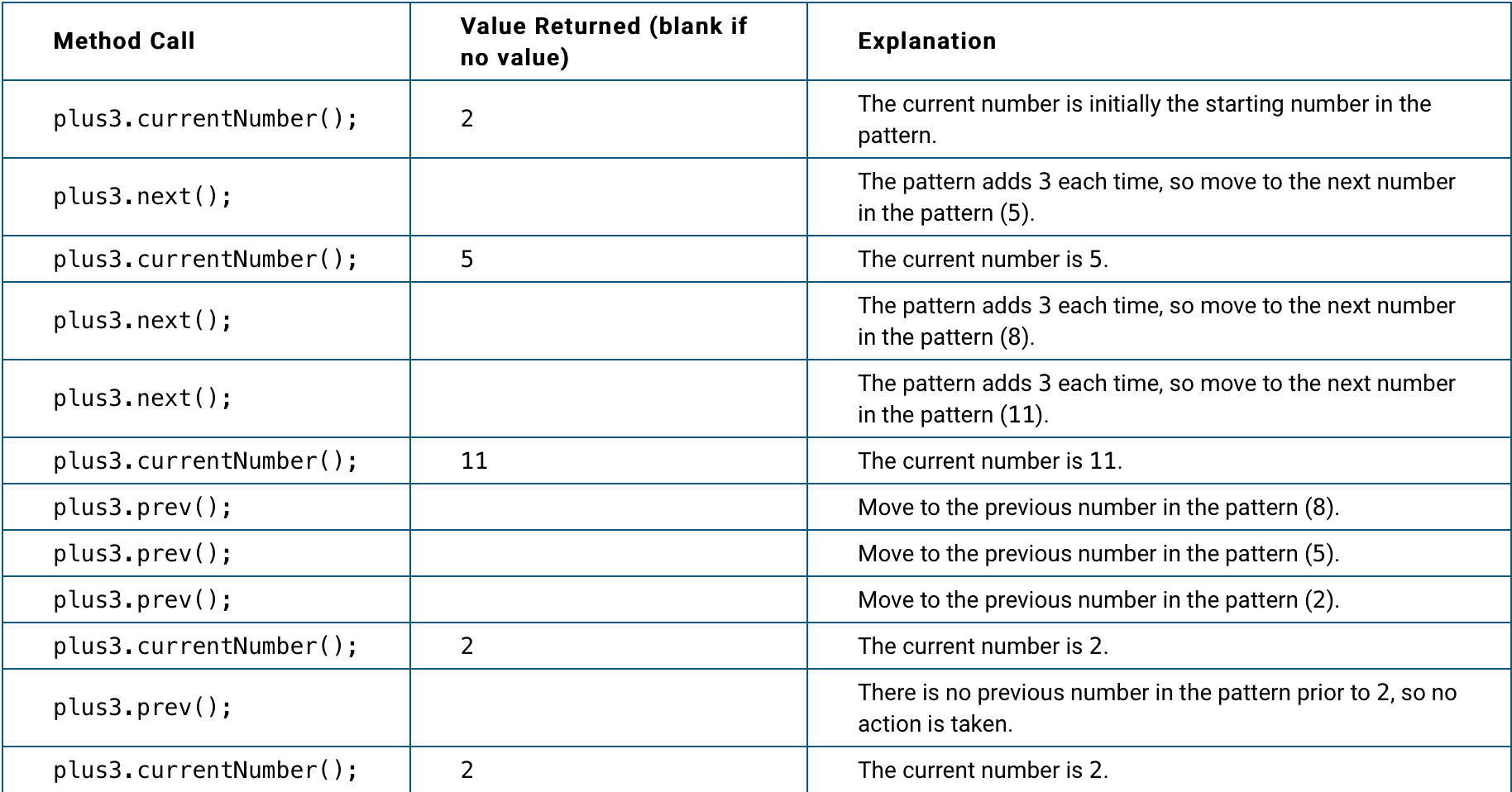
The following table illustrates the behavior of anAdditionPatternobject that is instantiated by the following statement.
AdditionPattern plus3 = new AdditionPattern(2, 3);
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


