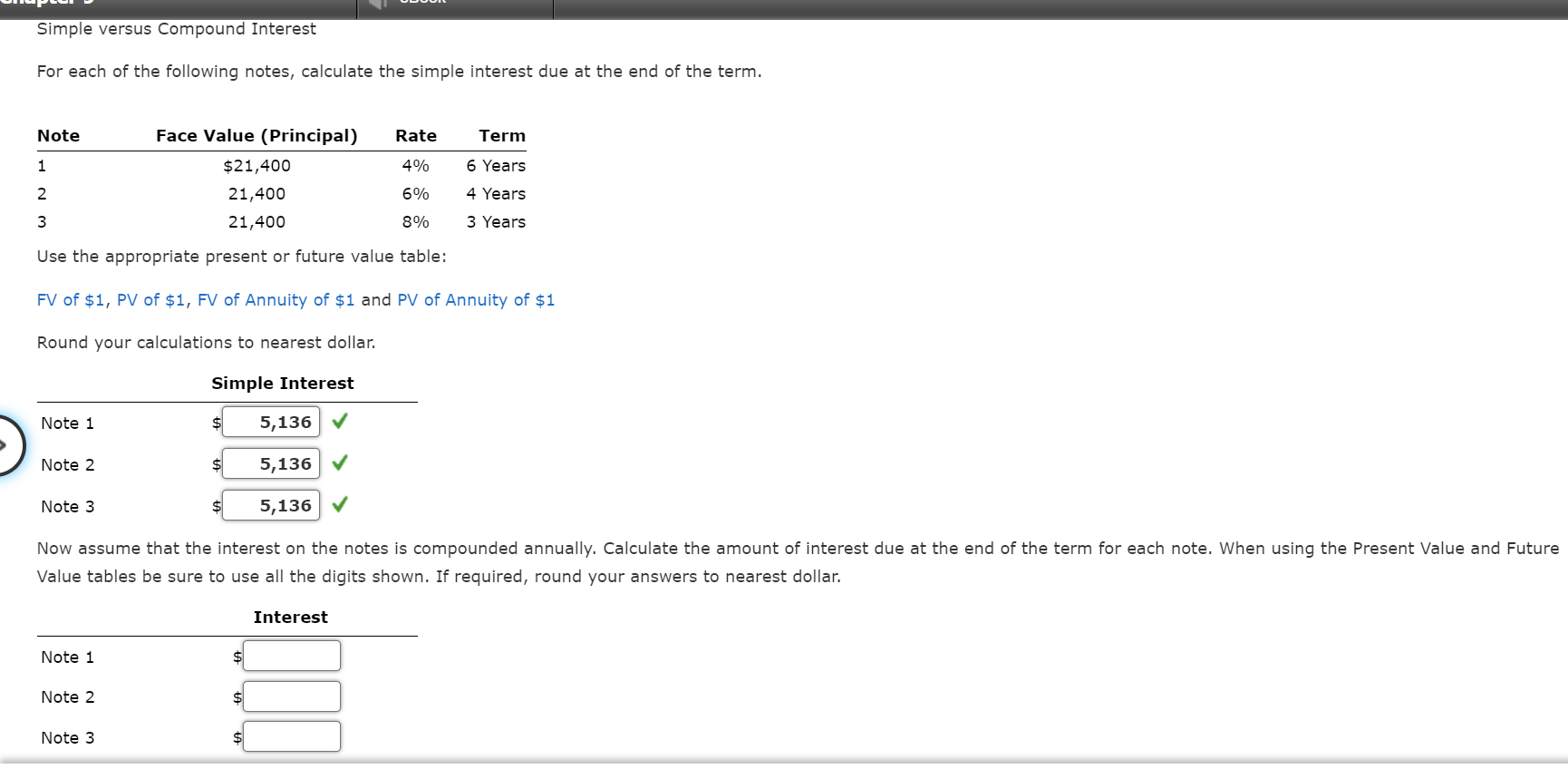

Simple versus Compound Interest For each of the following notes, calculate the simple interest due at the end of the term. Note Rate Term 1 4% 6 Years Face Value (Principal) $21,400 21,400 21,400 2 6% 4 Years 3 8% 3 Years Use the appropriate present or future value table: FV of $1, PV of $1, FV of Annuity of $1 and PV of Annuity of $1 Round your calculations to nearest dollar. Simple Interest Note 1 $ 5,136 Note 2 5,136 Note 3 5,136 Now assume that the interest on the notes is compounded annually. Calculate the amount of interest due at the end of the term for each note. When using the Present Value and Future Value tables be sure to use all the digits shown. If required, round your answers to nearest dollar. Interest Note 1 $ Note 2 $ Note 3 Finally, assume that the interest on the notes is compounded semiannually. Calculate the amount of interest due at the end of the term for each note. When using the Present Value and Future Value tables be sure to use all the digits shown. If required, round your answers to nearest dollar. Interest Note 1 Note 2 $ Note 3 $ All other factors being equal, which of the following is an accurate statement regarding the choice of an investment? a. Higher interest rates, less frequent compounding, and a longer term will increase the future value of an investment. b. Higher interest rates, more frequent compounding, and a shorter term will increase the future value of an investment. c. Higher interest rates, more frequent compounding, and a longer term will increase the future value of an investment. d. Lower interest rates, more frequent compounding, and a longer term will increase the future value of an investment. Simple versus Compound Interest For each of the following notes, calculate the simple interest due at the end of the term. Note Rate Term 1 4% 6 Years Face Value (Principal) $21,400 21,400 21,400 2 6% 4 Years 3 8% 3 Years Use the appropriate present or future value table: FV of $1, PV of $1, FV of Annuity of $1 and PV of Annuity of $1 Round your calculations to nearest dollar. Simple Interest Note 1 $ 5,136 Note 2 5,136 Note 3 5,136 Now assume that the interest on the notes is compounded annually. Calculate the amount of interest due at the end of the term for each note. When using the Present Value and Future Value tables be sure to use all the digits shown. If required, round your answers to nearest dollar. Interest Note 1 $ Note 2 $ Note 3 Finally, assume that the interest on the notes is compounded semiannually. Calculate the amount of interest due at the end of the term for each note. When using the Present Value and Future Value tables be sure to use all the digits shown. If required, round your answers to nearest dollar. Interest Note 1 Note 2 $ Note 3 $ All other factors being equal, which of the following is an accurate statement regarding the choice of an investment? a. Higher interest rates, less frequent compounding, and a longer term will increase the future value of an investment. b. Higher interest rates, more frequent compounding, and a shorter term will increase the future value of an investment. c. Higher interest rates, more frequent compounding, and a longer term will increase the future value of an investment. d. Lower interest rates, more frequent compounding, and a longer term will increase the future value of an investment








