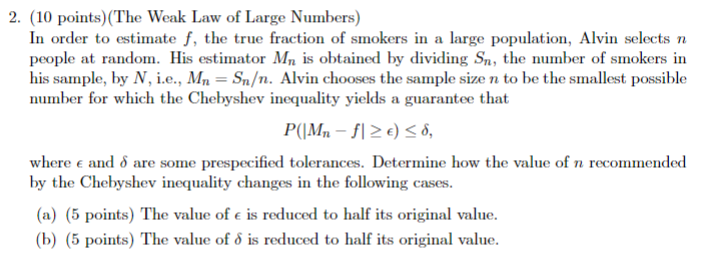Solve all of the following questions please.
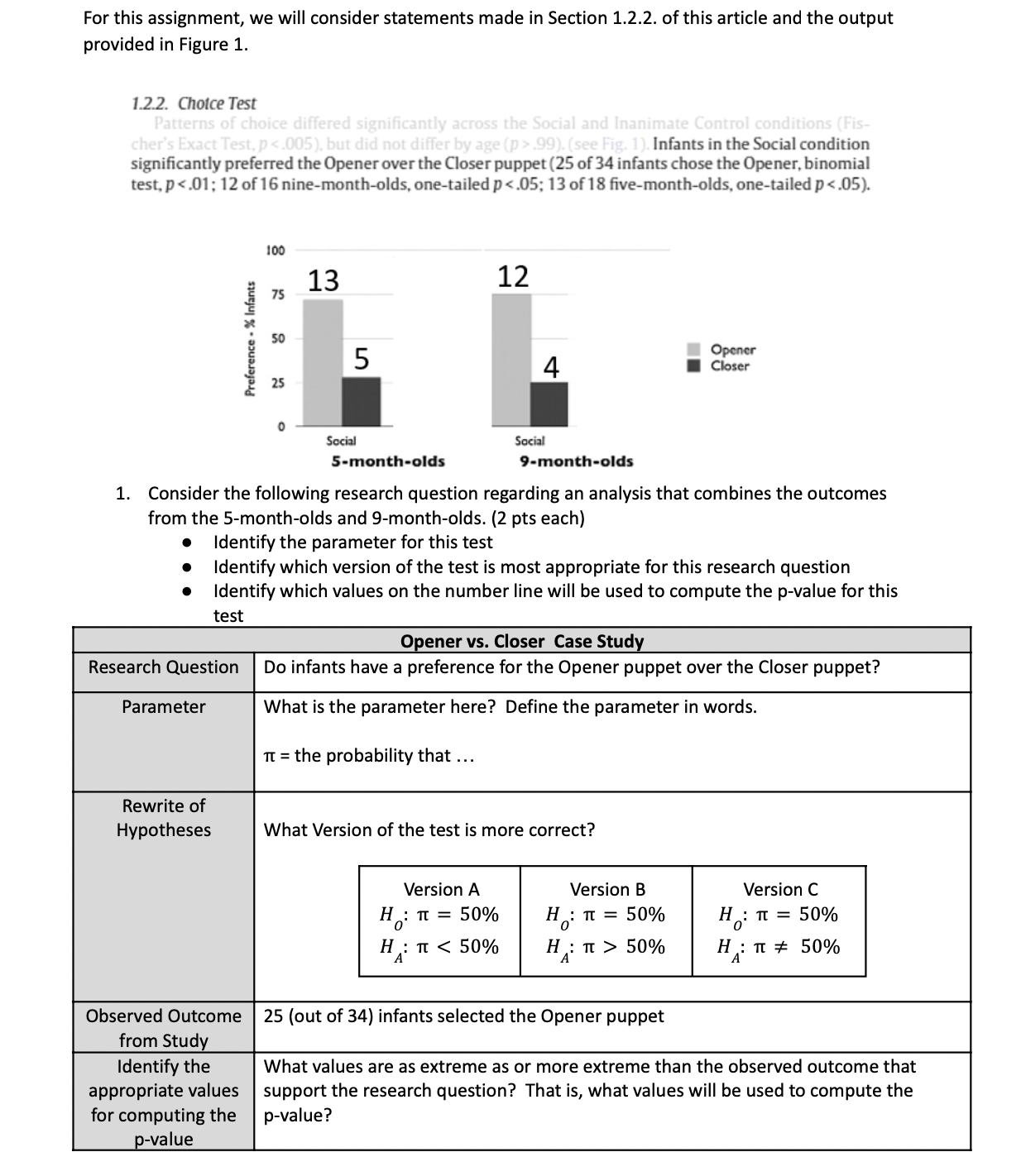
2. (10 points) Consider a continuous-time Markov chain with the transition rate matrix 4 2 2 Q = 3 1 5 0 -5 (a) What is the expected amount of time spent in each state? (b) What is the transition probability matrix of the embedded discrete-time Markov chain? (c) Is this continuous-time Markov chain irreducible? (d) Compute the stationary distribution for the continuous-time Markov chain and the em- bedded discrete-time Markov chain and compare the two.Goods that are not scarce. and therefore have no cost, might be called... Select one: Q scarcit5l macroeconomics subjective values microeconomics rationing free goods rational decisionmaking scarce goods economics normative economics positive economics OOOOOOOOOOO ceteris paribus 2. (10 points) (The Weak Law of Large Numbers) In order to estimate f, the true fraction of smokers in a large population, Alvin selects n people at random. His estimator Mn is obtained by dividing Sn, the number of smokers in his sample, by N, i.e., Mn = Sn. Alvin chooses the sample size n to be the smallest possible number for which the Chebyshev inequality yields a guarantee that P(IMn - f1 2 E) So, where e and o are some prespecified tolerances. Determine how the value of n recommended by the Chebyshev inequality changes in the following cases. (a) (5 points) The value of e is reduced to half its original value. (b) (5 points) The value of o is reduced to half its original value.Which of the following is an advantage of multivariate correlational research over bivariate correlational research? O Bivariate correlational studies help address internal validity, whereas multivariate correlational studies do not. Multivariate correlational studies establish covariance, whereas bivariate correlational studies do not. O Some multivariate correlational studies help to address temporal precedence, whereas bivariate correlational studies do not. Multivariate correlational studies help to address external validity, whereas bivariate correlational studies do not.For this assignment, we will consider statements made in Section 1.2.2. of this article and the output provided in Figure 1. 1.2.2. Choice Test Patterns of choice differed significantly across the Social and Inanimate Control conditions (Fis- cher's Exact Test, p <.005 but did not differ by age> .99). (see Fig. 1). Infants in the Social condition significantly preferred the Opener over the Closer puppet (25 of 34 infants chose the Opener, binomial test, p <.01 of nine-month-olds one-tailed p five-month-olds preference . infants opener closer social consider the following research question regarding an analysis that combines outcomes from and pts each identify parameter for this test which version is most appropriate values on number line will be used to compute p-value vs. case study do have a puppet over what here define in words. it="the" probability ... rewrite hypotheses more correct b c h : t="50%"> 50% H : T # 50% Observed Outcome 25 (out of 34) infants selected the Opener puppet from Study Identify the What values are as extreme as or more extreme than the observed outcome that appropriate values support the research question? That is, what values will be used to compute the for computing the p-value? p-value