Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Solve polymath /matlab also Solve complete and correctly I will give you thumb up 4-22 Alkylated cyclohexanols are important intermediates in the fragrance and perfume


Solve polymath /matlab also Solve complete and correctly I will give you thumb up
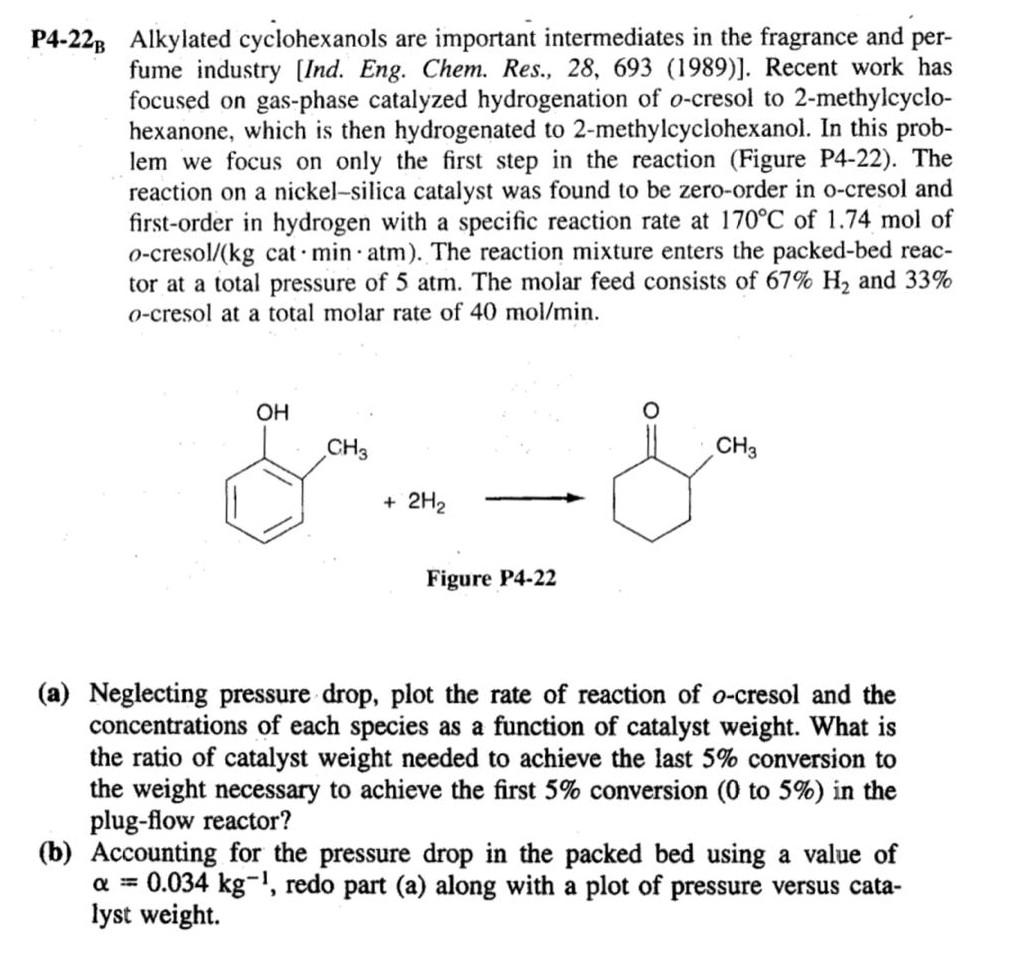
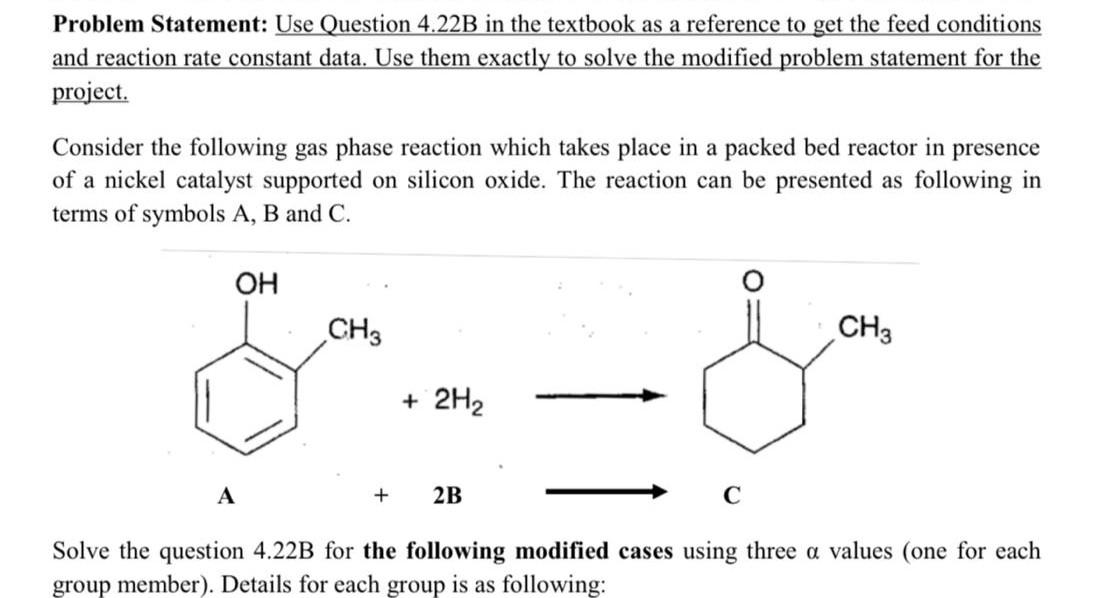
4-22 Alkylated cyclohexanols are important intermediates in the fragrance and perfume industry [Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 28, 693 (1989)]. Recent work has focused on gas-phase catalyzed hydrogenation of o-cresol to 2-methylcyclohexanone, which is then hydrogenated to 2-methylcyclohexanol. In this problem we focus on only the first step in the reaction (Figure P4-22). The reaction on a nickel-silica catalyst was found to be zero-order in o-cresol and first-order in hydrogen with a specific reaction rate at 170C of 1.74mol of ocresol/(kg cat minatm). The reaction mixture enters the packed-bed reactor at a total pressure of 5 atm. The molar feed consists of 67%H2 and 33% o-cresol at a total molar rate of 40mol/min. Figure P422 (a) Neglecting pressure drop, plot the rate of reaction of o-cresol and the concentrations of each species as a function of catalyst weight. What is the ratio of catalyst weight needed to achieve the last 5% conversion to the weight necessary to achieve the first 5% conversion (0 to 5% ) in the plug-flow reactor? (b) Accounting for the pressure drop in the packed bed using a value of =0.034kg1, redo part (a) along with a plot of pressure versus catalyst weight. Problem Statement: Use Question 4.22B in the textbook as a reference to get the feed conditions and reaction rate constant data. Use them exactly to solve the modified problem statement for the project. Consider the following gas phase reaction which takes place in a packed bed reactor in presence of a nickel catalyst supported on silicon oxide. The reaction can be presented as following in terms of symbols A, B and C. Solve the question 4.22B for the following modified cases using three values (one for each group member). Details for each group is as following: Group 6. Reaction: A+2B4C 1=0.03kg1,2=0.035kg1,3=0.04kg1 Requirements: Provide a detailed solution of the question by developing the differential equations for concentration of individual components and pressure drop along the PBR as a function of catalyst weight. The submission file should include: 1. A document containing the derivation of differential equations, solution graphs as required in question 4.22B. The values used by each member must be indicated clearly. 2. Polymath/MATLAB files. No need to write a separate full report. The textbook question 4.22B is presented below for your referenceStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


