Someone please help.
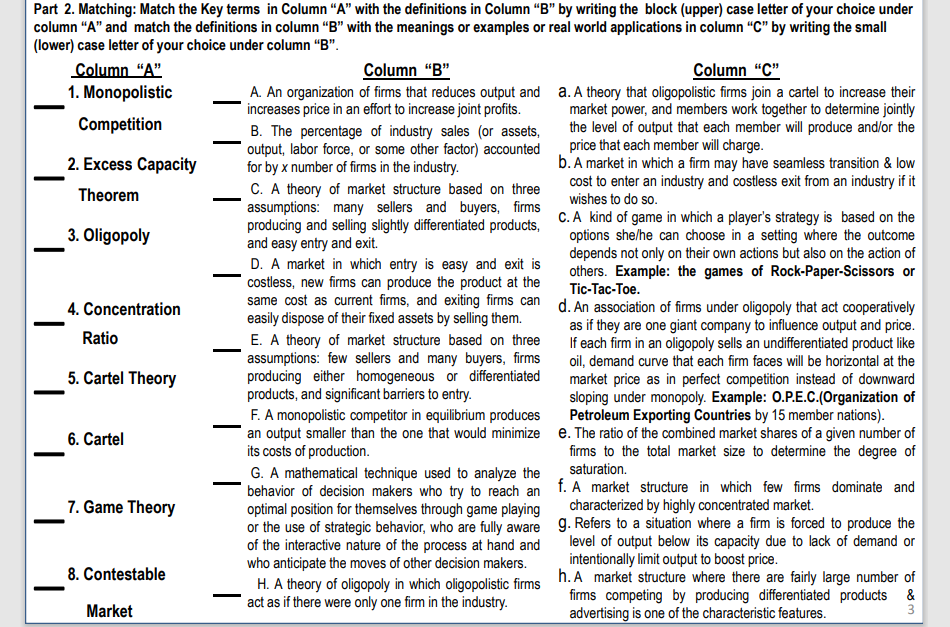
Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block (upper) case letter of your choice under column "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or real world applications in column "C" by writing the small (lower) case letter of your choice under column "B". Column "A" 1. Monopolistic Competition 2. Excess Capacity Theorem 3. Oligopoly 4. Concentration Ratio 5. Cartel Theory 6. Cartel 7. Game Theory 8. Contestable Market Column "B" A. An organization of firms that reduces output and increases price in an effort to increase joint profits. B. The percentage of industry sales (or assets, output, labor force, or some other factor) accounted for by x number of firms in the industry. C. A theory of market structure based on three assumptions: many sellers and buyers, firms producing and selling slightly differentiated products, and easy entry and exit. D. A market in which entry is easy and exit is costless, new firms can produce the product at the same cost as current firms, and exiting firms can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them. E. A theory of market structure based on three assumptions: few sellers and many buyers, firms producing either homogeneous or differentiated products, and significant barriers to entry. F. A monopolistic competitor in equilibrium produces an output smaller than the one that would minimize its costs of production. G. A mathematical technique used to analyze the behavior of decision makers who try to reach an optimal position for themselves through game playing or the use of strategic behavior, who are fully aware of the interactive nature of the process at hand and who anticipate the moves of other decision makers. Column "C" a. A theory that oligopolistic firms join a cartel to increase their market power, and members work together to determine jointly the level of output that each member will produce and/or the price that each member will charge. b. A market in which a firm may have seamless transition & low cost to enter an industry and costless exit from an industry if it wishes to do so. C. A kind of game in which a player's strategy is based on the options she/he can choose in a setting where the outcome depends not only on their own actions but also on the action of others. Example: the games of Rock-Paper-Scissors or Tic-Tac-Toe. d. An association of firms under oligopoly that act cooperatively as if they are one giant company to influence output and price. If each firm in an oligopoly sells an undifferentiated product like oil, demand curve that each firm faces will be horizontal at the market price as in perfect competition instead of downward sloping under monopoly. Example: O.P.E.C.(Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries by 15 member nations). e. The ratio of the combined market shares of a given number of firms to the total market size to determine the degree of saturation. f. A market structure in which few firms dominate and characterized by highly concentrated market. 9. Refers to a situation where a firm is forced to produce the level of output below its capacity due to lack of demand or intentionally limit output to boost price. H. A theory of oligopoly in which oligopolistic firms h. A market structure where there are fairly large number of act as if there were only one firm in the industry. firms competing by producing differentiated products & advertising is one of the characteristic features. 3 Part 2. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block (upper) case letter of your choice under column "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or real world applications in column "C" by writing the small (lower) case letter of your choice under column "B". Column "A" 1. Monopolistic Competition 2. Excess Capacity Theorem 3. Oligopoly 4. Concentration Ratio 5. Cartel Theory 6. Cartel 7. Game Theory 8. Contestable Market Column "B" A. An organization of firms that reduces output and increases price in an effort to increase joint profits. B. The percentage of industry sales (or assets, output, labor force, or some other factor) accounted for by x number of firms in the industry. C. A theory of market structure based on three assumptions: many sellers and buyers, firms producing and selling slightly differentiated products, and easy entry and exit. D. A market in which entry is easy and exit is costless, new firms can produce the product at the same cost as current firms, and exiting firms can easily dispose of their fixed assets by selling them. E. A theory of market structure based on three assumptions: few sellers and many buyers, firms producing either homogeneous or differentiated products, and significant barriers to entry. F. A monopolistic competitor in equilibrium produces an output smaller than the one that would minimize its costs of production. G. A mathematical technique used to analyze the behavior of decision makers who try to reach an optimal position for themselves through game playing or the use of strategic behavior, who are fully aware of the interactive nature of the process at hand and who anticipate the moves of other decision makers. Column "C" a. A theory that oligopolistic firms join a cartel to increase their market power, and members work together to determine jointly the level of output that each member will produce and/or the price that each member will charge. b. A market in which a firm may have seamless transition & low cost to enter an industry and costless exit from an industry if it wishes to do so. C. A kind of game in which a player's strategy is based on the options she/he can choose in a setting where the outcome depends not only on their own actions but also on the action of others. Example: the games of Rock-Paper-Scissors or Tic-Tac-Toe. d. An association of firms under oligopoly that act cooperatively as if they are one giant company to influence output and price. If each firm in an oligopoly sells an undifferentiated product like oil, demand curve that each firm faces will be horizontal at the market price as in perfect competition instead of downward sloping under monopoly. Example: O.P.E.C.(Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries by 15 member nations). e. The ratio of the combined market shares of a given number of firms to the total market size to determine the degree of saturation. f. A market structure in which few firms dominate and characterized by highly concentrated market. 9. Refers to a situation where a firm is forced to produce the level of output below its capacity due to lack of demand or intentionally limit output to boost price. H. A theory of oligopoly in which oligopolistic firms h. A market structure where there are fairly large number of act as if there were only one firm in the industry. firms competing by producing differentiated products & advertising is one of the characteristic features. 3







